Guitar Reverb
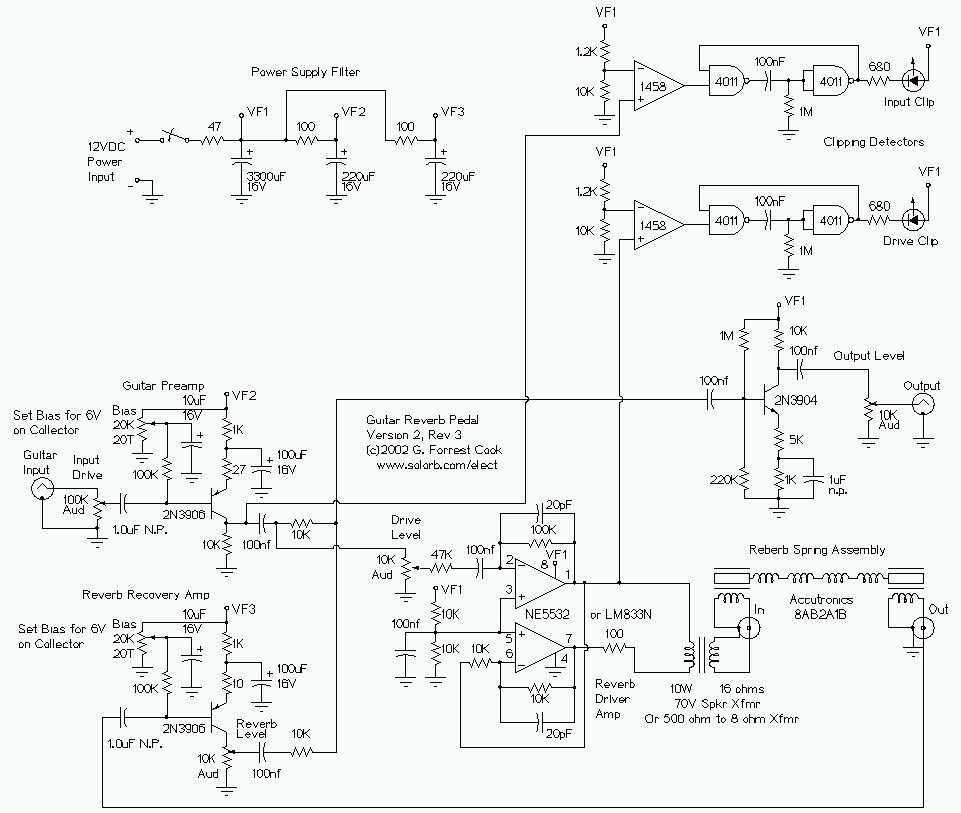
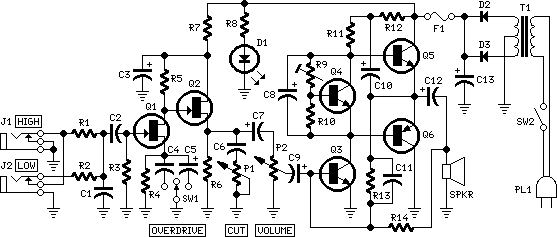
This is my second-generation guitar reverb circuit. The fidelity is much improved over the earlier design, it is suitable for use as a front-end to a guitar amplifier. This circuit features clipping indicators on the preamp and reverb recovery stages, allowing for the optimal gain settings. The guitar input stage is a class A amplifier with adjustable bias. A 2N3906 PNP transistor is used for a low noise design on this stage. The output of the preamp stage is sent to three places: the output mixer amp, the reverb driver amp, and the input clipping detector.
The reverb driver amp consists of a phase inverting push-pull circuit made from dual sections of a 5532 high quality audio op-amp. This provides a voltage swing of approximate twice the supply voltage to the reverb impedance matching transformer, allowing higher power transfer. The transformer matches the impedance of the driver amplifier to the reverb driver coil and allows a dual phase driving signal to power a reverb coil with one grounded side. The transformer is a standard "70 volt" audio line transformer that is o
The second-generation guitar reverb circuit is designed to enhance audio fidelity significantly compared to its predecessor, making it an effective front-end solution for guitar amplifiers. The circuit architecture includes a class A input stage, which utilizes a 2N3906 PNP transistor to ensure low noise operation. This transistor is configured with an adjustable bias to optimize performance based on varying input conditions.
The output from the preamp stage is strategically routed to three destinations: the output mixer amplifier, the reverb driver amplifier, and the input clipping detector. This multi-path design allows for versatile signal processing and monitoring of gain levels. The inclusion of clipping indicators at both the preamp and reverb recovery stages aids in achieving optimal gain settings, preventing distortion and ensuring signal integrity.
The reverb driver amplifier is constructed using a phase-inverting push-pull configuration, which leverages dual sections of a 5532 op-amp. This configuration is crucial as it allows for a voltage swing that can reach approximately twice the supply voltage, thereby enhancing the power transfer to the reverb impedance matching transformer. This transformer plays a vital role in ensuring that the output from the driver amplifier is efficiently matched to the reverb driver coil.
The use of a standard "70 volt" audio line transformer facilitates the generation of a dual phase driving signal, which is essential for powering the reverb coil while maintaining one grounded side. This setup not only optimizes the transfer of power but also contributes to the overall fidelity and performance of the reverb effect, making it suitable for professional audio applications. The design considerations in this circuit ensure that it meets the demands of modern guitar amplification systems, providing musicians with enhanced sound quality and versatile functionality.This is my second-generation guitar reverb circuit. The fidelity is much improved over the earlier design, it is suitable for use as a front-end to a guitar amplifier. This circuit features clipping indicators on the preamp and reverb recovery stages, allowing for the optimal gain settings.
The guitar input stage is a class A amplifier with adjustable bias. A 2N3906 PNP tranistor is used for a low noise design on this stage. The output of the preamp stage is sent to three places: the output mixer amp, the reverb driver amp, and the input clipping detector. The reverb driver amp consists of a phase inverting push-pull circuit made from dual sections of a 5532 high quality audio op-amp.
This provides a voltage swing of approximate twice the supply voltage to the reverb impedance matching transformer, allowing higher power transfer. The transformer matches the impedance of the driver amplifer to the reverb driver coil and allows a dual phase driving signal to power a reverb coil with one grounded side. The transformer is a standard "70 volt" audio line transformer that is o 🔗 External reference
The reverb driver amp consists of a phase inverting push-pull circuit made from dual sections of a 5532 high quality audio op-amp. This provides a voltage swing of approximate twice the supply voltage to the reverb impedance matching transformer, allowing higher power transfer. The transformer matches the impedance of the driver amplifier to the reverb driver coil and allows a dual phase driving signal to power a reverb coil with one grounded side. The transformer is a standard "70 volt" audio line transformer that is o
The second-generation guitar reverb circuit is designed to enhance audio fidelity significantly compared to its predecessor, making it an effective front-end solution for guitar amplifiers. The circuit architecture includes a class A input stage, which utilizes a 2N3906 PNP transistor to ensure low noise operation. This transistor is configured with an adjustable bias to optimize performance based on varying input conditions.
The output from the preamp stage is strategically routed to three destinations: the output mixer amplifier, the reverb driver amplifier, and the input clipping detector. This multi-path design allows for versatile signal processing and monitoring of gain levels. The inclusion of clipping indicators at both the preamp and reverb recovery stages aids in achieving optimal gain settings, preventing distortion and ensuring signal integrity.
The reverb driver amplifier is constructed using a phase-inverting push-pull configuration, which leverages dual sections of a 5532 op-amp. This configuration is crucial as it allows for a voltage swing that can reach approximately twice the supply voltage, thereby enhancing the power transfer to the reverb impedance matching transformer. This transformer plays a vital role in ensuring that the output from the driver amplifier is efficiently matched to the reverb driver coil.
The use of a standard "70 volt" audio line transformer facilitates the generation of a dual phase driving signal, which is essential for powering the reverb coil while maintaining one grounded side. This setup not only optimizes the transfer of power but also contributes to the overall fidelity and performance of the reverb effect, making it suitable for professional audio applications. The design considerations in this circuit ensure that it meets the demands of modern guitar amplification systems, providing musicians with enhanced sound quality and versatile functionality.This is my second-generation guitar reverb circuit. The fidelity is much improved over the earlier design, it is suitable for use as a front-end to a guitar amplifier. This circuit features clipping indicators on the preamp and reverb recovery stages, allowing for the optimal gain settings.
The guitar input stage is a class A amplifier with adjustable bias. A 2N3906 PNP tranistor is used for a low noise design on this stage. The output of the preamp stage is sent to three places: the output mixer amp, the reverb driver amp, and the input clipping detector. The reverb driver amp consists of a phase inverting push-pull circuit made from dual sections of a 5532 high quality audio op-amp.
This provides a voltage swing of approximate twice the supply voltage to the reverb impedance matching transformer, allowing higher power transfer. The transformer matches the impedance of the driver amplifer to the reverb driver coil and allows a dual phase driving signal to power a reverb coil with one grounded side. The transformer is a standard "70 volt" audio line transformer that is o 🔗 External reference