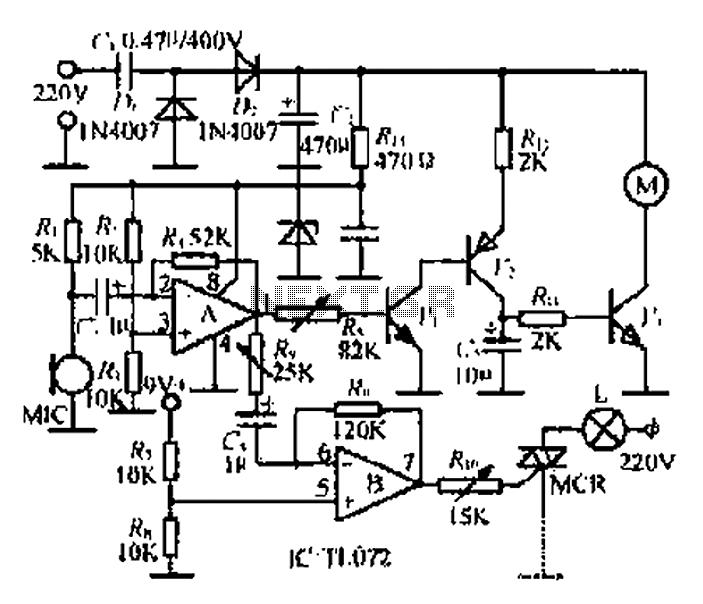
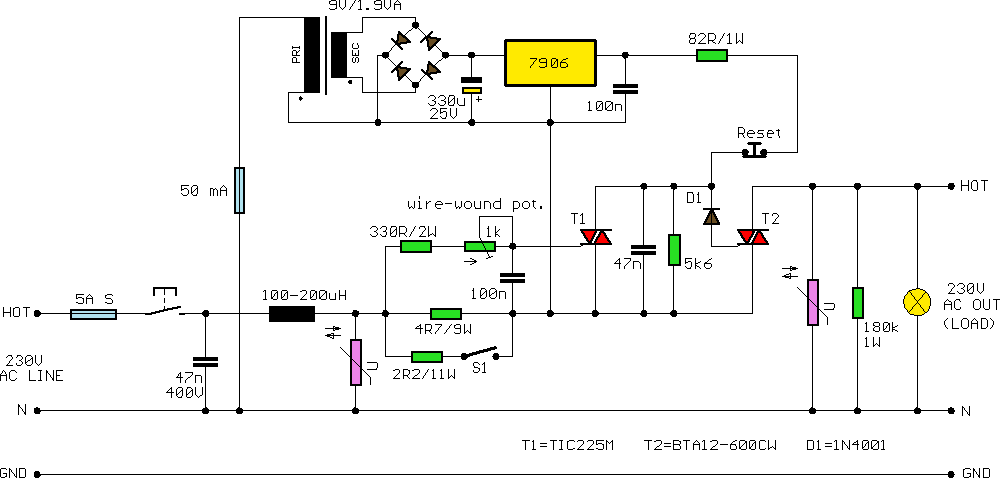
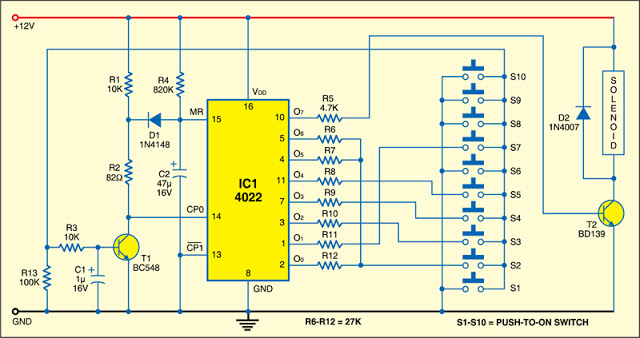
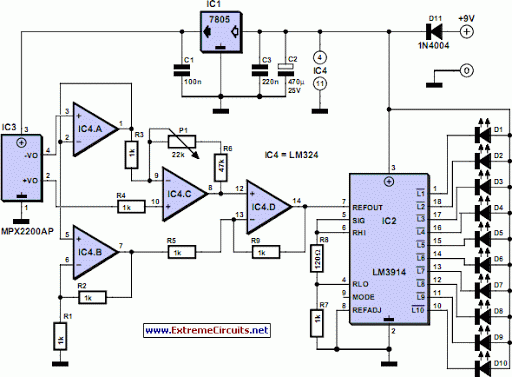
Electronic Door Buzzer
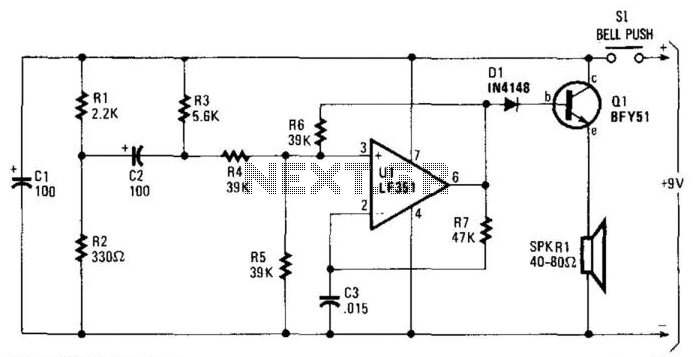
When the switch SI is pressed, a positive voltage is applied to capacitor C2 and the non-inverting terminal of operational amplifier U1. The circuit oscillates at a low frequency initially. As capacitor C2 charges through resistor R3, there is a rapid increase in the frequency of oscillation, resulting in a high-pitched sound output at speaker SPKR1. This sound is easily distinguishable above ambient noise.
The described circuit functions as a simple audio oscillator that generates sound through a feedback mechanism involving an operational amplifier. When the switch SI is activated, it allows current to flow, charging capacitor C2. The initial application of voltage to the non-inverting terminal of U1 sets the stage for oscillation. The operational amplifier, configured in a feedback loop, begins to oscillate at a low frequency determined by the values of resistors and capacitors in the circuit.
As C2 charges through resistor R3, the voltage across C2 increases, which in turn affects the input to the operational amplifier. The change in voltage causes the frequency of oscillation to increase rapidly. The relationship between the charging time constant of C2 and the resistance of R3 is crucial in determining the frequency shift. The rapid increase in frequency results in a higher-pitched sound output at the speaker SPKR1.
The speaker converts the electrical oscillations into audible sound waves. The design ensures that the generated sound is of a frequency that can easily cut through background noise, making it effective for signaling or alerting purposes in various applications. This circuit can be utilized in alarm systems, toys, or any application where an audible alert is required. Proper selection of component values will allow for tuning the circuit to achieve desired frequency ranges and sound characteristics. When SI is depressed, an initial positive voltage is placed on C2 and the noninverting terminal of Ul. The circuit o scillates at a low frequency. As C2 charges up through R3, a rapid increase in frequency of oscillation results, producing (at SPKR1) a rapidly rising pitched sound. This sound is easily recognized over ambient noise. