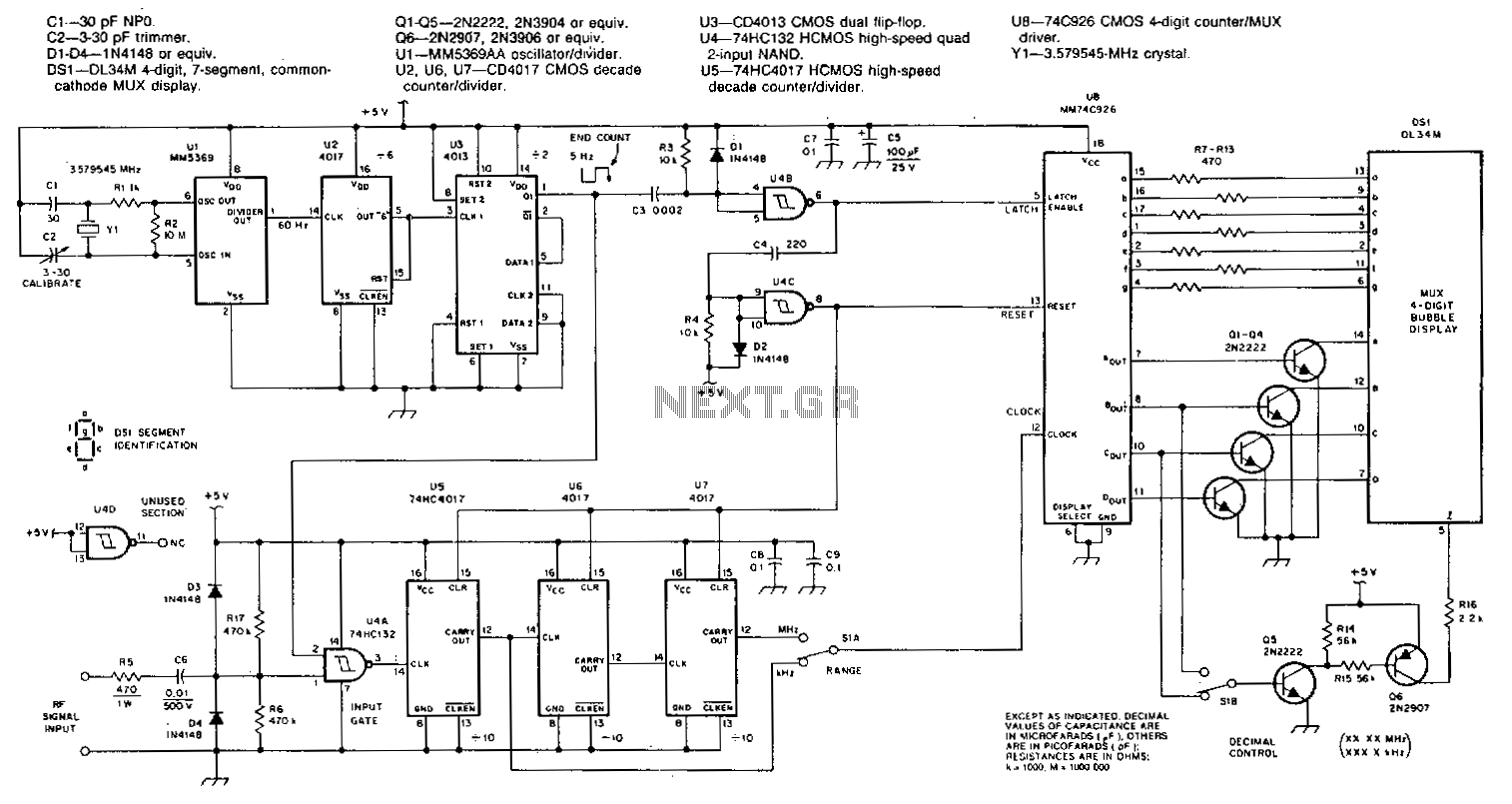
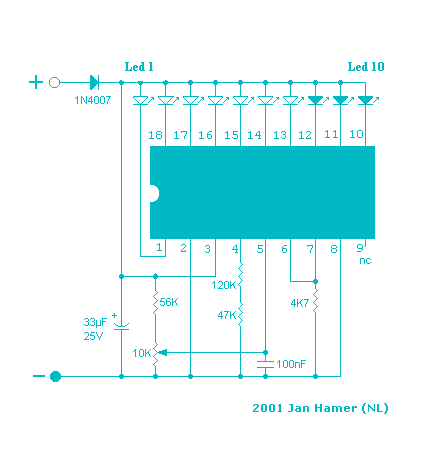
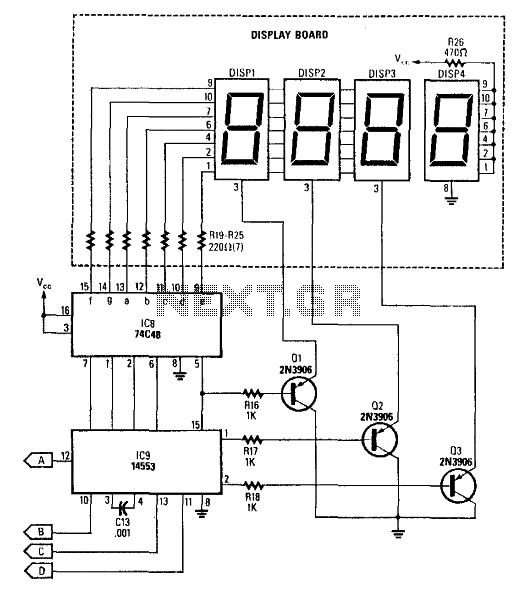
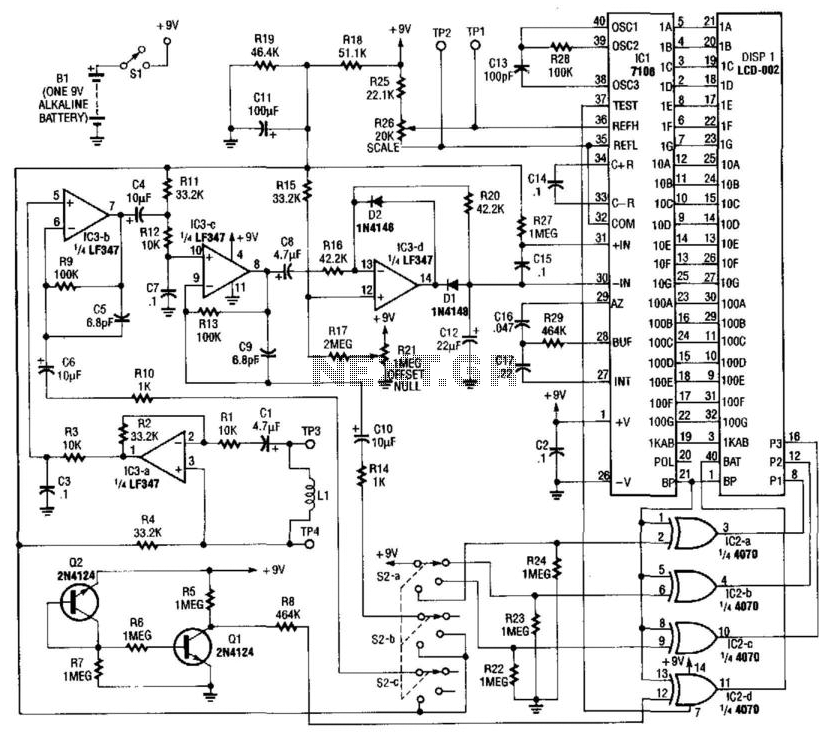
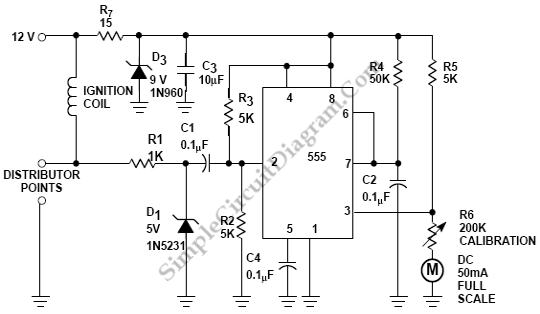
Frequency To Voltage Converter: Change Your Voltmeter To Frequency Meter
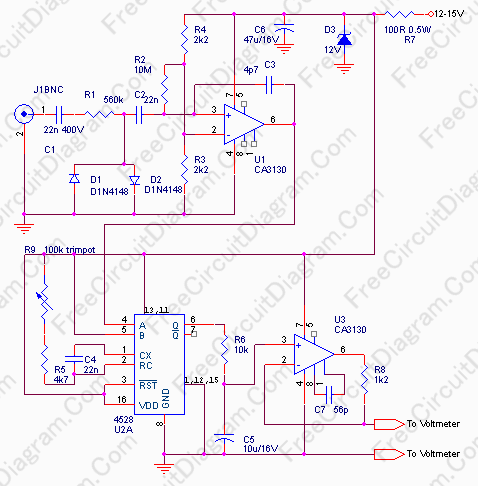
A frequency meter can be utilized in speed sensors, tachometers, or any application that requires the measurement of repetitive signals. This frequency-to-voltage converter (FVC) is designed to facilitate the conversion process.
The frequency meter is an essential instrument in various applications, including automotive speed sensing and industrial tachometry. It operates by measuring the frequency of input signals, which can be derived from rotating machinery, electrical pulses, or other periodic phenomena. The output from the frequency meter can be used to determine the speed of a rotating object or the frequency of an electrical signal.
The frequency-to-voltage converter (FVC) plays a crucial role in this measurement process. It takes the frequency input and converts it into a proportional voltage output. This conversion is typically achieved through the use of operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors configured in a specific manner to ensure accurate linearity and response time.
