HiFI Headphone Amplifier
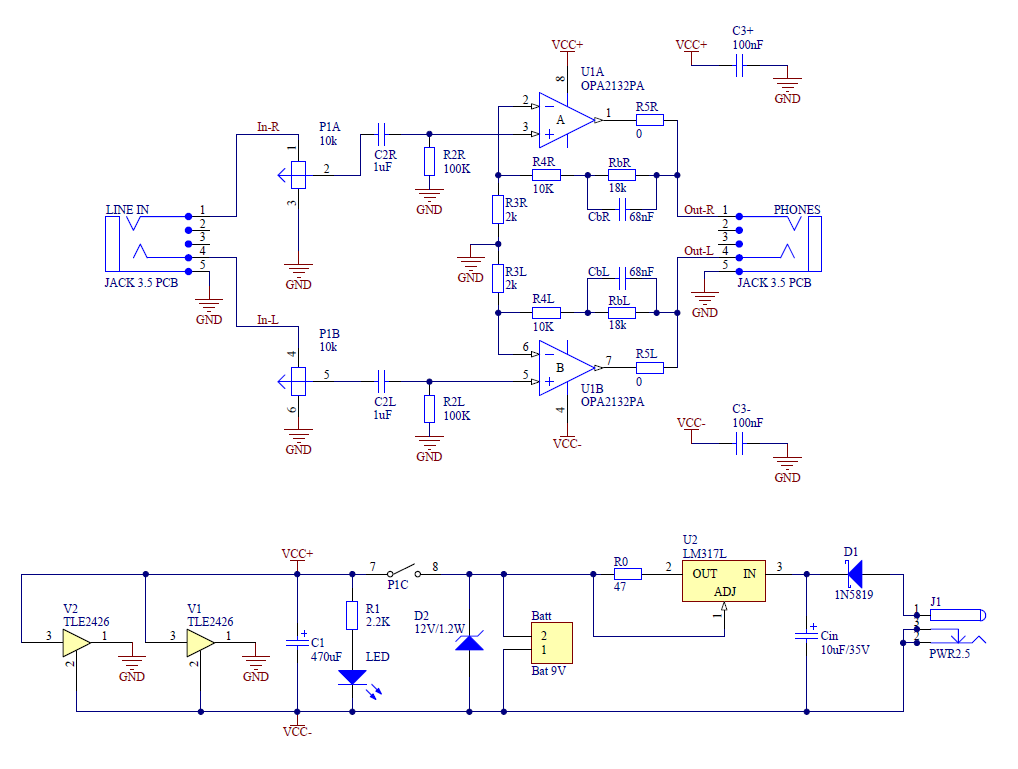
This article discusses a new PCB design for a CMoy headphone amplifier. A key feature of this design is that it fits perfectly into a standard Altoids tin can. The new CMoy amplifier includes a bass-boost circuit and a constant current charger for a 9V battery. P1 serves as the volume potentiometer with an On/Off switch. C2 acts as a coupling capacitor. R2 establishes the input impedance of the operational amplifier. Resistors R3 and R4 set the amplifier's gain to 5x. Rb and Cb are components of the bass-boost circuit, which enhances gain for low frequencies, achieving a gain of 14 for those frequencies. Increasing the Rb resistor values raises the low-frequency gain, while decreasing them lowers it. The cutoff frequency can be adjusted by varying the Cb capacitor values. The bass-boost feature can be disabled by shorting the Rb resistors. The operational amplifier used is the OPA2132, although alternatives such as OPA2134, OPA2227, and NE5532 can also be utilized. C3+ and C3- serve as blocking capacitors for the op-amp power supply. R5 is optional but is recommended to be around 22 ohms to minimize output bouncing. V1 functions as a Rail Splitter, creating a virtual ground. C1 is a high-quality blocking capacitor with low equivalent series resistance (ESR). Resistor R1 limits the current through the LED, with its value adjustable based on the LED type. D2 prevents the input voltage from exceeding 12V. U2, in conjunction with resistor R0, forms a constant current source for charging the 9V battery, with R0 typically set to 47 ohms to yield a current of approximately 25mA. Cin is a tantalum blocking capacitor for U2. D1 is a Schottky diode that protects against damage from reverse polarity connections. The PCB design features two rounded corners and is tailored to fit snugly within the Altoids tin. The layout includes aesthetic representations of the input jack and headphone connections. Vertical assembly of resistors and diodes is recommended to optimize space.
The CMoy headphone amplifier PCB design represents a compact and efficient solution for portable audio amplification. The integration of a bass-boost circuit enhances the listening experience by allowing users to tailor sound profiles to their preferences, particularly for low-frequency audio. The design's compatibility with various operational amplifiers provides flexibility in component selection, enabling users to customize performance characteristics based on specific audio requirements.
The implementation of a constant current charger for the 9V battery ensures that the amplifier remains powered during extended use, while the inclusion of blocking capacitors (C3+ and C3-) protects the op-amp from potential power supply fluctuations. The design's careful consideration of component placement, particularly the vertical orientation of resistors and diodes, maximizes space efficiency within the confined dimensions of the Altoids tin.
