Dual 25W stereo audio power amplifier circuit
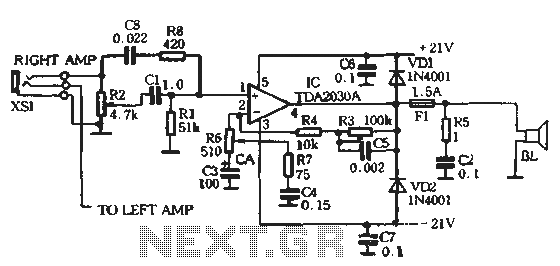
The circuit comprises two main components: the Lisheng power amplifier and the rectifier filter section. The stereo audio power amplifier circuit diagram, depicted in Figure 5-85, illustrates only one channel, with the other channel being identical. The audio signal is routed through the XS1 4.7kΩ volume potentiometer RP2 and subsequently enters the amplifier IC TDA2030A via resistor R1, which forms a high-pass filter circuit. The audio signal is processed through this intersection, where capacitor C1 is critically valued at 0.1μF, and resistor R1 is set to 51kΩ to ensure that low-frequency signals below 20Hz do not adversely affect the IC input. The feedback loop, consisting of resistor R6 and capacitor C3, influences the frequency response of the circuit. Capacitor C3, which can vary between 10μF and 220μF, works in conjunction with resistor R6 to establish a low corner frequency of 3Hz. Resistors R4 and R6, along with capacitor C3, form a negative feedback loop, where the gain of the circuit is determined by the ratio of R4 to R6, following the formula Gain = 1 + (R4/R6). The output from R6 connects to R7 and capacitor C4, forming a treble boosting circuit that enhances frequencies between 3.3kHz and 16kHz, providing a gain of approximately 15dB for improved playback clarity. Capacitors C5 and resistors R3 and R4 create a bass boost circuit that elevates frequencies between 20Hz and 200Hz, achieving a maximum boost of up to 20dB, which enhances the playback strength and bass response. This adjustment allows for a more balanced sound across the frequency spectrum, catering to various listening preferences. Resistors R5 and C2 form a Joubert network, with a transition frequency around 160kHz, which interacts with the speaker system by attenuating high-frequency signals above 20kHz to prevent interference. Capacitors C6 and C7 serve as decoupling capacitors to eliminate power supply noise, significantly improving the transient response. Diodes VD1 and VD2 protect the TDA2030A integrated amplifier circuit; they remain inactive during normal operation but safeguard the IC from potential damage under fault conditions, ensuring circuit reliability. Additionally, resistors R8 and RZ create a high-frequency compensation network, which includes loudness control features to enhance audio quality at lower volume levels.
The Lisheng power amplifier circuit is designed to deliver high-fidelity audio output while maintaining stability and reliability. The use of a high-pass filter ensures that only the desired audio frequencies are amplified, preventing low-frequency noise from interfering with the performance of the amplifier. The feedback loop plays a crucial role in shaping the amplifier's frequency response, allowing for tailored adjustments to the audio output.
The treble and bass boost circuits are particularly significant for achieving a rich audio experience, allowing the user to customize the listening experience based on personal preferences. The careful selection of component values, such as the capacitors and resistors, is essential for achieving the desired frequency response and ensuring that the amplifier operates within optimal parameters.
Furthermore, the inclusion of protection diodes enhances the longevity of the amplifier, making it robust against unexpected surges or faults. The overall design reflects a comprehensive understanding of audio amplification principles, ensuring that the circuit not only meets performance expectations but also provides a user-friendly experience.The entire circuit consists of two parts - Lisheng power amplifier and the rectifier filter crossing. As shown in Figure 5-85 is a stereo audio power amplifier circuit diagram t figure depicts only one channel, the other channel with this identical. The audio signal is applied to the XS1 4. 7k, 0 volume potentiometer RP2, and then by the ci, Rl away amplifier IC TDA2030A o cl, Rl to form a high-pass filter circuit, first as an audio signal through an intersection, it this value is crucial pregnant Cl was taken 0.1V: F, Ri taken 51k, fl, to ensure the above evidence ZOHz VLF signal destructive consumption ^ IC inlet port to the Further, the feedback loop R 6, C3 is the entire circuit affect the frequency response of a cross key point here C3 use 10Q ~ 220vF tantalum capacitors, and R6 so low corner frequency 3Hz hereinafter are for the same consideration o R4, R6. C3 composed negative feedback loop, R4 and R6 the ratio determines the gain of the circuit, the specific value by the formula f ,, - 1 + R4 / R6 wherein R6 fork and obtained export R7 and C4 form a treble boosting circuit to enhance the frequency of about 3.
3kHz - 16kHz, about promotion is 15dB, increase transparency playback Ca 6 R3, R4 and C5 bass boost circuit, lifting frequency 20 ~ 200Hz, focusing on ultra-low-frequency band, the maximum lift capacity of up to 20dB, for enhancing the strength and feeling in playback b appropriate to enhance the bass sound during playback, not only can improve tone Tan t also insufficient balance loudness entire band t fit everyone's listening habits. R5 and C2 form Joubert network, the transition frequency of about 160kHz, the connection with the speaker system from 20kHz above come into play, attenuating high frequency signals to prevent UHF since the withdrawal o C6 C7 back to power + decoupling capacitors to eliminate the interference noise power, greatly improve the transient response of the power supply.
VD1, VD2 for protecting the integrated amplifier circuit TDA2030A, when the circuit is working properly when they do not work, but the circuit is unexpected, it was to protect the IC from the port because a crucial role for the sake of improving reliable circuit, VD1 , VD2 is better fitted to the mouth c8.R8 and RZ form a high-frequency compensation network, with loudness control features, can improve the small volume playback quality mouth
The Lisheng power amplifier circuit is designed to deliver high-fidelity audio output while maintaining stability and reliability. The use of a high-pass filter ensures that only the desired audio frequencies are amplified, preventing low-frequency noise from interfering with the performance of the amplifier. The feedback loop plays a crucial role in shaping the amplifier's frequency response, allowing for tailored adjustments to the audio output.
The treble and bass boost circuits are particularly significant for achieving a rich audio experience, allowing the user to customize the listening experience based on personal preferences. The careful selection of component values, such as the capacitors and resistors, is essential for achieving the desired frequency response and ensuring that the amplifier operates within optimal parameters.
Furthermore, the inclusion of protection diodes enhances the longevity of the amplifier, making it robust against unexpected surges or faults. The overall design reflects a comprehensive understanding of audio amplification principles, ensuring that the circuit not only meets performance expectations but also provides a user-friendly experience.The entire circuit consists of two parts - Lisheng power amplifier and the rectifier filter crossing. As shown in Figure 5-85 is a stereo audio power amplifier circuit diagram t figure depicts only one channel, the other channel with this identical. The audio signal is applied to the XS1 4. 7k, 0 volume potentiometer RP2, and then by the ci, Rl away amplifier IC TDA2030A o cl, Rl to form a high-pass filter circuit, first as an audio signal through an intersection, it this value is crucial pregnant Cl was taken 0.1V: F, Ri taken 51k, fl, to ensure the above evidence ZOHz VLF signal destructive consumption ^ IC inlet port to the Further, the feedback loop R 6, C3 is the entire circuit affect the frequency response of a cross key point here C3 use 10Q ~ 220vF tantalum capacitors, and R6 so low corner frequency 3Hz hereinafter are for the same consideration o R4, R6. C3 composed negative feedback loop, R4 and R6 the ratio determines the gain of the circuit, the specific value by the formula f ,, - 1 + R4 / R6 wherein R6 fork and obtained export R7 and C4 form a treble boosting circuit to enhance the frequency of about 3.
3kHz - 16kHz, about promotion is 15dB, increase transparency playback Ca 6 R3, R4 and C5 bass boost circuit, lifting frequency 20 ~ 200Hz, focusing on ultra-low-frequency band, the maximum lift capacity of up to 20dB, for enhancing the strength and feeling in playback b appropriate to enhance the bass sound during playback, not only can improve tone Tan t also insufficient balance loudness entire band t fit everyone's listening habits. R5 and C2 form Joubert network, the transition frequency of about 160kHz, the connection with the speaker system from 20kHz above come into play, attenuating high frequency signals to prevent UHF since the withdrawal o C6 C7 back to power + decoupling capacitors to eliminate the interference noise power, greatly improve the transient response of the power supply.
VD1, VD2 for protecting the integrated amplifier circuit TDA2030A, when the circuit is working properly when they do not work, but the circuit is unexpected, it was to protect the IC from the port because a crucial role for the sake of improving reliable circuit, VD1 , VD2 is better fitted to the mouth c8.R8 and RZ form a high-frequency compensation network, with loudness control features, can improve the small volume playback quality mouth
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713