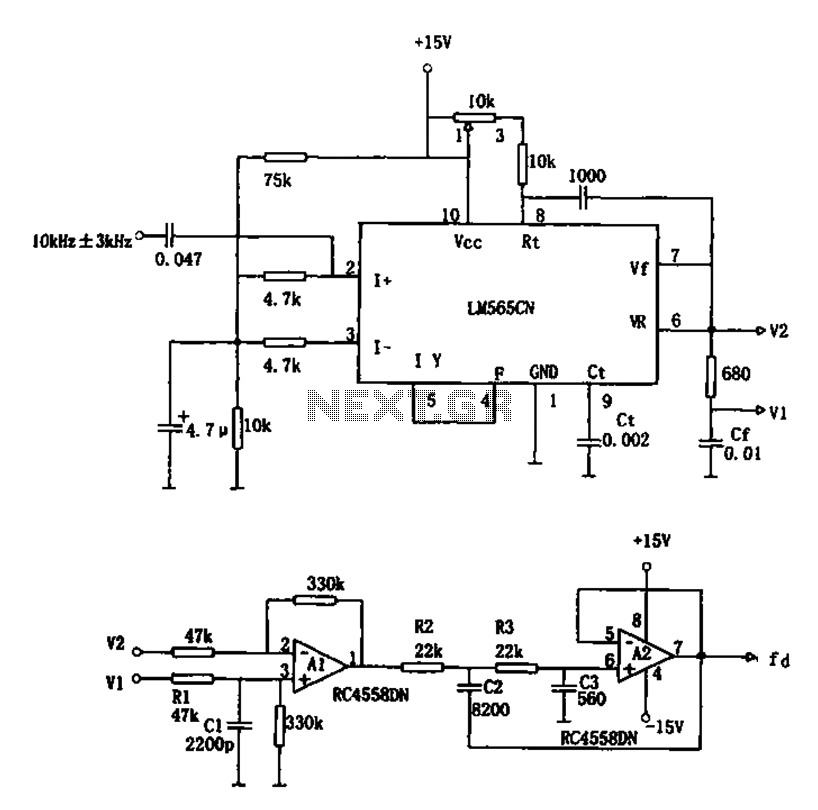
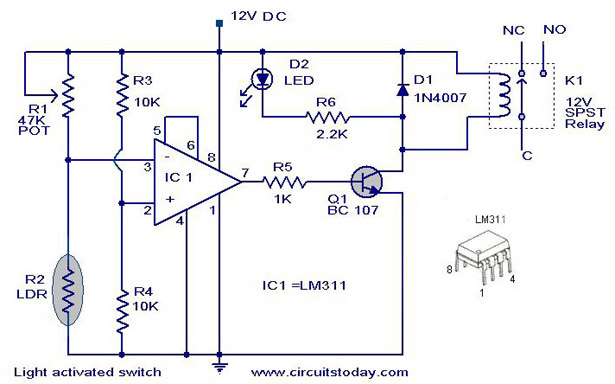
FM demodulator circuit diagram 567
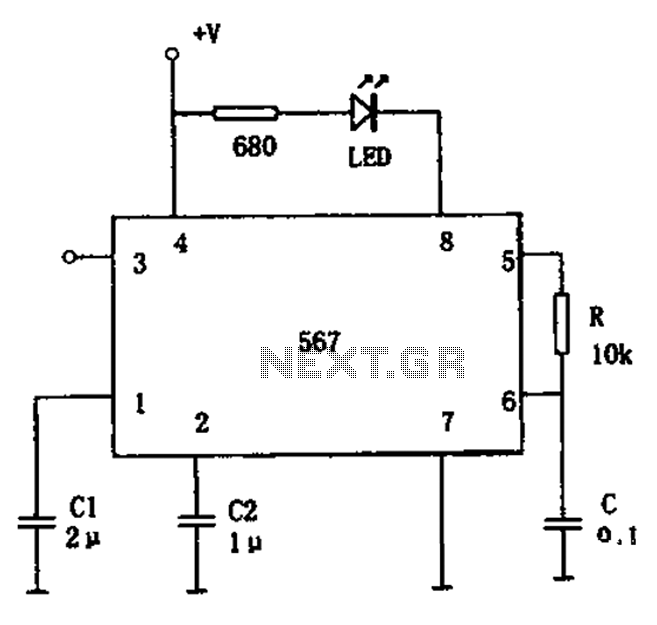
The FM demodulation circuit is illustrated in Figure 567. The FM signal is input at pin 3, and the demodulated signal is output from pin 5. The center frequency of the FM demodulation circuit is determined by the formula fo = 1.1/RC. In this configuration, C1 serves as the filter capacitor, while C2 is used for bandwidth adjustment. When the value of C2 is reduced, the demodulation bandwidth increases. The selection of C2 is based on specific criteria.
