Full-Wave Rectifier circuit
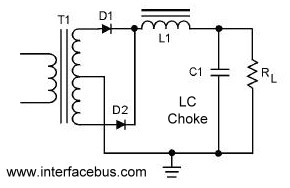
A circuit that utilizes both positive and negative alternations in an alternating current to generate direct current. There are two types of full-wave rectifier circuits: one that employs two diodes and requires a center-tapped transformer, and another that uses four diodes without the need for a center-tapped transformer. The schematic illustrates the direction of current flow during each cycle of the alternating AC waveform. During the positive cycle of the AC input, current flows through CR2, while during the negative AC cycle, it flows through CR1. The DC output voltage is depicted for both AC cycles, as well as the combination of the two cycles. This schematic also presents the same two-diode rectifier using an LC choke. The inductor in the filter aims to maintain a constant current, while the capacitor seeks to stabilize the output voltage.
The full-wave rectifier circuit is essential for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) effectively. The two-diode configuration typically requires a center-tapped transformer, which splits the AC waveform into two halves. Each diode conducts during its respective half-cycle: CR1 conducts during the negative cycle, and CR2 conducts during the positive cycle. This arrangement allows the circuit to utilize both halves of the AC waveform, thereby increasing the efficiency of the conversion process.
In contrast, the four-diode bridge rectifier configuration does not necessitate a center-tapped transformer, making it a more compact and versatile solution. This configuration allows for the same full-wave rectification by arranging the diodes in a bridge layout, where current can flow through the appropriate diode pair depending on the polarity of the input AC signal.
The schematic representation of the circuit provides a visual guide to the current flow, indicating how the diodes are oriented to allow current to pass during both cycles. The output voltage is smoothed by employing an LC filter, which consists of an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C). The inductor works to maintain a steady current, counteracting fluctuations that may arise due to the pulsating nature of the rectified output. Meanwhile, the capacitor acts to filter out voltage spikes and dips, ensuring that the output voltage remains as constant as possible.
The combination of these components results in a reliable DC output that can be used in various applications requiring stable voltage levels, such as power supplies for electronic devices, battery chargers, and other circuits that rely on DC power.A circuit that uses both positive and negative alternations in an alternating current to produce direct current. There are two types of Full-Wave Rectifier circuits; one that only uses two diodes but requires a center tapped transformer [shown below], and one that uses four diodes and does not require a center tapped transformer; The schematic shows the direction of current flow during each cycle of the alternating AC waveform.
The positive cycle of the AC input flows through CR2, while the negative AC cycle flows through CR1. The DC output voltage is shown for both AC cycles, as is the combination of the combined cycles. This schematic shows the same 2-diode rectifier using an LC Choke. The inductor of the filter attempts to keep the current constant while the capacitor attempts to keep the output voltage steady.
🔗 External reference
The full-wave rectifier circuit is essential for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) effectively. The two-diode configuration typically requires a center-tapped transformer, which splits the AC waveform into two halves. Each diode conducts during its respective half-cycle: CR1 conducts during the negative cycle, and CR2 conducts during the positive cycle. This arrangement allows the circuit to utilize both halves of the AC waveform, thereby increasing the efficiency of the conversion process.
In contrast, the four-diode bridge rectifier configuration does not necessitate a center-tapped transformer, making it a more compact and versatile solution. This configuration allows for the same full-wave rectification by arranging the diodes in a bridge layout, where current can flow through the appropriate diode pair depending on the polarity of the input AC signal.
The schematic representation of the circuit provides a visual guide to the current flow, indicating how the diodes are oriented to allow current to pass during both cycles. The output voltage is smoothed by employing an LC filter, which consists of an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C). The inductor works to maintain a steady current, counteracting fluctuations that may arise due to the pulsating nature of the rectified output. Meanwhile, the capacitor acts to filter out voltage spikes and dips, ensuring that the output voltage remains as constant as possible.
The combination of these components results in a reliable DC output that can be used in various applications requiring stable voltage levels, such as power supplies for electronic devices, battery chargers, and other circuits that rely on DC power.A circuit that uses both positive and negative alternations in an alternating current to produce direct current. There are two types of Full-Wave Rectifier circuits; one that only uses two diodes but requires a center tapped transformer [shown below], and one that uses four diodes and does not require a center tapped transformer; The schematic shows the direction of current flow during each cycle of the alternating AC waveform.
The positive cycle of the AC input flows through CR2, while the negative AC cycle flows through CR1. The DC output voltage is shown for both AC cycles, as is the combination of the combined cycles. This schematic shows the same 2-diode rectifier using an LC Choke. The inductor of the filter attempts to keep the current constant while the capacitor attempts to keep the output voltage steady.
🔗 External reference