fet audio mixer
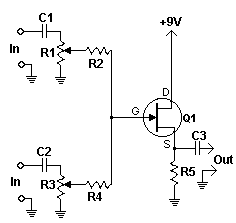
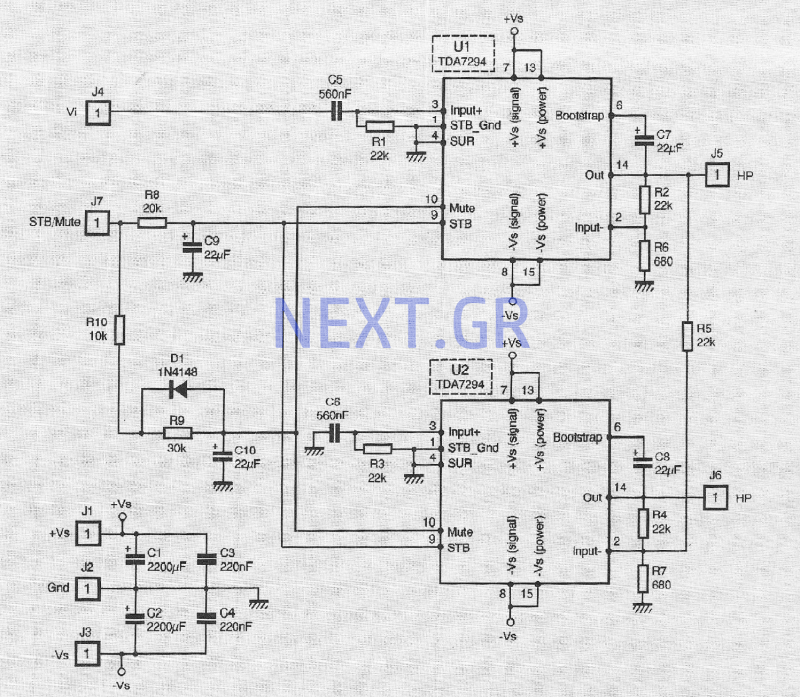
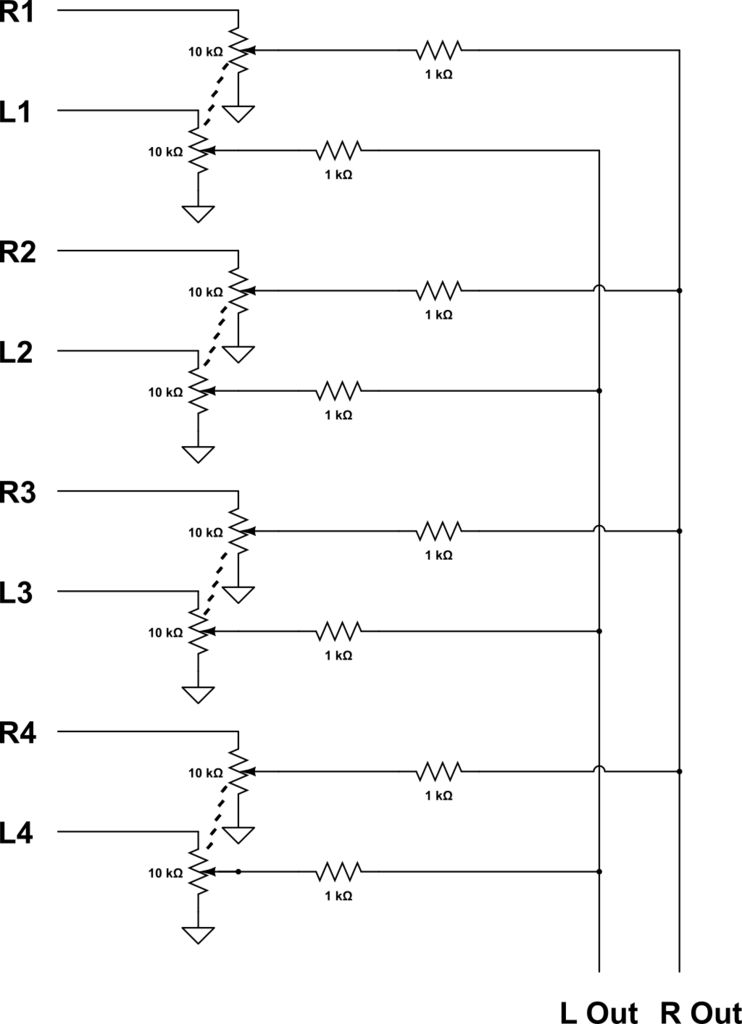
The mixer allows for the addition of multiple channels as needed. This can be accomplished by simply duplicating the input sections that are clearly indicated on the schematic. One variant of this mixer was observed to have 25 inputs.
The mixer circuit is designed to accommodate a flexible number of input channels, enabling customization based on specific requirements. Each input channel is represented by a dedicated section on the schematic, which consists of various components such as resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers. These components work together to ensure that the audio signals from each input are properly mixed and processed.
To expand the mixer, one can duplicate the input sections, maintaining the same configuration and component values to preserve the intended functionality. This modular approach allows for scalability, making it possible to create mixers with a wide range of input capabilities, from a minimal setup to more complex configurations with numerous channels.
For example, in a mixer with 25 inputs, each input section would typically include a preamplifier stage to boost the incoming signal, followed by a mixing stage where the signals are combined. The output stage would then provide a single mixed signal that can be sent to further processing or amplification stages.
Consideration should be given to the power supply requirements, as more channels may necessitate a more robust power supply to handle the increased load. Additionally, signal integrity must be maintained throughout the circuit, which may involve careful layout design to minimize interference and crosstalk between channels.
Overall, the design of the mixer circuit emphasizes flexibility, allowing for a wide range of applications in audio processing and production environments.As many or as few channels as are required can be added to the mixer. Do this by just duplicating the input "sections" which are clearly shown on the schematic. One version of this mixer I saw had 25 inputs! 🔗 External reference
The mixer circuit is designed to accommodate a flexible number of input channels, enabling customization based on specific requirements. Each input channel is represented by a dedicated section on the schematic, which consists of various components such as resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers. These components work together to ensure that the audio signals from each input are properly mixed and processed.
To expand the mixer, one can duplicate the input sections, maintaining the same configuration and component values to preserve the intended functionality. This modular approach allows for scalability, making it possible to create mixers with a wide range of input capabilities, from a minimal setup to more complex configurations with numerous channels.
For example, in a mixer with 25 inputs, each input section would typically include a preamplifier stage to boost the incoming signal, followed by a mixing stage where the signals are combined. The output stage would then provide a single mixed signal that can be sent to further processing or amplification stages.
Consideration should be given to the power supply requirements, as more channels may necessitate a more robust power supply to handle the increased load. Additionally, signal integrity must be maintained throughout the circuit, which may involve careful layout design to minimize interference and crosstalk between channels.
Overall, the design of the mixer circuit emphasizes flexibility, allowing for a wide range of applications in audio processing and production environments.As many or as few channels as are required can be added to the mixer. Do this by just duplicating the input "sections" which are clearly shown on the schematic. One version of this mixer I saw had 25 inputs! 🔗 External reference