Hartley Oscillator Tutorial and Oscillator Design
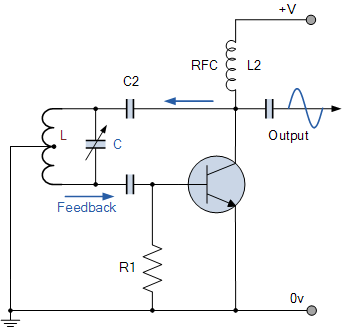
Hartley Oscillator tutorial and the theory behind the design of the Hartley Oscillator, which uses an LC oscillator tank circuit to generate sine waves.
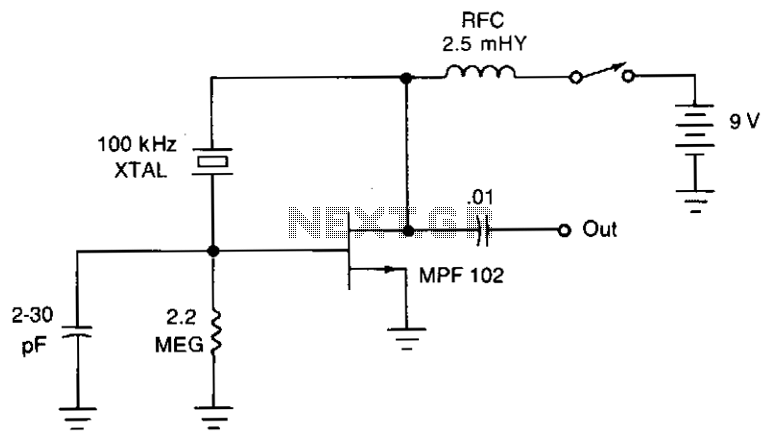
The Hartley oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves using an inductor-capacitor (LC) tank circuit. It is characterized by its use of two inductors and a single capacitor to determine the oscillation frequency. The basic configuration includes a transistor that acts as an amplifier, and the feedback necessary for oscillation is provided by the LC tank circuit.
In a typical Hartley oscillator circuit, two inductors (L1 and L2) are connected in series with a capacitor (C). The total inductance is given by the formula L_total = L1 + L2. The frequency of oscillation can be calculated using the formula:
f = 1 / (2π√(L_total * C))
where f is the frequency in hertz, L_total is the total inductance in henries, and C is the capacitance in farads. The choice of inductors and capacitors directly affects the output frequency and stability of the oscillator.
The transistor, which can be either bipolar junction or field-effect, amplifies the signal generated by the tank circuit. The feedback loop is critical for sustaining oscillations, and it is achieved by connecting a portion of the output back to the input through the LC circuit. The phase shift around the loop must be 360 degrees for sustained oscillation, which is typically achieved by ensuring that the total phase shift through the transistor and the tank circuit meets this requirement.
Hartley oscillators are commonly used in radio frequency applications due to their ability to produce stable sine wave signals. They are also valued for their simplicity and ease of tuning, which makes them suitable for various applications, including signal generation and modulation. When designing a Hartley oscillator, careful consideration must be given to component selection, layout, and power supply to ensure optimal performance and minimize distortion in the output waveform.Hartley Oscillator Tutorial and the theory behind the design of the Hartley Oscillator which uses a LC Oscillator tank circuit to generate sine waves.. 🔗 External reference
The Hartley oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves using an inductor-capacitor (LC) tank circuit. It is characterized by its use of two inductors and a single capacitor to determine the oscillation frequency. The basic configuration includes a transistor that acts as an amplifier, and the feedback necessary for oscillation is provided by the LC tank circuit.
In a typical Hartley oscillator circuit, two inductors (L1 and L2) are connected in series with a capacitor (C). The total inductance is given by the formula L_total = L1 + L2. The frequency of oscillation can be calculated using the formula:
f = 1 / (2π√(L_total * C))
where f is the frequency in hertz, L_total is the total inductance in henries, and C is the capacitance in farads. The choice of inductors and capacitors directly affects the output frequency and stability of the oscillator.
The transistor, which can be either bipolar junction or field-effect, amplifies the signal generated by the tank circuit. The feedback loop is critical for sustaining oscillations, and it is achieved by connecting a portion of the output back to the input through the LC circuit. The phase shift around the loop must be 360 degrees for sustained oscillation, which is typically achieved by ensuring that the total phase shift through the transistor and the tank circuit meets this requirement.
Hartley oscillators are commonly used in radio frequency applications due to their ability to produce stable sine wave signals. They are also valued for their simplicity and ease of tuning, which makes them suitable for various applications, including signal generation and modulation. When designing a Hartley oscillator, careful consideration must be given to component selection, layout, and power supply to ensure optimal performance and minimize distortion in the output waveform.Hartley Oscillator Tutorial and the theory behind the design of the Hartley Oscillator which uses a LC Oscillator tank circuit to generate sine waves.. 🔗 External reference