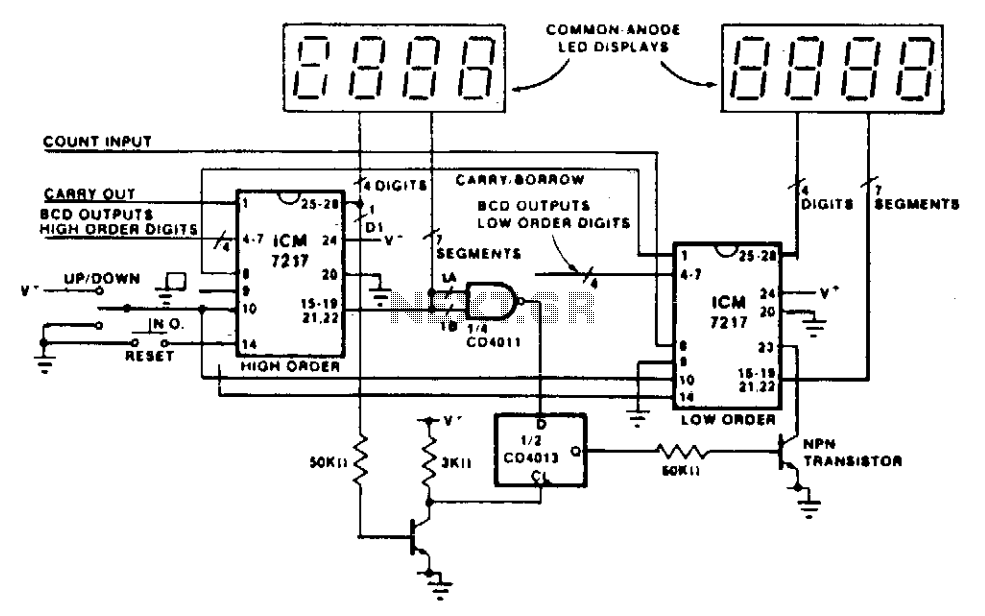
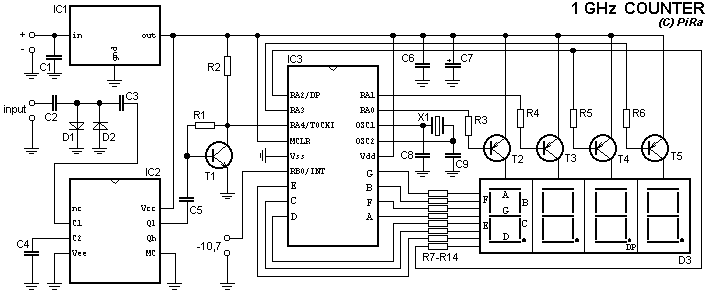
Geiger counter
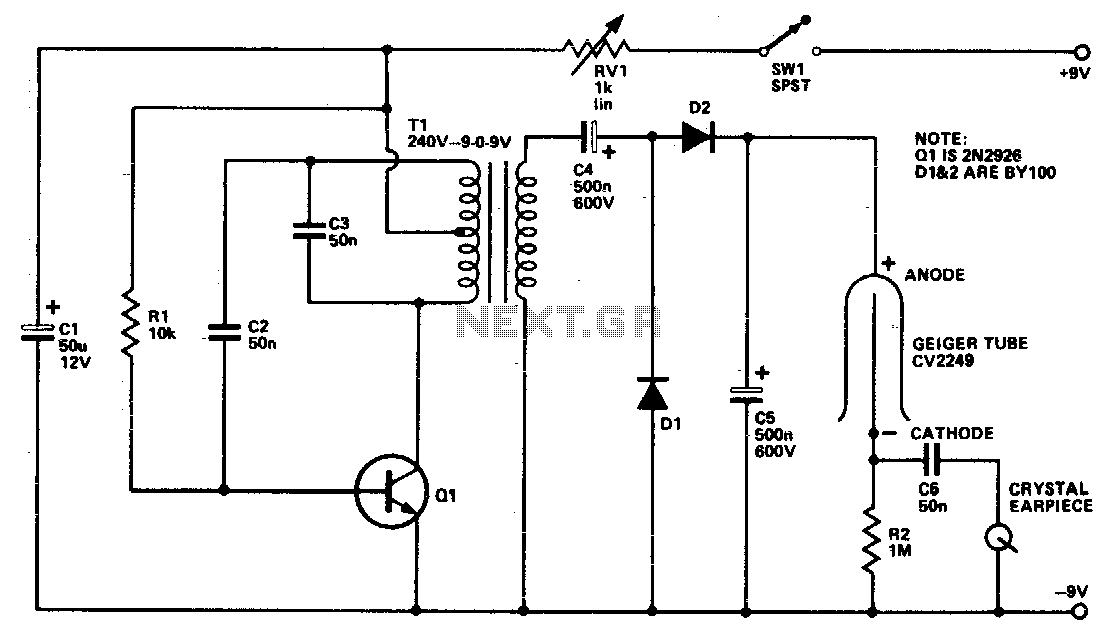
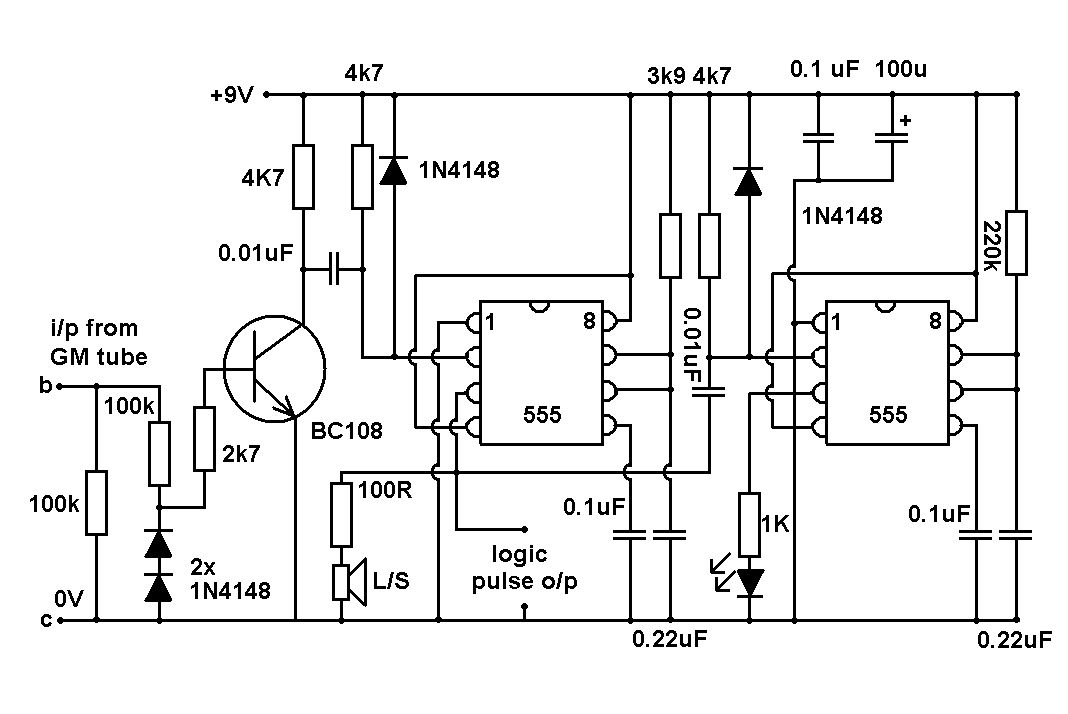
The Geiger tube requires a high voltage supply, which is formed by Q1 and its associated components. The transformer is connected in reverse; the secondary is configured as a Hartley oscillator, while R1 provides base bias. Diodes D1 and D2, along with capacitors C4 and C5, create a voltage doubler circuit. It is important to adjust RV1 to ensure that each click produced is clear and distinct, as exceeding a certain voltage range will result in a continuous buzzing sound.
The described circuit features a Geiger tube, which functions as a radiation detector, necessitating a high voltage supply for its operation. The high voltage is generated by a transistor Q1 and its associated components, which serve to amplify the voltage to the level required by the Geiger tube. The transformer is configured in reverse, allowing the secondary winding to act as a Hartley oscillator. This configuration is instrumental in generating the necessary high-frequency oscillations that are vital for the operation of the Geiger tube.
R1 plays a crucial role in providing the base bias for the transistor Q1, ensuring that it operates within the desired region of its characteristic curve. The diodes D1 and D2, along with capacitors C4 and C5, form a voltage doubler circuit. This arrangement effectively doubles the input voltage, enhancing the efficiency of the high voltage supply. The voltage doubler is essential for achieving the high voltage levels required by the Geiger tube without the need for a bulky transformer.
Furthermore, RV1 is a variable resistor that allows for fine-tuning of the output voltage. Proper adjustment of RV1 is critical; it ensures that the clicks generated by the Geiger tube are audible and clear. If the voltage exceeds a specified range, the output may become distorted, resulting in a continuous buzzing noise rather than distinct clicks. This phenomenon can hinder the usability of the Geiger counter, as clear auditory feedback is necessary for effective operation. Therefore, careful calibration of the circuit is imperative to maintain optimal performance and ensure accurate detection of radiation levels.The Geiger tube needs a high voltage supply which consists of Ql and its associated components. The transformer is connected in reverse; the secondary is connected as a Hartley oscillator, and Rl provides base bias. Dl, D2, C4, and C5 comprise a voltage doubler RVl should be set so that each click heard is nice and clean because over a certain voltage range all that will be heard is a continuous buzz. