Design of astable multivibrator
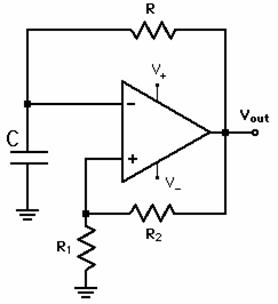
An astable multivibrator needs to be designed, and the maximum and minimum frequencies generated at the output must be calculated.
An astable multivibrator is a type of oscillator circuit that continuously switches between its high and low states without requiring any external triggering. This circuit is commonly built using bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) or operational amplifiers (op-amps), but it can also be constructed using integrated circuits such as the 555 timer.
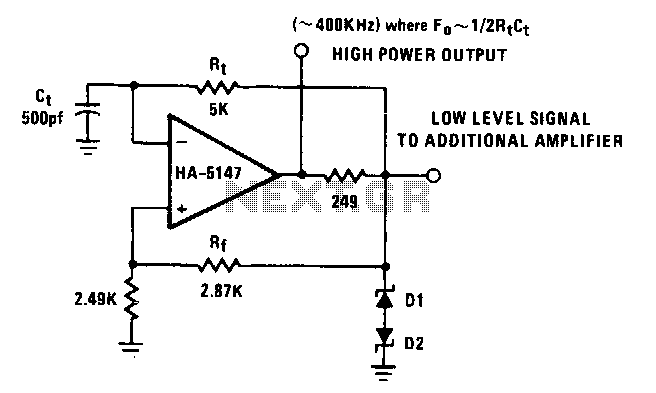
The basic configuration consists of two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C) connected to the timing circuit. The output frequency (f) of the astable multivibrator can be calculated using the formula:
f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 * R2) * C)
In this equation, R1 and R2 are the resistances in ohms, and C is the capacitance in farads. The maximum frequency occurs when R1 and R2 are minimized, while the minimum frequency occurs when these resistances are maximized.
To derive the maximum frequency, the values of R1 and R2 should be as low as possible. Conversely, for the minimum frequency, the resistances should be maximized. The choice of capacitor value (C) also plays a significant role, as it directly influences the timing intervals.
In practical applications, it is essential to consider the tolerances of the components used, as variations can affect the output frequency. Additionally, the supply voltage and power ratings of the components must be suitable for the intended application to ensure reliable operation.
In summary, designing an astable multivibrator requires careful selection of resistor and capacitor values to achieve the desired output frequencies. Calculating the maximum and minimum frequencies is crucial for ensuring that the circuit meets its intended performance specifications.Hello sir, I need to design an astable multivibrator and supposed to calculate the maximum and minimum frequency generated at the output. Can you.. 🔗 External reference
An astable multivibrator is a type of oscillator circuit that continuously switches between its high and low states without requiring any external triggering. This circuit is commonly built using bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) or operational amplifiers (op-amps), but it can also be constructed using integrated circuits such as the 555 timer.
The basic configuration consists of two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C) connected to the timing circuit. The output frequency (f) of the astable multivibrator can be calculated using the formula:
f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 * R2) * C)
In this equation, R1 and R2 are the resistances in ohms, and C is the capacitance in farads. The maximum frequency occurs when R1 and R2 are minimized, while the minimum frequency occurs when these resistances are maximized.
To derive the maximum frequency, the values of R1 and R2 should be as low as possible. Conversely, for the minimum frequency, the resistances should be maximized. The choice of capacitor value (C) also plays a significant role, as it directly influences the timing intervals.
In practical applications, it is essential to consider the tolerances of the components used, as variations can affect the output frequency. Additionally, the supply voltage and power ratings of the components must be suitable for the intended application to ensure reliable operation.
In summary, designing an astable multivibrator requires careful selection of resistor and capacitor values to achieve the desired output frequencies. Calculating the maximum and minimum frequencies is crucial for ensuring that the circuit meets its intended performance specifications.Hello sir, I need to design an astable multivibrator and supposed to calculate the maximum and minimum frequency generated at the output. Can you.. 🔗 External reference