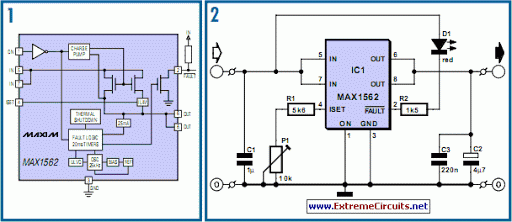
Fast Electronic Fuse
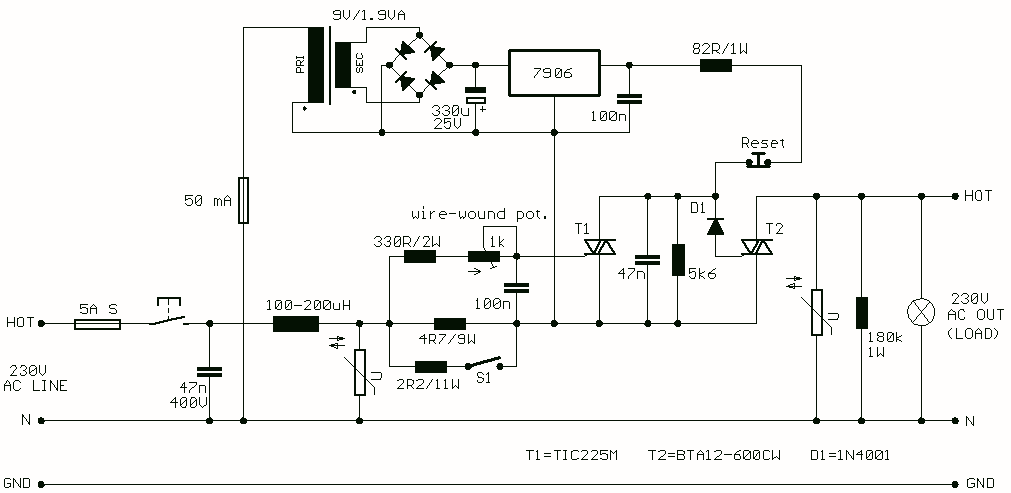
When the current through the load exceeds a level determined by the position of the wiper on the 1k wire-wound pot, this circuit cuts off the load immediately. If S1 is open, the range is approximately 300-650 mA, and 0.8-2A when it is closed. The key variable in the operation of the fuse is the voltage drop across the power resistor(s) which are connected in series with the load. This voltage drop is directly proportional to the current the load draws. When this current is low, the voltage across the resistors is also small and cannot trigger T1.
The described circuit functions as an overcurrent protection mechanism, utilizing a variable resistor (1k wire-wound potentiometer) to set a threshold for current flow through the load. The potentiometer's wiper position determines the maximum allowable current, and when the load current exceeds this set point, the circuit responds by cutting off the load immediately.
The inclusion of switch S1 allows for two distinct operating ranges. When S1 is open, the circuit is configured to handle lower current loads, specifically in the range of approximately 300-650 mA. In contrast, closing S1 enables a higher current threshold, accommodating loads up to 0.8-2A. This dual-range feature enhances the versatility of the circuit, making it suitable for various applications.
Central to the operation of the circuit is the power resistor or resistors connected in series with the load. These resistors serve a critical role in monitoring the current flow. The voltage drop across these resistors is directly proportional to the load current, following Ohm's Law (V = I × R). When the load current is below the set threshold, the resulting voltage drop across the resistors remains insufficient to activate the transistor T1, which is likely configured as a switch to interrupt the load current.
As the load current increases and approaches the set threshold, the voltage drop across the resistors rises correspondingly. Once this voltage exceeds a certain level, it triggers T1, which then activates a mechanism to cut off the load. This immediate response is crucial for protecting both the load and the power supply from potential damage due to excessive current flow.
Overall, this circuit design effectively combines adjustable current limiting with immediate disconnect functionality, making it a robust solution for overcurrent protection in electronic systems.When the current through the load exceeds a level determined by the position of the wiper on the 1k wire-wound pot, this circuit cuts off the load immediately. If S1 is open, the range is approximately 300-650 mA, and 0.8-2A when it is closed. The key variable in the operation of the fuse is the voltage drop across the power resistor(s) which are connected in series with the load.
This voltage drop is directly proportional to the current the load draws. When this current is low, the voltage across the resistors is also small and cannot trigger T1. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as an overcurrent protection mechanism, utilizing a variable resistor (1k wire-wound potentiometer) to set a threshold for current flow through the load. The potentiometer's wiper position determines the maximum allowable current, and when the load current exceeds this set point, the circuit responds by cutting off the load immediately.
The inclusion of switch S1 allows for two distinct operating ranges. When S1 is open, the circuit is configured to handle lower current loads, specifically in the range of approximately 300-650 mA. In contrast, closing S1 enables a higher current threshold, accommodating loads up to 0.8-2A. This dual-range feature enhances the versatility of the circuit, making it suitable for various applications.
Central to the operation of the circuit is the power resistor or resistors connected in series with the load. These resistors serve a critical role in monitoring the current flow. The voltage drop across these resistors is directly proportional to the load current, following Ohm's Law (V = I × R). When the load current is below the set threshold, the resulting voltage drop across the resistors remains insufficient to activate the transistor T1, which is likely configured as a switch to interrupt the load current.
As the load current increases and approaches the set threshold, the voltage drop across the resistors rises correspondingly. Once this voltage exceeds a certain level, it triggers T1, which then activates a mechanism to cut off the load. This immediate response is crucial for protecting both the load and the power supply from potential damage due to excessive current flow.
Overall, this circuit design effectively combines adjustable current limiting with immediate disconnect functionality, making it a robust solution for overcurrent protection in electronic systems.When the current through the load exceeds a level determined by the position of the wiper on the 1k wire-wound pot, this circuit cuts off the load immediately. If S1 is open, the range is approximately 300-650 mA, and 0.8-2A when it is closed. The key variable in the operation of the fuse is the voltage drop across the power resistor(s) which are connected in series with the load.
This voltage drop is directly proportional to the current the load draws. When this current is low, the voltage across the resistors is also small and cannot trigger T1. 🔗 External reference