The FM demodulation circuit operates by converting frequency variations in the incoming FM signal into amplitude variations in the output signal. The input signal is fed into the circuit through pin 3, where it is processed to extract the original audio or information signal. The center frequency, fo, plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate demodulation, and it is set according to the formula fo = 1.1/RC, where R is the resistance and C is the capacitance in the circuit.
C1, the filter capacitor, is essential for smoothing out the output signal, minimizing high-frequency noise that could interfere with the clarity of the demodulated audio. C2, the bandwidth adjustment capacitor, allows for fine-tuning of the circuit's response to different frequencies. By adjusting C2, the bandwidth can be increased or decreased, affecting the circuit's sensitivity to adjacent channel interference. A smaller capacitance value for C2 results in a broader bandwidth, which can be beneficial in certain applications where signal strength is variable or where multiple signals are present.
In practical applications, the selection of C2 should be based on the specific requirements of the FM signal being demodulated, including the desired signal-to-noise ratio and the presence of adjacent channel signals. The design of the circuit must also consider the characteristics of the components used, as variations in component values can impact overall performance. The output from pin 5 delivers the demodulated signal, which can then be further processed or amplified for use in audio applications or data transmission systems. Proper layout and shielding of the circuit are also recommended to prevent interference and ensure optimal performance. As shown in Figure 567 FM demodulation circuit. The figure, the FM signal from the input pin 3, the demodulated signal output from 5 feet. FM demodulation circuit can signal ce nter frequency: fo 1.1/RC figure, C1 for the filter capacitor, C2 is the bandwidth adjustment capacitor C2 is reduced when, demodulates the bandwidth increases. C2 is selected on the basis of:
The FM demodulation circuit operates by converting frequency variations in the incoming FM signal into amplitude variations in the output signal. The input signal is fed into the circuit through pin 3, where it is processed to extract the original audio or information signal. The center frequency, fo, plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate demodulation, and it is set according to the formula fo = 1.1/RC, where R is the resistance and C is the capacitance in the circuit.
C1, the filter capacitor, is essential for smoothing out the output signal, minimizing high-frequency noise that could interfere with the clarity of the demodulated audio. C2, the bandwidth adjustment capacitor, allows for fine-tuning of the circuit's response to different frequencies. By adjusting C2, the bandwidth can be increased or decreased, affecting the circuit's sensitivity to adjacent channel interference. A smaller capacitance value for C2 results in a broader bandwidth, which can be beneficial in certain applications where signal strength is variable or where multiple signals are present.
In practical applications, the selection of C2 should be based on the specific requirements of the FM signal being demodulated, including the desired signal-to-noise ratio and the presence of adjacent channel signals. The design of the circuit must also consider the characteristics of the components used, as variations in component values can impact overall performance. The output from pin 5 delivers the demodulated signal, which can then be further processed or amplified for use in audio applications or data transmission systems. Proper layout and shielding of the circuit are also recommended to prevent interference and ensure optimal performance. As shown in Figure 567 FM demodulation circuit. The figure, the FM signal from the input pin 3, the demodulated signal output from 5 feet. FM demodulation circuit can signal ce nter frequency: fo 1.1/RC figure, C1 for the filter capacitor, C2 is the bandwidth adjustment capacitor C2 is reduced when, demodulates the bandwidth increases. C2 is selected on the basis of: