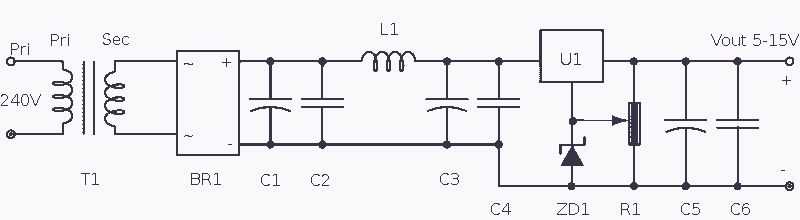
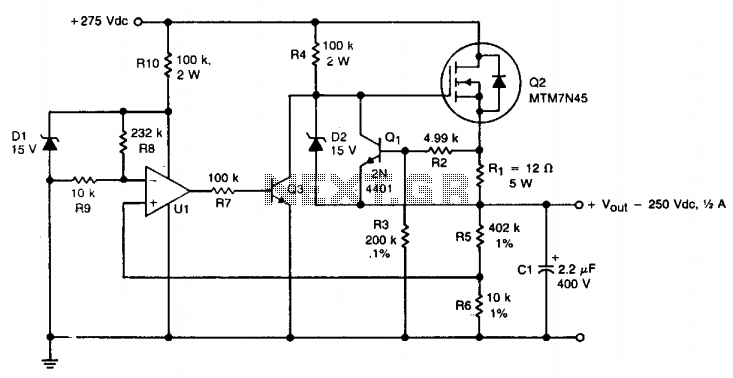
Fixed-Current Regulator
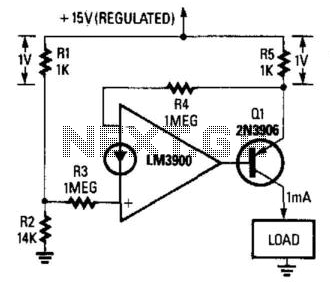
This fixed 1-mA current source delivers a constant current to a load connected between Q1's collector and ground. The load can range from 0 to 14 ohms. The circuit is powered by a regulated 15-V supply, and the R1/R2 voltage divider applies a 14-V reference to R3. The output of the operational amplifier automatically adjusts to maintain an identical voltage at the junction of R4 and R5. This configuration produces 1 V across R5, resulting in a current of 1 mA through R5. Since this current is sourced from Q1's emitter, and the emitter and collector currents of a transistor are nearly equal, the circuit functions as a fixed current source. The output current can be increased by halving the resistance of R5.
The described circuit functions as a precise current source, essential for various electronic applications where stable current is required. The use of a transistor (Q1) allows for efficient current management, as the transistor's characteristics ensure minimal variation between collector and emitter currents. The operational amplifier plays a crucial role in maintaining the desired output by continuously adjusting its output to match the reference voltage set by the voltage divider formed by resistors R1 and R2.
In this configuration, the voltage divider outputs a stable 14 V, which is critical for the operation of the circuit. Resistor R3 serves as a reference input to the operational amplifier, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable despite variations in load or supply voltage. The feedback mechanism provided by the operational amplifier guarantees that the voltage at the junction of R4 and R5 remains constant, thereby stabilizing the current flowing through R5.
The choice of R5 is particularly important, as it directly influences the output current. By adjusting R5, the current can be precisely controlled; halving R5 will double the output current to 2 mA, demonstrating the flexibility of the circuit design. This feature is beneficial in applications requiring different current levels without the need for redesigning the entire circuit.
Overall, this fixed current source design is robust and adaptable, making it suitable for integration into larger electronic systems where consistent current delivery is paramount. Proper selection of components and careful consideration of circuit parameters will ensure optimal performance and reliability in practical applications. This fixed 1-mA current source delivers a fixed current to a load connected between Ql"s collector and ground; the load can be anywhere in the range from 0 to 14 . The circuit is powered from a regulated 15-V supply, and the R1/R2 voltage divider applies a 14-V reference to R3. The op amp"s output automatically adjusts to provide an identical voltage at the junction of R4 and R5.
That produces 1 V across R5, resulting in an R5 current of 1 mA. Because that current is derived from Ql"s emitter, and the emitter and collector currents of a transistor are almost identical, the circuit provides a fixed-current source. The output current can be doubled by halving the value of R5.
The described circuit functions as a precise current source, essential for various electronic applications where stable current is required. The use of a transistor (Q1) allows for efficient current management, as the transistor's characteristics ensure minimal variation between collector and emitter currents. The operational amplifier plays a crucial role in maintaining the desired output by continuously adjusting its output to match the reference voltage set by the voltage divider formed by resistors R1 and R2.
In this configuration, the voltage divider outputs a stable 14 V, which is critical for the operation of the circuit. Resistor R3 serves as a reference input to the operational amplifier, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable despite variations in load or supply voltage. The feedback mechanism provided by the operational amplifier guarantees that the voltage at the junction of R4 and R5 remains constant, thereby stabilizing the current flowing through R5.
The choice of R5 is particularly important, as it directly influences the output current. By adjusting R5, the current can be precisely controlled; halving R5 will double the output current to 2 mA, demonstrating the flexibility of the circuit design. This feature is beneficial in applications requiring different current levels without the need for redesigning the entire circuit.
Overall, this fixed current source design is robust and adaptable, making it suitable for integration into larger electronic systems where consistent current delivery is paramount. Proper selection of components and careful consideration of circuit parameters will ensure optimal performance and reliability in practical applications. This fixed 1-mA current source delivers a fixed current to a load connected between Ql"s collector and ground; the load can be anywhere in the range from 0 to 14 . The circuit is powered from a regulated 15-V supply, and the R1/R2 voltage divider applies a 14-V reference to R3. The op amp"s output automatically adjusts to provide an identical voltage at the junction of R4 and R5.
That produces 1 V across R5, resulting in an R5 current of 1 mA. Because that current is derived from Ql"s emitter, and the emitter and collector currents of a transistor are almost identical, the circuit provides a fixed-current source. The output current can be doubled by halving the value of R5.