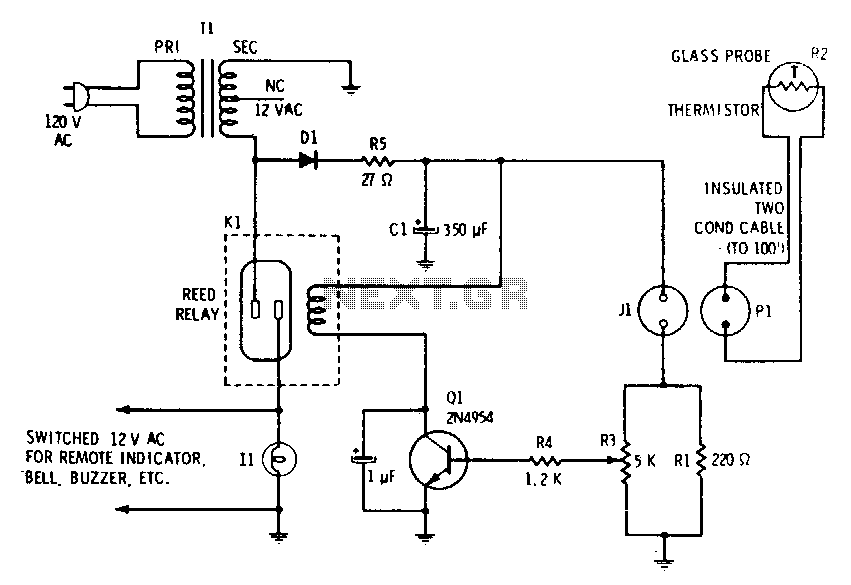
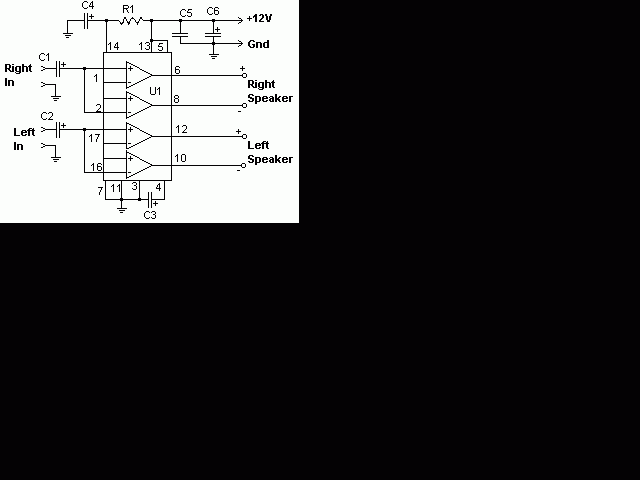
expandable transistor based burglar alarm
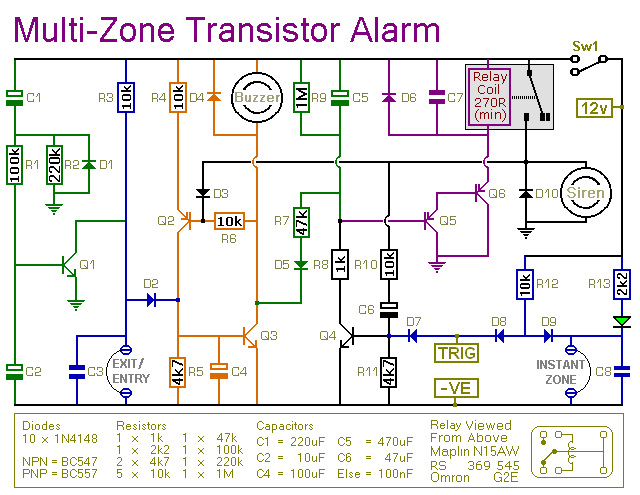
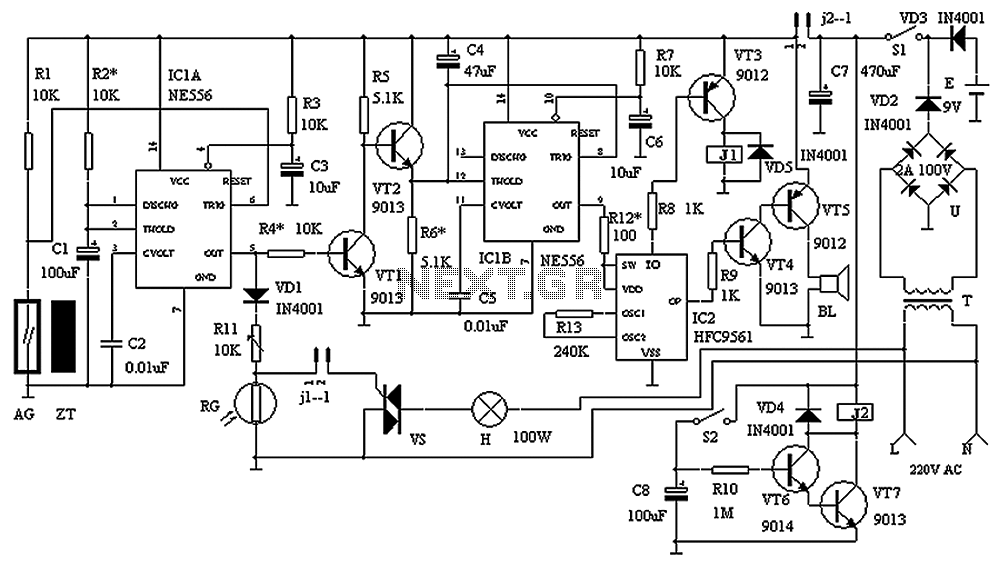
This transistor-based alarm system incorporates automatic exit and entry delays, along with a timed bell cut-off and system reset functionality. In addition to the exit/entry zone, the fundamental alarm board includes one instant zone, which is sufficient for many applications. The modular design allows for easy expansion, enabling the addition of multiple zones to the system. Information regarding a four-zone expansion module is available.
The described alarm system utilizes a transistor-based architecture, leveraging the properties of transistors for reliable switching and control functionalities. The automatic exit and entry delays are implemented using a timer circuit, which can be configured to provide a delay period during which users can exit or enter the protected area without triggering the alarm. This is essential for user convenience and reduces false alarms.
The timed bell cut-off feature ensures that the alarm sound does not persist indefinitely, which is beneficial in preventing unnecessary disturbances. This function can be achieved through a simple RC (resistor-capacitor) timing circuit, which determines the duration of the alarm sound after activation. The system reset capability allows users to restore the alarm to its initial state after an event, ensuring that it is ready for subsequent use.
The basic alarm board's inclusion of one instant zone provides immediate detection capabilities, activating the alarm as soon as an intrusion is detected in that zone. This is critical for high-security areas where immediate response is necessary. The modular design of the system is a significant advantage, allowing for scalability according to user needs. The addition of a four-zone expansion module enhances the system's capability, permitting the integration of additional sensors or zones as required. Each zone can be customized to suit specific security requirements, making the system adaptable for various environments, from residential to commercial applications.