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit features a Geiger tube, which functions as a radiation detector, necessitating a high voltage supply for its operation. The high voltage is generated by a transistor Q1 and its associated components, which serve to amplify the voltage to the level required by the Geiger tube. The transformer is configured in reverse, allowing the secondary winding to act as a Hartley oscillator. This configuration is instrumental in generating the necessary high-frequency oscillations that are vital for the operation of the Geiger tube.
R1 plays a crucial role in providing the base bias for the transistor Q1, ensuring that it operates within the desired region of its characteristic curve. The diodes D1 and D2, along with capacitors C4 and C5, form a voltage doubler circuit. This arrangement effectively doubles the input voltage, enhancing the efficiency of the high voltage supply. The voltage doubler is essential for achieving the high voltage levels required by the Geiger tube without the need for a bulky transformer.
Furthermore, RV1 is a variable resistor that allows for fine-tuning of the output voltage. Proper adjustment of RV1 is critical; it ensures that the clicks generated by the Geiger tube are audible and clear. If the voltage exceeds a specified range, the output may become distorted, resulting in a continuous buzzing noise rather than distinct clicks. This phenomenon can hinder the usability of the Geiger counter, as clear auditory feedback is necessary for effective operation. Therefore, careful calibration of the circuit is imperative to maintain optimal performance and ensure accurate detection of radiation levels.The Geiger tube needs a high voltage supply which consists of Ql and its associated components. The transformer is connected in reverse; the secondary is connected as a Hartley oscillator, and Rl provides base bias. Dl, D2, C4, and C5 comprise a voltage doubler RVl should be set so that each click heard is nice and clean because over a certain voltage range all that will be heard is a continuous buzz. 🔗 External reference