H-Bridge Motor Driver using MOSFETs and Transistors
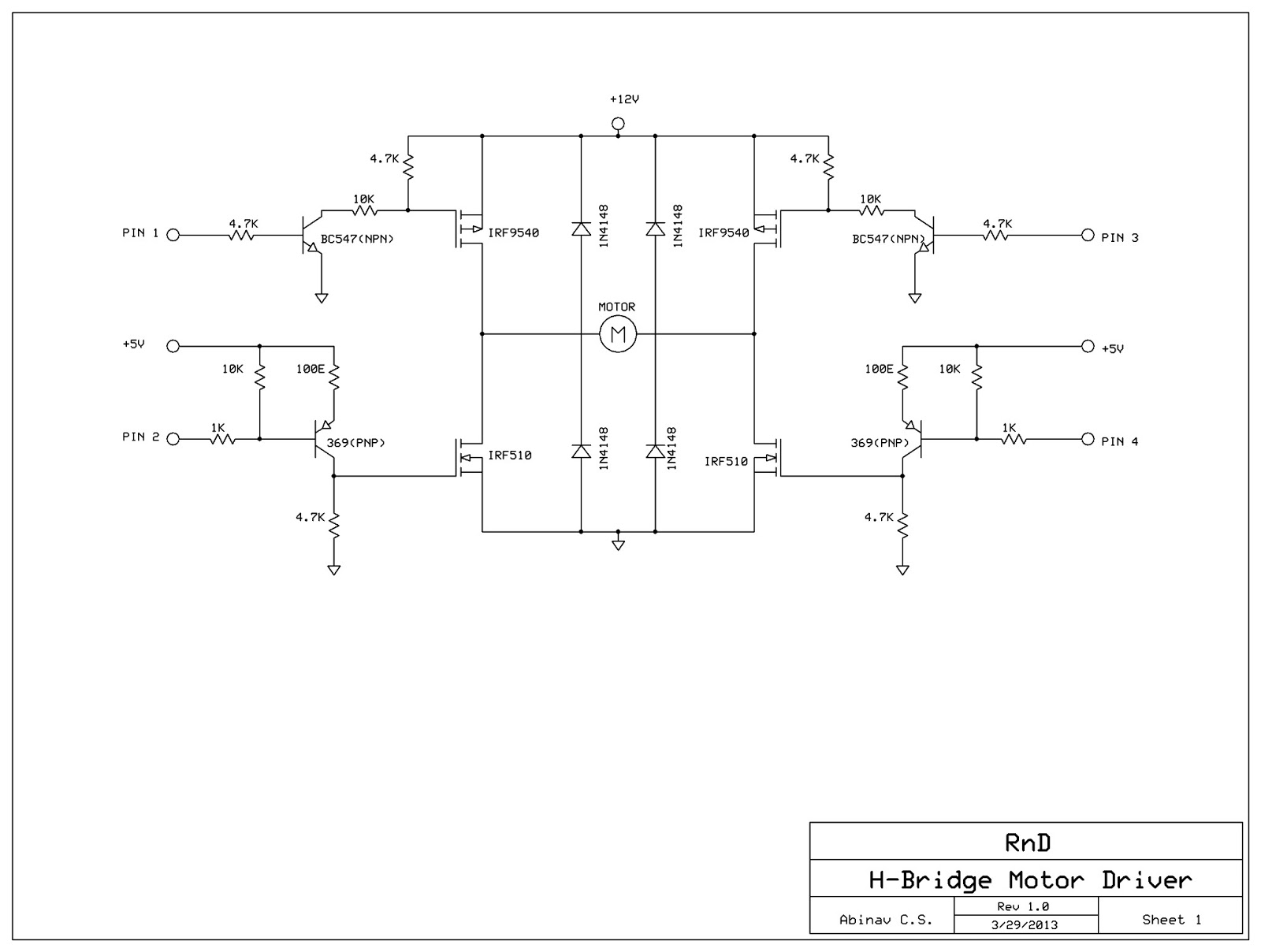
This post discusses the construction of an H-Bridge Motor Driver circuit using simple MOSFETs and transistors. The primary feature of this H-Bridge is its ability to drive a motor in both directions. An H-Bridge is a circuit that allows voltage to be applied across any load, such as a motor in this experiment, in two directions. The term 'H' refers to the configuration of the circuit and does not relate to any specific individual. The H-Bridge arrangement is typically used to reverse the polarity of the motor and to enable the motor to 'free run' to a stop, as it effectively disconnects the motor from the circuit. The following table summarizes the operation, with S1-S4 corresponding to the diagram above.
