Dynamic braking with the two-speed motor reversing control circuit
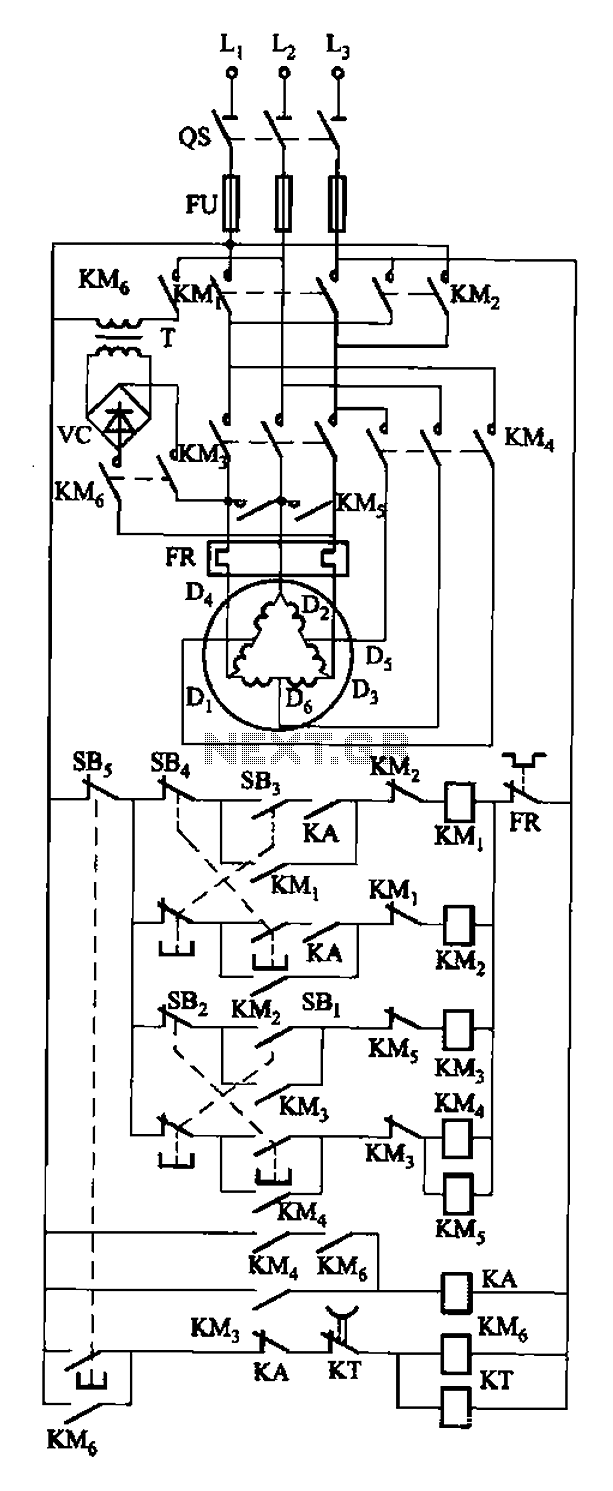
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-108 includes various control buttons: SB3 for the forward button, SI for the reverse button, SBi as the low start button, SB2 for the speed start button, and SBs for the stop button. KMs represents the brake contactor, with the braking time regulated by the time relay KT. The intermediate relay KA is responsible for ensuring that the desired speed is selected before enabling the reversing operation.
The circuit comprises several components that work together to control a motor's operation in both forward and reverse directions while incorporating speed control and safety features. The forward button (SB3) initiates the motor in the forward direction, while the reverse button (SI) allows for a change in direction. The low start button (SBi) is designed to enable the motor to start at a reduced speed, which is particularly useful for applications requiring a gentle ramp-up to full speed. The speed start button (SB2) allows the user to select a specific speed setting for the motor, providing versatility in operation.
The stop button (SBs) serves as an emergency stop mechanism, immediately cutting power to the motor and ensuring a quick cessation of operation. The brake contactor (KMs) plays a critical role in the motor's braking system, allowing for controlled deceleration. The time relay (KT) is integral in managing the braking time, ensuring that the motor stops safely and within a specified time frame to avoid mechanical stress.
The intermediate relay (KA) acts as a safeguard, ensuring that the motor is set to the desired speed before any reversing operation is initiated. This feature prevents potential damage to the motor and associated components by avoiding abrupt changes in direction without proper speed settings. Overall, the circuit design emphasizes safety and operational efficiency, making it suitable for various industrial applications where precise motor control is essential. Circuit shown in Figure 3-108. SB3 for the forward button; S Island reverse button; SBi as low start button; SB2 to speed the start button; SBs for the stop button; KMs for the brake contactor, braking time is controlled by the time relay KT; intermediate relay KA the role is to ensure first select the desired speed, then you can select reversing operation.
The circuit comprises several components that work together to control a motor's operation in both forward and reverse directions while incorporating speed control and safety features. The forward button (SB3) initiates the motor in the forward direction, while the reverse button (SI) allows for a change in direction. The low start button (SBi) is designed to enable the motor to start at a reduced speed, which is particularly useful for applications requiring a gentle ramp-up to full speed. The speed start button (SB2) allows the user to select a specific speed setting for the motor, providing versatility in operation.
The stop button (SBs) serves as an emergency stop mechanism, immediately cutting power to the motor and ensuring a quick cessation of operation. The brake contactor (KMs) plays a critical role in the motor's braking system, allowing for controlled deceleration. The time relay (KT) is integral in managing the braking time, ensuring that the motor stops safely and within a specified time frame to avoid mechanical stress.
The intermediate relay (KA) acts as a safeguard, ensuring that the motor is set to the desired speed before any reversing operation is initiated. This feature prevents potential damage to the motor and associated components by avoiding abrupt changes in direction without proper speed settings. Overall, the circuit design emphasizes safety and operational efficiency, making it suitable for various industrial applications where precise motor control is essential. Circuit shown in Figure 3-108. SB3 for the forward button; S Island reverse button; SBi as low start button; SB2 to speed the start button; SBs for the stop button; KMs for the brake contactor, braking time is controlled by the time relay KT; intermediate relay KA the role is to ensure first select the desired speed, then you can select reversing operation.