Hi Fi Stereo Preamp Circuit
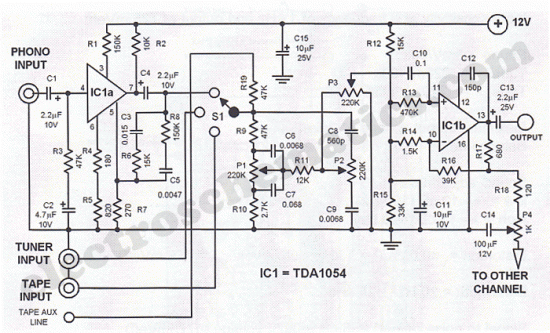
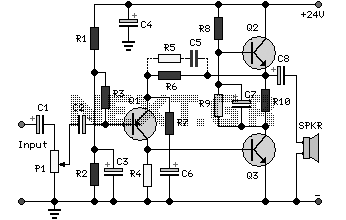
The first half of the circuit (IC1a) features an input sensitivity of 3 mV and includes a frequency correction network consisting of capacitors C5, C3, and resistors R6 and R8. The bass signal from the phono input is amplified, while higher frequencies are attenuated. Signal source selection is managed by switch S1. Potentiometers P1 and P2 are part of a dual potentiometer configuration, controlling high and low tones, respectively. The circuit design mitigates the risk of overdrive due to the passive nature of the sound control elements.
The circuit described is a typical audio processing stage, where IC1a serves as the primary operational amplifier. The input sensitivity of 3 mV indicates its capability to handle low-level signals, making it suitable for phono inputs from turntables or other audio sources. The frequency correction network, composed of capacitors C5 and C3, along with resistors R6 and R8, plays a crucial role in shaping the frequency response of the circuit. This network ensures that the bass frequencies are amplified while high frequencies are attenuated, providing a tailored audio output that emphasizes lower frequencies, which is often desirable in music playback.
The switch S1 allows the user to select between different input sources, facilitating versatility in audio signal management. The dual potentiometer configuration, represented by P1 and P2, enables independent control over high and low tone adjustments. This design allows for fine-tuning of the audio output, accommodating various listening preferences and audio characteristics.
The passive nature of the sound control elements within the circuit effectively reduces the risk of overdrive, a common issue in audio amplification circuits where excessive signal levels can lead to distortion. By utilizing passive components for tone control, the circuit maintains a more stable response and minimizes the potential for unwanted clipping or distortion, ensuring a clean and high-fidelity audio output. Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a thoughtful approach to audio processing, balancing sensitivity, frequency response, and user control in a cohesive manner.The first half of the circuit (IC1a) it has an input sensitivity of 3 mV and has a frequency correction composed of C5, C3, R6 and R8. The bass signal coming from phono input is amplified while the high signal is attenuated. The selection of the input signal sources is done with switch S1. P1 and P2 are parte of a double potentiometer. They contro l the high tones and bass. There is no risk of overdrive in circuit due to the passive nature of the sound control. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described is a typical audio processing stage, where IC1a serves as the primary operational amplifier. The input sensitivity of 3 mV indicates its capability to handle low-level signals, making it suitable for phono inputs from turntables or other audio sources. The frequency correction network, composed of capacitors C5 and C3, along with resistors R6 and R8, plays a crucial role in shaping the frequency response of the circuit. This network ensures that the bass frequencies are amplified while high frequencies are attenuated, providing a tailored audio output that emphasizes lower frequencies, which is often desirable in music playback.
The switch S1 allows the user to select between different input sources, facilitating versatility in audio signal management. The dual potentiometer configuration, represented by P1 and P2, enables independent control over high and low tone adjustments. This design allows for fine-tuning of the audio output, accommodating various listening preferences and audio characteristics.
The passive nature of the sound control elements within the circuit effectively reduces the risk of overdrive, a common issue in audio amplification circuits where excessive signal levels can lead to distortion. By utilizing passive components for tone control, the circuit maintains a more stable response and minimizes the potential for unwanted clipping or distortion, ensuring a clean and high-fidelity audio output. Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a thoughtful approach to audio processing, balancing sensitivity, frequency response, and user control in a cohesive manner.The first half of the circuit (IC1a) it has an input sensitivity of 3 mV and has a frequency correction composed of C5, C3, R6 and R8. The bass signal coming from phono input is amplified while the high signal is attenuated. The selection of the input signal sources is done with switch S1. P1 and P2 are parte of a double potentiometer. They contro l the high tones and bass. There is no risk of overdrive in circuit due to the passive nature of the sound control. 🔗 External reference