Dual Relay Driver Board Circuit
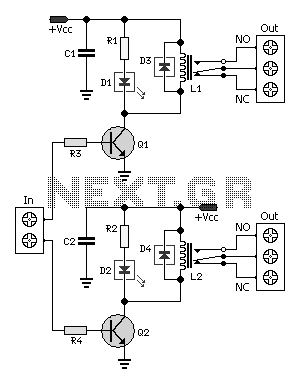
This circuit provides a straightforward and efficient method for interfacing two relays in switching applications. The relay driver utilizes a standard BC547 NPN transistor (or equivalent) to enhance the input impedance. It is a widely used driver capable of operating various types of relays, including reed relays. Transistors Q1 and Q2 function as common-emitter amplifiers, amplifying the effective sensitivity of the 12-volt relay coil by approximately 100 times, which translates to a current gain of 100 for this configuration. This arrangement decreases the relay's sensitivity to just a few volts. Resistors R3 and R4 limit the input current to Q1 and Q2, ensuring safe operation. Diodes D3 and D4 serve as EMF dampers, mitigating sparking when the relay is de-energized.
This relay driver circuit is designed to facilitate the control of relays in various electronic applications, making it an essential component in automation and control systems. The BC547 NPN transistors Q1 and Q2 are crucial for amplifying the control signal, allowing for the activation of relays that require a higher current than the control signal can provide. The common-emitter configuration of these transistors not only increases sensitivity but also enhances the overall performance of the relay driver.
The resistors R3 and R4 play a vital role in protecting the transistors from excessive input current, which could lead to thermal runaway or damage. By carefully selecting the resistor values based on the input voltage and desired current levels, the circuit can be optimized for different applications while maintaining reliability.
Diodes D3 and D4 are placed in parallel with the relay coils to handle back electromotive force (EMF) generated when the relay is turned off. This EMF can produce voltage spikes that may damage the driving circuit components. The inclusion of these diodes ensures that such spikes are safely dissipated, enhancing the longevity and stability of the entire circuit.
Overall, this relay driver circuit is a robust solution for interfacing relays in various electronic projects, providing a reliable means of controlling higher power loads while ensuring the protection of sensitive components.A simple and convenient way to interface 2 relays for switching application in your project. This relay driver boosts the input impedance with a regular BC547 NPN transistor (or equivalent). Very common driver. It can drive a variety of relays, including a reed-relay. Transistor Q1and Q2 are a simple common-emitter amplifier that increases the effective sensitivity of the 12 volt relay coil about a 100 times, or in other words, the current gain for this circuit is 100. Using this setup reduces the relay sensitivity to a few volts. R3 and R4 restricts the input current to Q1 and Q2 to a safe limit. Diodes D3 and D4 are EMF dampers and filter off any sparking when the relay de-energizes.. 🔗 External reference
This relay driver circuit is designed to facilitate the control of relays in various electronic applications, making it an essential component in automation and control systems. The BC547 NPN transistors Q1 and Q2 are crucial for amplifying the control signal, allowing for the activation of relays that require a higher current than the control signal can provide. The common-emitter configuration of these transistors not only increases sensitivity but also enhances the overall performance of the relay driver.
The resistors R3 and R4 play a vital role in protecting the transistors from excessive input current, which could lead to thermal runaway or damage. By carefully selecting the resistor values based on the input voltage and desired current levels, the circuit can be optimized for different applications while maintaining reliability.
Diodes D3 and D4 are placed in parallel with the relay coils to handle back electromotive force (EMF) generated when the relay is turned off. This EMF can produce voltage spikes that may damage the driving circuit components. The inclusion of these diodes ensures that such spikes are safely dissipated, enhancing the longevity and stability of the entire circuit.
Overall, this relay driver circuit is a robust solution for interfacing relays in various electronic projects, providing a reliable means of controlling higher power loads while ensuring the protection of sensitive components.A simple and convenient way to interface 2 relays for switching application in your project. This relay driver boosts the input impedance with a regular BC547 NPN transistor (or equivalent). Very common driver. It can drive a variety of relays, including a reed-relay. Transistor Q1and Q2 are a simple common-emitter amplifier that increases the effective sensitivity of the 12 volt relay coil about a 100 times, or in other words, the current gain for this circuit is 100. Using this setup reduces the relay sensitivity to a few volts. R3 and R4 restricts the input current to Q1 and Q2 to a safe limit. Diodes D3 and D4 are EMF dampers and filter off any sparking when the relay de-energizes.. 🔗 External reference