Overall, the transistor-based alarm system presents a flexible and efficient solution for security needs, combining essential features with the potential for future expansion.This transistor based alarm features automatic Exit and Entry delays - together with a timed Bell Cut-off and system Reset. Along with the Exit/Entry zone - the basic alarm board has one Instant Zone. This will be adequate in many situations. However - the modular design means that it`s easy to add as many zones as you like to the system. Details of a Four-Zone expansion module are provided.. 🔗 External reference
The described alarm system utilizes a transistor-based architecture, leveraging the properties of transistors for reliable switching and control functionalities. The automatic exit and entry delays are implemented using a timer circuit, which can be configured to provide a delay period during which users can exit or enter the protected area without triggering the alarm. This is essential for user convenience and reduces false alarms.
The timed bell cut-off feature ensures that the alarm sound does not persist indefinitely, which is beneficial in preventing unnecessary disturbances. This function can be achieved through a simple RC (resistor-capacitor) timing circuit, which determines the duration of the alarm sound after activation. The system reset capability allows users to restore the alarm to its initial state after an event, ensuring that it is ready for subsequent use.
The basic alarm board's inclusion of one instant zone provides immediate detection capabilities, activating the alarm as soon as an intrusion is detected in that zone. This is critical for high-security areas where immediate response is necessary. The modular design of the system is a significant advantage, allowing for scalability according to user needs. The addition of a four-zone expansion module enhances the system's capability, permitting the integration of additional sensors or zones as required. Each zone can be customized to suit specific security requirements, making the system adaptable for various environments, from residential to commercial applications.
Overall, the transistor-based alarm system presents a flexible and efficient solution for security needs, combining essential features with the potential for future expansion.This transistor based alarm features automatic Exit and Entry delays - together with a timed Bell Cut-off and system Reset. Along with the Exit/Entry zone - the basic alarm board has one Instant Zone. This will be adequate in many situations. However - the modular design means that it`s easy to add as many zones as you like to the system. Details of a Four-Zone expansion module are provided.. 🔗 External reference