current reuse enhances uwb lna
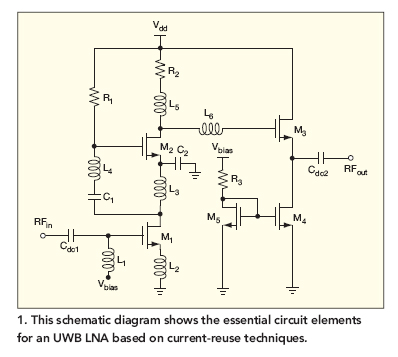
This broadband low-noise CMOS amplifier operates within the ultrawideband (UWB) communications frequency range of 3.1 to 10.6 GHz, utilizing current-reuse techniques.
The broadband low-noise CMOS amplifier is designed to enhance signal integrity and minimize noise within the specified UWB frequency range. It employs advanced current-reuse techniques, which allow for improved efficiency and reduced power consumption while maintaining high gain and low noise figure characteristics.
The amplifier's architecture typically includes multiple stages, each optimized for performance in the UWB spectrum. The use of CMOS technology not only facilitates integration with digital circuits but also provides scalability for various applications, such as wireless communication systems, radar, and sensor networks.
In terms of design considerations, the amplifier must address key parameters such as gain flatness, input/output matching, and stability across the entire operational frequency range. The implementation of feedback mechanisms can help stabilize the gain and minimize distortion, while careful selection of passive components ensures optimal impedance matching.
Thermal management is also crucial, as high-frequency operation can lead to increased power dissipation. The amplifier may incorporate techniques such as heat sinking or thermal vias to maintain operational stability and reliability.
Overall, this low-noise CMOS amplifier serves as a critical component in UWB communication systems, facilitating high-speed data transmission and reliable performance in various electronic applications.This broadband low-noise CMOS amplifier covers the ultrawideband (UWB) communications frequencies from 3.1 to 10.6 GHz with the aid of current-reuse techniques.. 🔗 External reference
The broadband low-noise CMOS amplifier is designed to enhance signal integrity and minimize noise within the specified UWB frequency range. It employs advanced current-reuse techniques, which allow for improved efficiency and reduced power consumption while maintaining high gain and low noise figure characteristics.
The amplifier's architecture typically includes multiple stages, each optimized for performance in the UWB spectrum. The use of CMOS technology not only facilitates integration with digital circuits but also provides scalability for various applications, such as wireless communication systems, radar, and sensor networks.
In terms of design considerations, the amplifier must address key parameters such as gain flatness, input/output matching, and stability across the entire operational frequency range. The implementation of feedback mechanisms can help stabilize the gain and minimize distortion, while careful selection of passive components ensures optimal impedance matching.
Thermal management is also crucial, as high-frequency operation can lead to increased power dissipation. The amplifier may incorporate techniques such as heat sinking or thermal vias to maintain operational stability and reliability.
Overall, this low-noise CMOS amplifier serves as a critical component in UWB communication systems, facilitating high-speed data transmission and reliable performance in various electronic applications.This broadband low-noise CMOS amplifier covers the ultrawideband (UWB) communications frequencies from 3.1 to 10.6 GHz with the aid of current-reuse techniques.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713