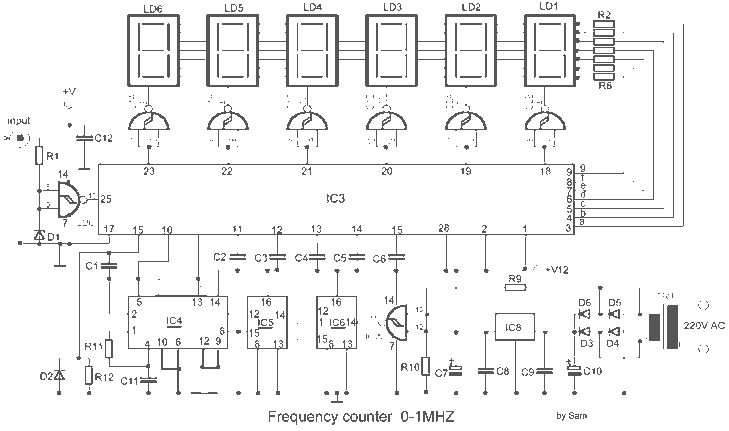
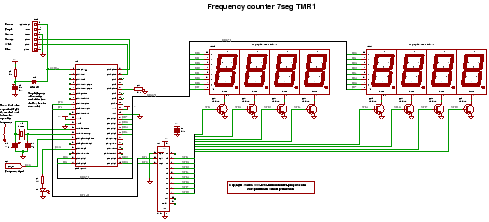
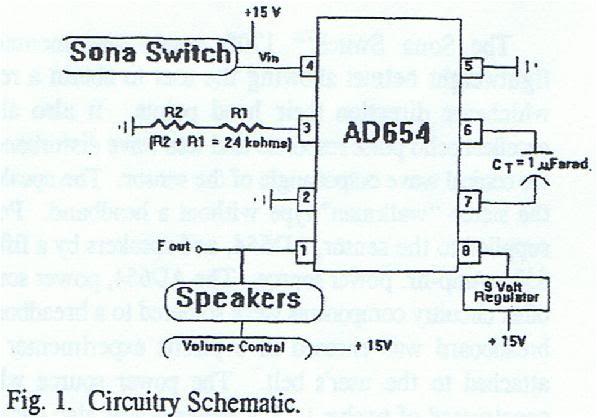
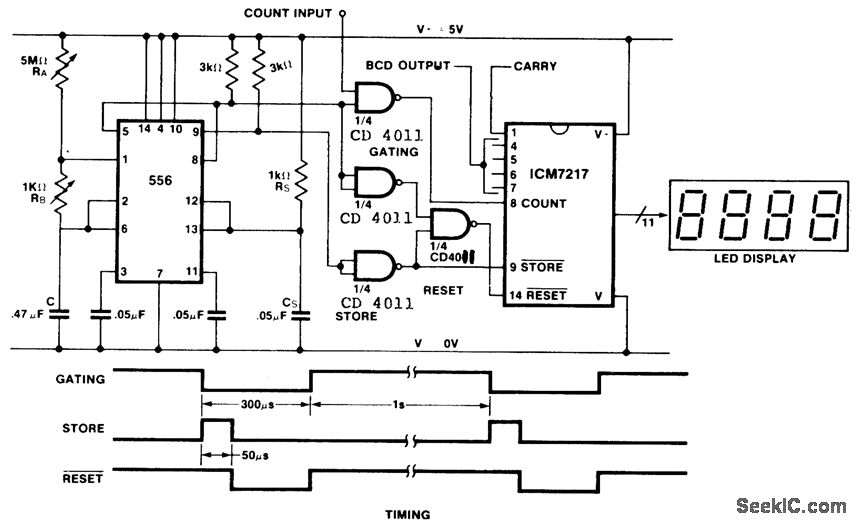
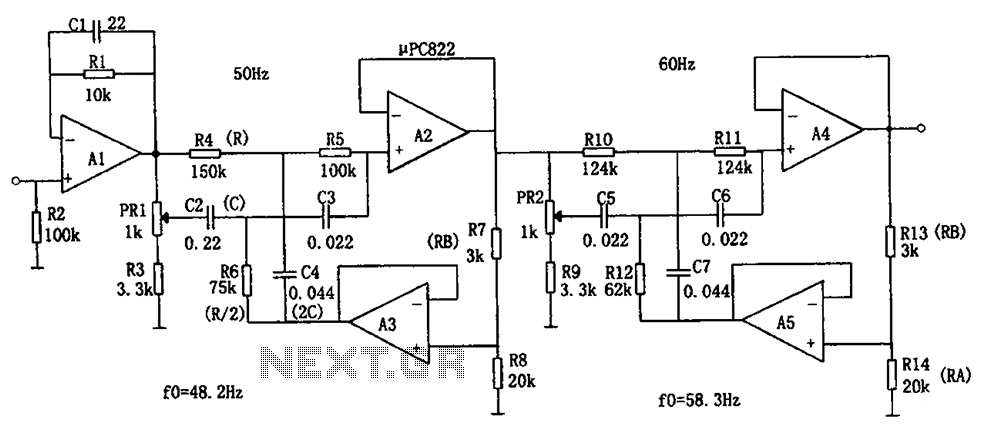
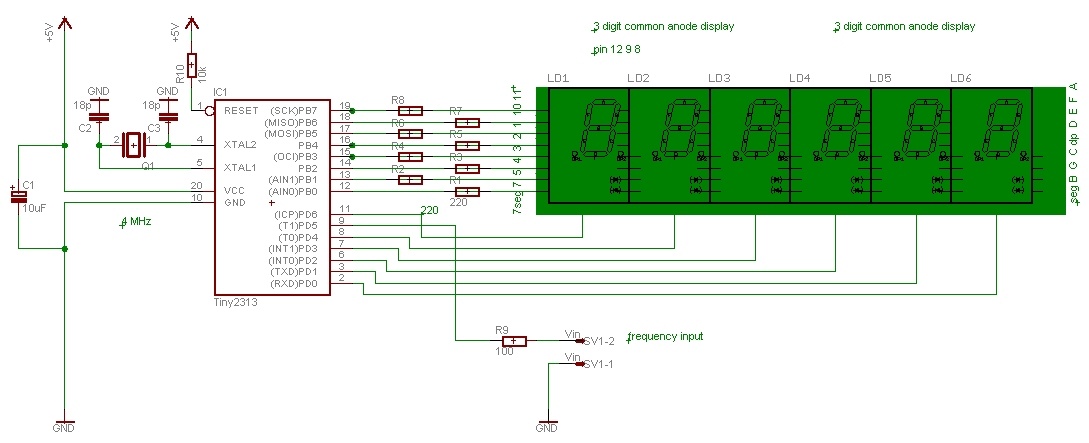
Frequency divider
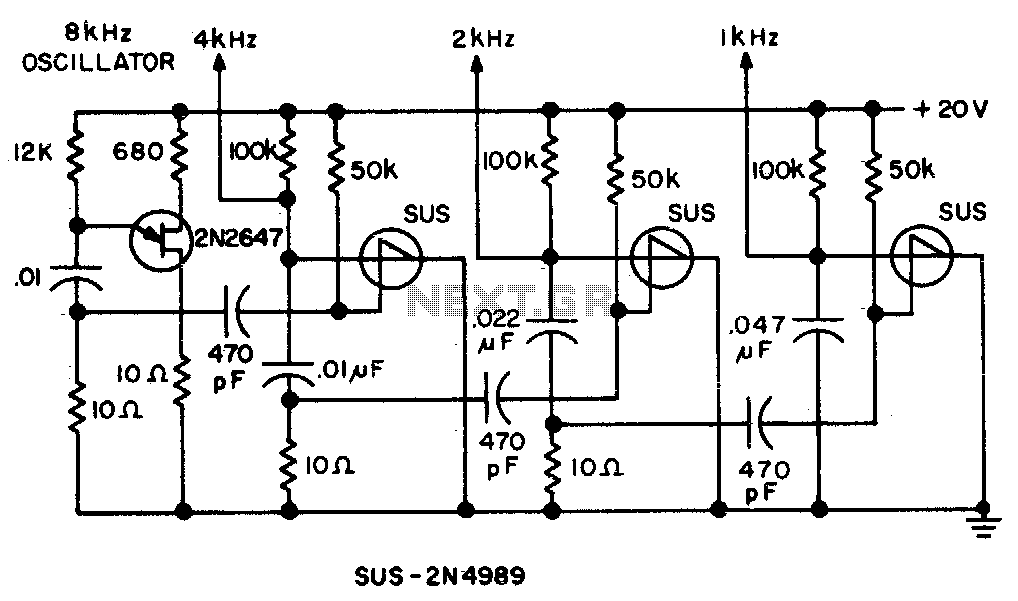
Spikes in the center of a sawtooth wave are eliminated in this circuit by triggering at specific intervals.
This circuit is designed to mitigate unwanted spikes that occur in the center of a sawtooth waveform. The sawtooth wave, characterized by its linear rise and abrupt fall, is commonly used in various applications such as signal generation and waveform synthesis. However, spikes can distort the intended signal, leading to inaccuracies in performance.
The circuit achieves spike elimination through a triggering mechanism. This involves monitoring the sawtooth waveform and identifying the precise moment when a spike occurs. A comparator or a similar device can be employed to detect these anomalies. Once a spike is identified, a control signal is generated to modify the waveform, effectively suppressing the spike.
The design may incorporate operational amplifiers to enhance the detection sensitivity and speed of response. Additionally, filtering components such as capacitors and resistors can be included to smooth out the waveform further, ensuring that the output remains clean and stable.
In summary, this circuit provides a robust solution for spike elimination in sawtooth waves, enhancing the quality and reliability of the signal for various electronic applications.Spikes in the center of a sawtooth wave are eliminated in this circuit by triggering at. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to mitigate unwanted spikes that occur in the center of a sawtooth waveform. The sawtooth wave, characterized by its linear rise and abrupt fall, is commonly used in various applications such as signal generation and waveform synthesis. However, spikes can distort the intended signal, leading to inaccuracies in performance.
The circuit achieves spike elimination through a triggering mechanism. This involves monitoring the sawtooth waveform and identifying the precise moment when a spike occurs. A comparator or a similar device can be employed to detect these anomalies. Once a spike is identified, a control signal is generated to modify the waveform, effectively suppressing the spike.
The design may incorporate operational amplifiers to enhance the detection sensitivity and speed of response. Additionally, filtering components such as capacitors and resistors can be included to smooth out the waveform further, ensuring that the output remains clean and stable.
In summary, this circuit provides a robust solution for spike elimination in sawtooth waves, enhancing the quality and reliability of the signal for various electronic applications.Spikes in the center of a sawtooth wave are eliminated in this circuit by triggering at. 🔗 External reference