The use of a Rail Splitter (V1) to establish a virtual ground is critical for the proper functioning of the op-amp circuit, as it allows for balanced operation in a single-supply configuration. The high-quality blocking capacitor (C1) with low ESR contributes to improved audio fidelity by minimizing signal distortion.
Overall, this PCB design not only meets functional requirements but also considers user experience through its compact form factor and customizable features, making it an excellent choice for audiophiles seeking portable amplification solutions.This is an article about my new PCB design for CMoy headphone amplifier. Main feature is that the new PCB fits exactly to the classic Altoids tin-can. This new CMoy incorporates moreover bass-boost circuit and constant current charger for 9V battery. P1 is the volume potentiometer with On/Off switch. C2 is coupling capacitor. R2 defines the input impedance of opamp. R3 and R4 define the gain of the amplifier (5x in this case). Rb and Cb form bass-boost circuit. These components increase the gain for low frequencies. For the low frequencies the gain is 14. By increasing the Rb resistors you can increase the gain for low frequencies and vice verse. You can decrease the cutting frequency by increasing the Cb capacitors. Bass-boost can be deactivated by shorting out Rb resistors. As a opamp I use OPA2132, but many others can be used as well like OPA2134, OPA2227, NE5532, . C3+ and C3- are blocking capacitors for power supply for opamp. R5 is optional, but to avoid some bouncing at the output the value should be around 22 ohms. V1 is a Rail Splitter which creates virtual ground. C1 is high quality blocking capacitor with low ESR. Resistor R1 limits the current through LED. The value should be modify according the type of LED. D2 limits the maximum voltage in the input to 12V. U2 together with resistor R0 create constant current source for charging the 9V battery. In my case the R0 has value 47 ohms and then the current is around 25mA. Cin is tantalum blocking capacitor for U2. D1 is Schottky diode for avoiding any damage when the voltage with opposite polarity is connected. I designed the PCB with two rounded corners. The PCB fits exactly to the Altoids tin (see pictures below). On the PCB are also nice pictures of input jack and headphones. The resistors and diodes must be assembled vertically to reduce occupied space. 🔗 External reference
The CMoy headphone amplifier PCB design represents a compact and efficient solution for portable audio amplification. The integration of a bass-boost circuit enhances the listening experience by allowing users to tailor sound profiles to their preferences, particularly for low-frequency audio. The design's compatibility with various operational amplifiers provides flexibility in component selection, enabling users to customize performance characteristics based on specific audio requirements.
The implementation of a constant current charger for the 9V battery ensures that the amplifier remains powered during extended use, while the inclusion of blocking capacitors (C3+ and C3-) protects the op-amp from potential power supply fluctuations. The design's careful consideration of component placement, particularly the vertical orientation of resistors and diodes, maximizes space efficiency within the confined dimensions of the Altoids tin.
The use of a Rail Splitter (V1) to establish a virtual ground is critical for the proper functioning of the op-amp circuit, as it allows for balanced operation in a single-supply configuration. The high-quality blocking capacitor (C1) with low ESR contributes to improved audio fidelity by minimizing signal distortion.
Overall, this PCB design not only meets functional requirements but also considers user experience through its compact form factor and customizable features, making it an excellent choice for audiophiles seeking portable amplification solutions.This is an article about my new PCB design for CMoy headphone amplifier. Main feature is that the new PCB fits exactly to the classic Altoids tin-can. This new CMoy incorporates moreover bass-boost circuit and constant current charger for 9V battery. P1 is the volume potentiometer with On/Off switch. C2 is coupling capacitor. R2 defines the input impedance of opamp. R3 and R4 define the gain of the amplifier (5x in this case). Rb and Cb form bass-boost circuit. These components increase the gain for low frequencies. For the low frequencies the gain is 14. By increasing the Rb resistors you can increase the gain for low frequencies and vice verse. You can decrease the cutting frequency by increasing the Cb capacitors. Bass-boost can be deactivated by shorting out Rb resistors. As a opamp I use OPA2132, but many others can be used as well like OPA2134, OPA2227, NE5532, . C3+ and C3- are blocking capacitors for power supply for opamp. R5 is optional, but to avoid some bouncing at the output the value should be around 22 ohms. V1 is a Rail Splitter which creates virtual ground. C1 is high quality blocking capacitor with low ESR. Resistor R1 limits the current through LED. The value should be modify according the type of LED. D2 limits the maximum voltage in the input to 12V. U2 together with resistor R0 create constant current source for charging the 9V battery. In my case the R0 has value 47 ohms and then the current is around 25mA. Cin is tantalum blocking capacitor for U2. D1 is Schottky diode for avoiding any damage when the voltage with opposite polarity is connected. I designed the PCB with two rounded corners. The PCB fits exactly to the Altoids tin (see pictures below). On the PCB are also nice pictures of input jack and headphones. The resistors and diodes must be assembled vertically to reduce occupied space. 🔗 External reference