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a simple audio oscillator that generates sound through a feedback mechanism involving an operational amplifier. When the switch SI is activated, it allows current to flow, charging capacitor C2. The initial application of voltage to the non-inverting terminal of U1 sets the stage for oscillation. The operational amplifier, configured in a feedback loop, begins to oscillate at a low frequency determined by the values of resistors and capacitors in the circuit.
As C2 charges through resistor R3, the voltage across C2 increases, which in turn affects the input to the operational amplifier. The change in voltage causes the frequency of oscillation to increase rapidly. The relationship between the charging time constant of C2 and the resistance of R3 is crucial in determining the frequency shift. The rapid increase in frequency results in a higher-pitched sound output at the speaker SPKR1.
The speaker converts the electrical oscillations into audible sound waves. The design ensures that the generated sound is of a frequency that can easily cut through background noise, making it effective for signaling or alerting purposes in various applications. This circuit can be utilized in alarm systems, toys, or any application where an audible alert is required. Proper selection of component values will allow for tuning the circuit to achieve desired frequency ranges and sound characteristics. When SI is depressed, an initial positive voltage is placed on C2 and the noninverting terminal of Ul. The circuit o scillates at a low frequency. As C2 charges up through R3, a rapid increase in frequency of oscillation results, producing (at SPKR1) a rapidly rising pitched sound. This sound is easily recognized over ambient noise. 🔗 External reference