In practical applications, the FVC can be integrated into a microcontroller or microprocessor system for further processing and display. The output voltage can be calibrated to represent different units, such as RPM (revolutions per minute) or Hz (hertz), allowing for easy interpretation of the data.
When designing a frequency meter circuit, considerations must include the frequency range to be measured, the input signal characteristics, and the desired output format. Additionally, filtering techniques may be employed to eliminate noise and ensure the integrity of the measurements.
Overall, the combination of a frequency meter and a frequency-to-voltage converter provides a versatile solution for measuring and interpreting repetitive signals in various engineering and industrial applications.Frequency meter can be used in speed sensor, tachometer, or any measurement of repetitive signals. This frequency to voltage converter (FVC) can be used to turn. 🔗 External reference
The frequency meter is an essential instrument in various applications, including automotive speed sensing and industrial tachometry. It operates by measuring the frequency of input signals, which can be derived from rotating machinery, electrical pulses, or other periodic phenomena. The output from the frequency meter can be used to determine the speed of a rotating object or the frequency of an electrical signal.
The frequency-to-voltage converter (FVC) plays a crucial role in this measurement process. It takes the frequency input and converts it into a proportional voltage output. This conversion is typically achieved through the use of operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors configured in a specific manner to ensure accurate linearity and response time.
In practical applications, the FVC can be integrated into a microcontroller or microprocessor system for further processing and display. The output voltage can be calibrated to represent different units, such as RPM (revolutions per minute) or Hz (hertz), allowing for easy interpretation of the data.
When designing a frequency meter circuit, considerations must include the frequency range to be measured, the input signal characteristics, and the desired output format. Additionally, filtering techniques may be employed to eliminate noise and ensure the integrity of the measurements.
Overall, the combination of a frequency meter and a frequency-to-voltage converter provides a versatile solution for measuring and interpreting repetitive signals in various engineering and industrial applications.Frequency meter can be used in speed sensor, tachometer, or any measurement of repetitive signals. This frequency to voltage converter (FVC) can be used to turn. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713