The H-Bridge Motor Driver circuit is an essential component in various applications, including robotics and automation, where bidirectional control of a motor is required. The circuit consists of four switching elements, typically MOSFETs or transistors, arranged in an 'H' formation. These switches control the flow of current through the motor, allowing it to rotate in either clockwise or counterclockwise directions.
In operation, the H-Bridge can be controlled by applying signals to the gates of the MOSFETs. For instance, turning on switches S1 and S4 allows current to flow through the motor in one direction, while activating switches S2 and S3 reverses the current flow, thus reversing the motor's direction. This capability is crucial for applications that require precise control over motor movement.
Additionally, when all switches are turned off, the motor is effectively disconnected from the power source, allowing it to coast to a stop. This feature is beneficial for energy efficiency and helps to prevent unnecessary power consumption when the motor is not in use.
In a typical implementation, the control signals for the MOSFETs can be provided by a microcontroller or a dedicated motor driver IC. The choice of MOSFETs should be based on the motor's voltage and current ratings to ensure reliable operation. Proper heat dissipation mechanisms, such as heat sinks, may also be necessary to manage thermal performance during operation.
The comprehensive understanding of the H-Bridge circuit's operation, along with its configuration and control mechanisms, is vital for engineers and designers working with motor control applications.In this post, we shall be covering on how to construct a H-Bridge Motor Driver circuit using simple MOSFET`s and Transistors. The main feature of this H-Bridge is that the motor can be driven in both directions. AnH-bridgeis a circuitthat allows a voltage to be applied across any load, like a motor in our experiment, in dual directions.
The `H` h ere just represents the formation of the circuit and has no reference to anyone. The H-bridge arrangement is generally used to reverse the polarity of the motor and to let the motor `free run` to a stop, as the motor is effectively disconnected from the circuit. The following table summarizes operation, with S1-S4 corresponding to the diagram above. 🔗 External reference
The H-Bridge Motor Driver circuit is an essential component in various applications, including robotics and automation, where bidirectional control of a motor is required. The circuit consists of four switching elements, typically MOSFETs or transistors, arranged in an 'H' formation. These switches control the flow of current through the motor, allowing it to rotate in either clockwise or counterclockwise directions.
In operation, the H-Bridge can be controlled by applying signals to the gates of the MOSFETs. For instance, turning on switches S1 and S4 allows current to flow through the motor in one direction, while activating switches S2 and S3 reverses the current flow, thus reversing the motor's direction. This capability is crucial for applications that require precise control over motor movement.
Additionally, when all switches are turned off, the motor is effectively disconnected from the power source, allowing it to coast to a stop. This feature is beneficial for energy efficiency and helps to prevent unnecessary power consumption when the motor is not in use.
In a typical implementation, the control signals for the MOSFETs can be provided by a microcontroller or a dedicated motor driver IC. The choice of MOSFETs should be based on the motor's voltage and current ratings to ensure reliable operation. Proper heat dissipation mechanisms, such as heat sinks, may also be necessary to manage thermal performance during operation.
The comprehensive understanding of the H-Bridge circuit's operation, along with its configuration and control mechanisms, is vital for engineers and designers working with motor control applications.In this post, we shall be covering on how to construct a H-Bridge Motor Driver circuit using simple MOSFET`s and Transistors. The main feature of this H-Bridge is that the motor can be driven in both directions. AnH-bridgeis a circuitthat allows a voltage to be applied across any load, like a motor in our experiment, in dual directions.
The `H` h ere just represents the formation of the circuit and has no reference to anyone. The H-bridge arrangement is generally used to reverse the polarity of the motor and to let the motor `free run` to a stop, as the motor is effectively disconnected from the circuit. The following table summarizes operation, with S1-S4 corresponding to the diagram above. 🔗 External reference