Grid Dip Oscillator (GDO) Instrument
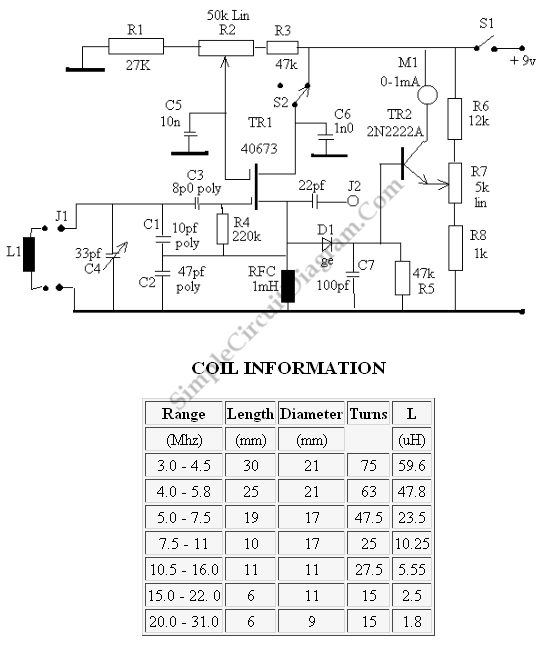
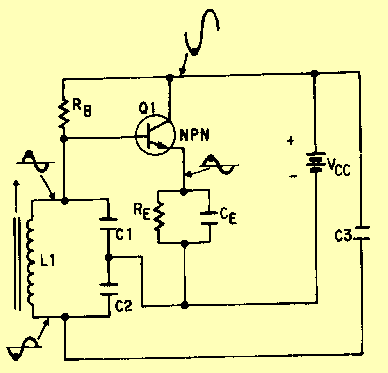
This is a grid dip oscillator (GDO) circuit developed by Luigi Falcone. The circuit uses seven plug-in coils that cover the frequency range of 3.0 to 30 MHz. It can be connected to a frequency meter through the coaxial socket J2. The circuit schematic and coil information are provided in the accompanying figure. A DC amplifier is created using TR2, which allows for the use of a 1 mA full-scale deflection (FSD) meter. Resistor R7 is utilized to control the sensitivity of the 1 mA FSD meter. A field strength meter or RF sniffer is formed by the instrument when TR1 is switched off via switch S2. The coils are wound on Teflon formers with two female sockets that plug into two male sockets on the instrument.
The grid dip oscillator (GDO) circuit is an essential tool for RF engineers and hobbyists, enabling the measurement of resonant frequencies in various circuits. The design features a range of seven plug-in coils, each tailored for specific frequency bands between 3.0 MHz and 30 MHz. This versatility allows users to explore a wide spectrum of radio frequencies with ease.
The connection to a frequency meter via coaxial socket J2 enables accurate frequency readings, enhancing the functionality of the GDO. The inclusion of TR2 as a DC amplifier is crucial; it amplifies the output signal, making it suitable for driving a 1 mA FSD meter. The sensitivity control provided by resistor R7 ensures that the meter can be calibrated to display accurate readings across different signal strengths.
In addition to its primary function, the circuit can also operate as a field strength meter or RF sniffer when TR1 is deactivated using switch S2. This feature allows users to measure the strength of RF signals in the vicinity, providing valuable insights during troubleshooting or experimentation.
The coils used in this circuit are constructed on Teflon formers, which offer excellent dielectric properties and stability. The design incorporates two female sockets that securely connect to male sockets on the main instrument, ensuring reliable coil swapping and ease of use.
Overall, this grid dip oscillator circuit exemplifies a well-engineered solution for frequency measurement and RF signal analysis, making it a valuable addition to any electronics laboratory or workshop.This is a grid dip oscillator (GDO) circuit developed by Luigi Falcone. This circuit uses seven plug in coils covering 3. 0 to 30Mhz. This circuit can be connected to the a frequency meter by using The coaxial socket J2. The figure below shows the schematic diagram of the circuit and the coil information: DC amplifier is formed by TR2 that permit the use of a 1mA FSD meter. R7 is used to control the sensitivity of 1mA FSD meter. a field strength meter/RF sniffer is formed by the instrument with TR1 switched off (via S2). The coils are wound on Teflon formers with two female sockets which plug-in to two male sockets on the instrument. [Source: qsl. net] We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems.
We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference
The grid dip oscillator (GDO) circuit is an essential tool for RF engineers and hobbyists, enabling the measurement of resonant frequencies in various circuits. The design features a range of seven plug-in coils, each tailored for specific frequency bands between 3.0 MHz and 30 MHz. This versatility allows users to explore a wide spectrum of radio frequencies with ease.
The connection to a frequency meter via coaxial socket J2 enables accurate frequency readings, enhancing the functionality of the GDO. The inclusion of TR2 as a DC amplifier is crucial; it amplifies the output signal, making it suitable for driving a 1 mA FSD meter. The sensitivity control provided by resistor R7 ensures that the meter can be calibrated to display accurate readings across different signal strengths.
In addition to its primary function, the circuit can also operate as a field strength meter or RF sniffer when TR1 is deactivated using switch S2. This feature allows users to measure the strength of RF signals in the vicinity, providing valuable insights during troubleshooting or experimentation.
The coils used in this circuit are constructed on Teflon formers, which offer excellent dielectric properties and stability. The design incorporates two female sockets that securely connect to male sockets on the main instrument, ensuring reliable coil swapping and ease of use.
Overall, this grid dip oscillator circuit exemplifies a well-engineered solution for frequency measurement and RF signal analysis, making it a valuable addition to any electronics laboratory or workshop.This is a grid dip oscillator (GDO) circuit developed by Luigi Falcone. This circuit uses seven plug in coils covering 3. 0 to 30Mhz. This circuit can be connected to the a frequency meter by using The coaxial socket J2. The figure below shows the schematic diagram of the circuit and the coil information: DC amplifier is formed by TR2 that permit the use of a 1mA FSD meter. R7 is used to control the sensitivity of 1mA FSD meter. a field strength meter/RF sniffer is formed by the instrument with TR1 switched off (via S2). The coils are wound on Teflon formers with two female sockets which plug-in to two male sockets on the instrument. [Source: qsl. net] We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems.
We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference