HeadPhone Amplifier OR PreAmplifier OutPut Stage
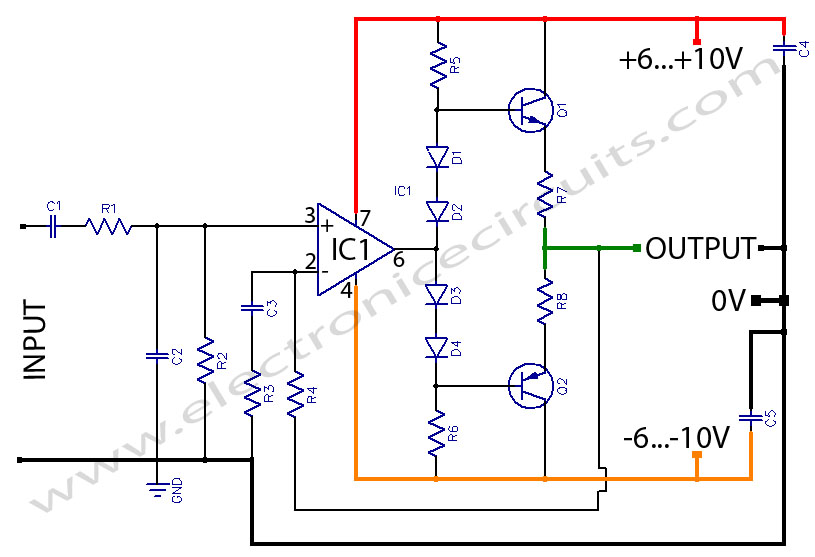
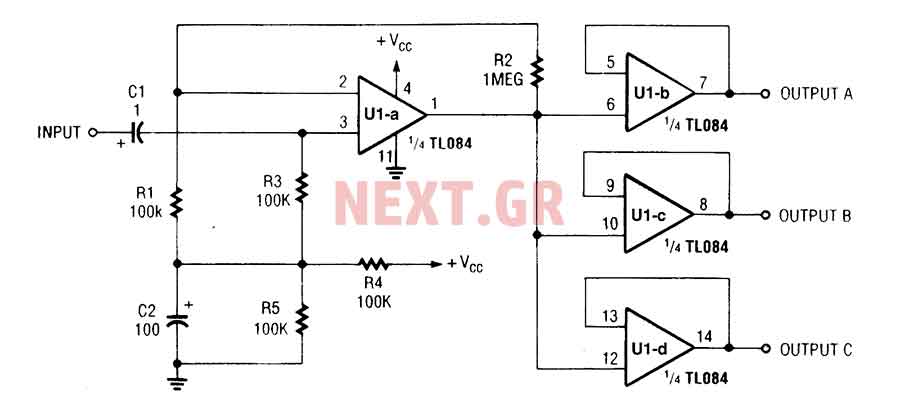
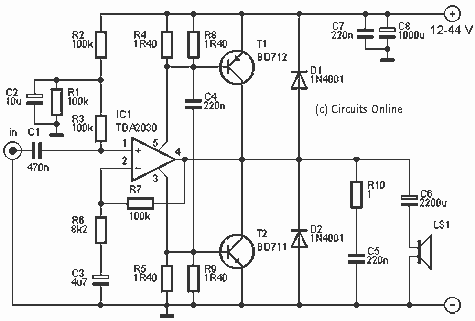
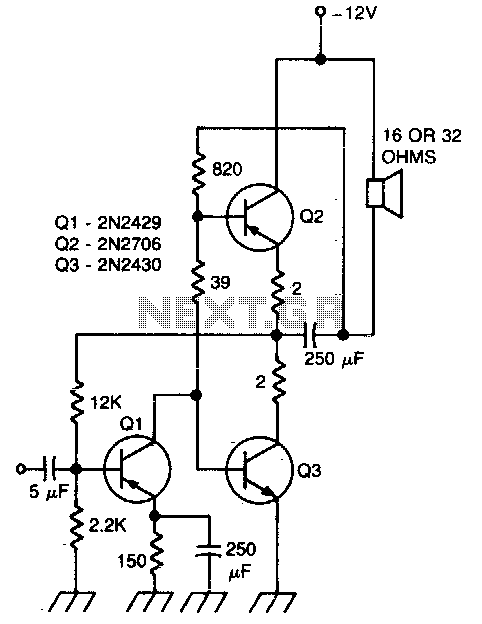
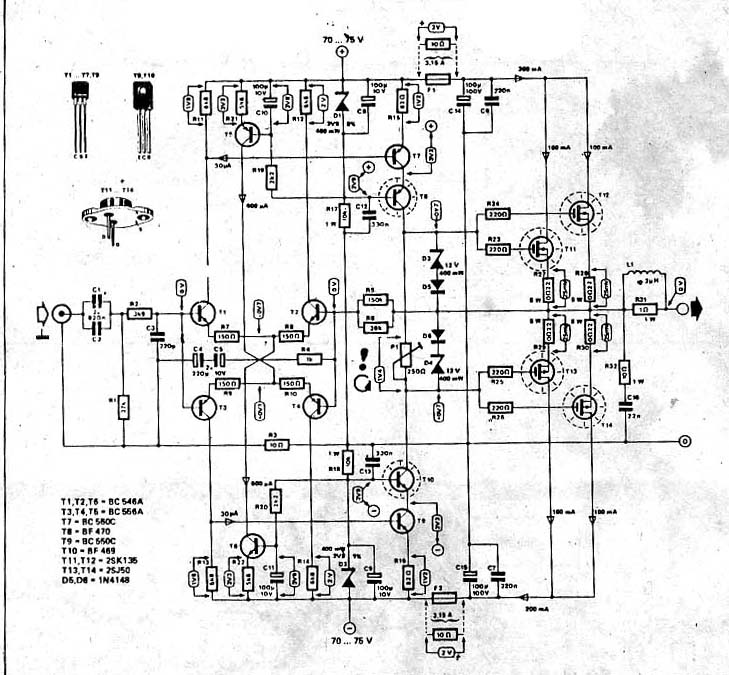
Headphone Amplifier or Pre-Amplifier Output Stage. This 1-watt amplifier is ideally suited for use as a driver for low-impedance headphones.
The headphone amplifier circuit is designed to provide an amplified audio signal to drive low-impedance headphones effectively. Operating at a power output of 1 watt, the amplifier can deliver sufficient audio levels while maintaining sound quality and clarity.
The circuit typically includes several key components: an input stage, amplification stage, and output stage. The input stage often consists of a differential amplifier configuration to ensure high input impedance and low noise. This is crucial for preserving audio fidelity, especially when dealing with low-level audio signals.
The amplification stage usually employs operational amplifiers or transistor-based designs, which are responsible for boosting the audio signal. The choice of components in this stage is essential, as they determine the overall gain, bandwidth, and linearity of the amplifier. For instance, using high-quality op-amps can significantly enhance performance by reducing distortion and improving dynamic range.
The output stage is designed to drive low-impedance loads, typically found in headphones. This stage may include a class A or class AB configuration to balance efficiency and audio quality. Proper heat dissipation methods, such as heat sinks or thermal pads, should be incorporated to prevent overheating during extended use.
Power supply considerations are also vital, as the amplifier requires a stable DC voltage to operate efficiently. A regulated power supply can help minimize noise and fluctuations in the audio output. Additionally, decoupling capacitors should be placed close to the power supply pins of the amplifier to filter out high-frequency noise.
In summary, the headphone amplifier circuit is a critical component for driving low-impedance headphones, ensuring that the audio signal is amplified without distortion, thereby providing an optimal listening experience.HeadPhone Amplifier OR PreAmplifier OutPut Stage This 1 watt amplifier lends itself par excellence for use as driver for low impedance headphone.. 🔗 External reference
