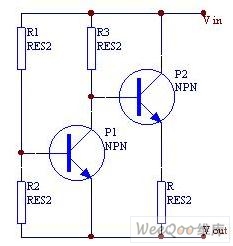
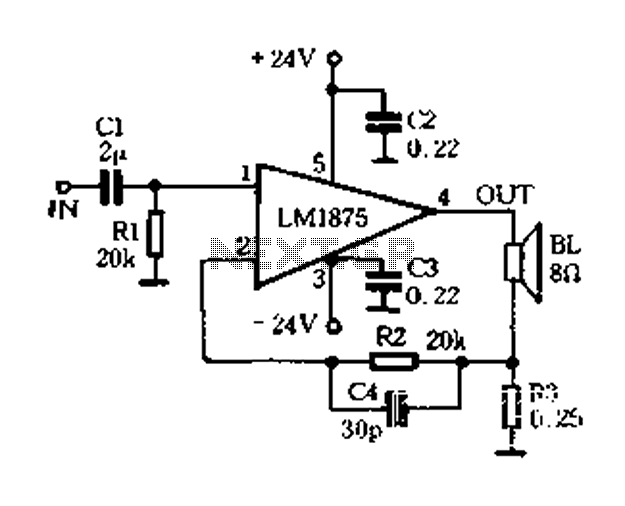
Fast Voltage-Driven Current Source
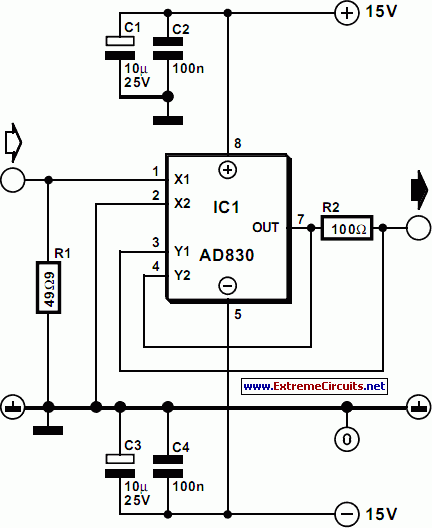
The current source in the diagram reacts very quickly to changes in the input signal and may be utilized in specific measurements. Differential.
The current source depicted in the schematic is designed to provide a stable output current that responds rapidly to variations in the input signal. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications requiring precise measurements, such as in differential measurement systems. The ability to react swiftly to input changes ensures that the current source can accurately track dynamic signals, minimizing lag and improving measurement fidelity.
In a typical configuration, the current source may utilize operational amplifiers to regulate the output current. The feedback mechanism employed in the design allows for quick adjustments in response to fluctuations in the input signal, thus maintaining a consistent current output. The differential nature of the current source can be advantageous in reducing common-mode noise, enhancing the overall signal integrity during measurement operations.
Furthermore, the current source may be integrated into various electronic systems, such as analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) or sensor interfaces, where rapid response times are critical. The design should also consider factors such as temperature stability and power supply variations, ensuring reliable performance across a range of operating conditions. Overall, the current source serves as a vital component in high-precision measurement applications, contributing to improved accuracy and reliability.The current source in the diagram, which react very fast to changes in the input signal, may be used, for instance, in certain measurements. Differential.. 🔗 External reference
The current source depicted in the schematic is designed to provide a stable output current that responds rapidly to variations in the input signal. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications requiring precise measurements, such as in differential measurement systems. The ability to react swiftly to input changes ensures that the current source can accurately track dynamic signals, minimizing lag and improving measurement fidelity.
In a typical configuration, the current source may utilize operational amplifiers to regulate the output current. The feedback mechanism employed in the design allows for quick adjustments in response to fluctuations in the input signal, thus maintaining a consistent current output. The differential nature of the current source can be advantageous in reducing common-mode noise, enhancing the overall signal integrity during measurement operations.
Furthermore, the current source may be integrated into various electronic systems, such as analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) or sensor interfaces, where rapid response times are critical. The design should also consider factors such as temperature stability and power supply variations, ensuring reliable performance across a range of operating conditions. Overall, the current source serves as a vital component in high-precision measurement applications, contributing to improved accuracy and reliability.The current source in the diagram, which react very fast to changes in the input signal, may be used, for instance, in certain measurements. Differential.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713