FET based audio preamplifier
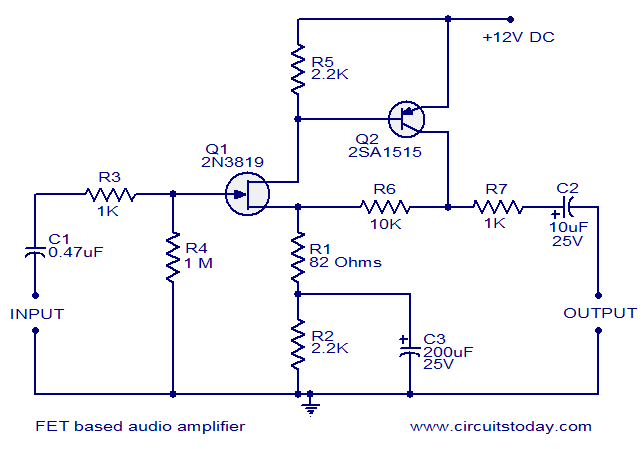
This circuit is a low-noise audio preamplifier that utilizes one FET and one BJT. The audio signal to be amplified is connected to the base of FET Q1 through capacitor C1 and resistor R3. The base of transistor Q2 is linked to the drain terminal of FET Q1, with transistor Q2 providing additional current gain. The final output signal is available at the collector of Q2. Capacitor C3 ensures necessary negative feedback, enhancing stability, while capacitor C2 serves as an output DC decoupling capacitor. Due to the use of an FET in the input stage, this amplifier circuit boasts a high bandwidth (10 kHz - 450 kHz) and an input impedance of approximately 1 MΩ.
The described audio preamplifier circuit is designed to amplify low-level audio signals with minimal noise interference. The use of a Field Effect Transistor (FET) at the input stage is critical for achieving high input impedance, which allows the circuit to interface effectively with various audio sources without loading them down. The FET Q1 acts as the primary amplifying element, where the audio signal is coupled to its gate via capacitor C1. This capacitor blocks any DC component from the input signal, ensuring that only the AC audio signal is amplified.
Resistor R3 serves as a biasing element, setting the appropriate operating point for FET Q1. The output from the drain of Q1 feeds directly into the base of bipolar junction transistor (BJT) Q2, which further amplifies the signal. The BJT is known for its higher current gain compared to FETs, which is advantageous in this configuration for achieving a significant increase in output signal strength.
The collector of Q2 is where the amplified audio signal is taken as the final output. The presence of capacitor C3 in the feedback loop is essential for stability; it introduces negative feedback that helps to mitigate any potential oscillations that could arise due to the high gain of the circuit. This feedback mechanism also contributes to a more linear response, improving the overall fidelity of the audio output.
Capacitor C2 is positioned at the output stage to decouple any DC component from the amplified signal, allowing only the AC audio signal to pass through. This is crucial for connecting the preamplifier to subsequent audio processing stages, such as power amplifiers or tone control circuits.
The overall design of this preamplifier circuit, with its specified bandwidth of 10 kHz to 450 kHz, makes it suitable for a wide range of audio applications, ensuring that it can faithfully reproduce audio signals across a broad frequency spectrum. The high input impedance of approximately 1 MΩ further enhances its versatility, allowing it to be used with various audio sources without significant signal loss.This is the circuit of a based audio preamplifier which has very low noise. One FET and one BJT are used in this circuit. The audio signal to be amplified is coupled to the base of FET Q1 using capacitor C1 and resistor R3. Base of transistor Q2 is coupled to the drain terminal of FET Q1. Transistor Q2 provides additional current gain. The final si gnal will be available at the collector of Q2. Capacitor C3 provides necessary negative feedback, which improves stability. Capacitor C2 is an output DC decoupling capacitor. Since an FET is used in the input stage this particular amplifier circuit has very high band width (10 KHz- 450 KHz) and input impedance (around 1M). 🔗 External reference
The described audio preamplifier circuit is designed to amplify low-level audio signals with minimal noise interference. The use of a Field Effect Transistor (FET) at the input stage is critical for achieving high input impedance, which allows the circuit to interface effectively with various audio sources without loading them down. The FET Q1 acts as the primary amplifying element, where the audio signal is coupled to its gate via capacitor C1. This capacitor blocks any DC component from the input signal, ensuring that only the AC audio signal is amplified.
Resistor R3 serves as a biasing element, setting the appropriate operating point for FET Q1. The output from the drain of Q1 feeds directly into the base of bipolar junction transistor (BJT) Q2, which further amplifies the signal. The BJT is known for its higher current gain compared to FETs, which is advantageous in this configuration for achieving a significant increase in output signal strength.
The collector of Q2 is where the amplified audio signal is taken as the final output. The presence of capacitor C3 in the feedback loop is essential for stability; it introduces negative feedback that helps to mitigate any potential oscillations that could arise due to the high gain of the circuit. This feedback mechanism also contributes to a more linear response, improving the overall fidelity of the audio output.
Capacitor C2 is positioned at the output stage to decouple any DC component from the amplified signal, allowing only the AC audio signal to pass through. This is crucial for connecting the preamplifier to subsequent audio processing stages, such as power amplifiers or tone control circuits.
The overall design of this preamplifier circuit, with its specified bandwidth of 10 kHz to 450 kHz, makes it suitable for a wide range of audio applications, ensuring that it can faithfully reproduce audio signals across a broad frequency spectrum. The high input impedance of approximately 1 MΩ further enhances its versatility, allowing it to be used with various audio sources without significant signal loss.This is the circuit of a based audio preamplifier which has very low noise. One FET and one BJT are used in this circuit. The audio signal to be amplified is coupled to the base of FET Q1 using capacitor C1 and resistor R3. Base of transistor Q2 is coupled to the drain terminal of FET Q1. Transistor Q2 provides additional current gain. The final si gnal will be available at the collector of Q2. Capacitor C3 provides necessary negative feedback, which improves stability. Capacitor C2 is an output DC decoupling capacitor. Since an FET is used in the input stage this particular amplifier circuit has very high band width (10 KHz- 450 KHz) and input impedance (around 1M). 🔗 External reference