The headphone amplifier circuit is designed to provide an amplified audio signal to drive low-impedance headphones effectively. Operating at a power output of 1 watt, the amplifier can deliver sufficient audio levels while maintaining sound quality and clarity.
The circuit typically includes several key components: an input stage, amplification stage, and output stage. The input stage often consists of a differential amplifier configuration to ensure high input impedance and low noise. This is crucial for preserving audio fidelity, especially when dealing with low-level audio signals.
The amplification stage usually employs operational amplifiers or transistor-based designs, which are responsible for boosting the audio signal. The choice of components in this stage is essential, as they determine the overall gain, bandwidth, and linearity of the amplifier. For instance, using high-quality op-amps can significantly enhance performance by reducing distortion and improving dynamic range.
The output stage is designed to drive low-impedance loads, typically found in headphones. This stage may include a class A or class AB configuration to balance efficiency and audio quality. Proper heat dissipation methods, such as heat sinks or thermal pads, should be incorporated to prevent overheating during extended use.
Power supply considerations are also vital, as the amplifier requires a stable DC voltage to operate efficiently. A regulated power supply can help minimize noise and fluctuations in the audio output. Additionally, decoupling capacitors should be placed close to the power supply pins of the amplifier to filter out high-frequency noise.
In summary, the headphone amplifier circuit is a critical component for driving low-impedance headphones, ensuring that the audio signal is amplified without distortion, thereby providing an optimal listening experience.HeadPhone Amplifier OR PreAmplifier OutPut Stage This 1 watt amplifier lends itself par excellence for use as driver for low impedance headphone.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713