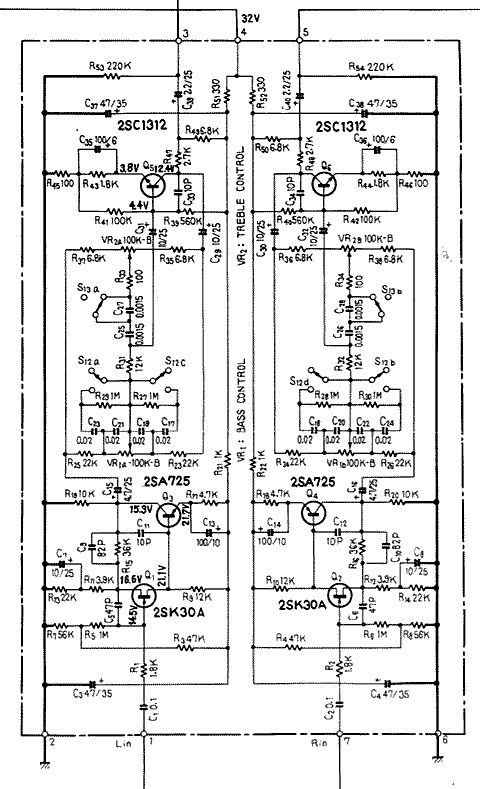
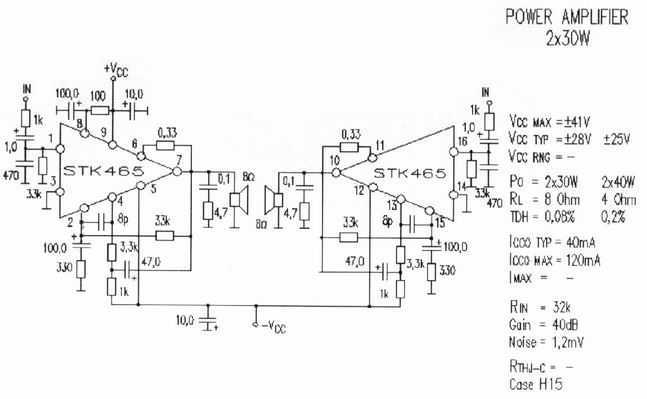
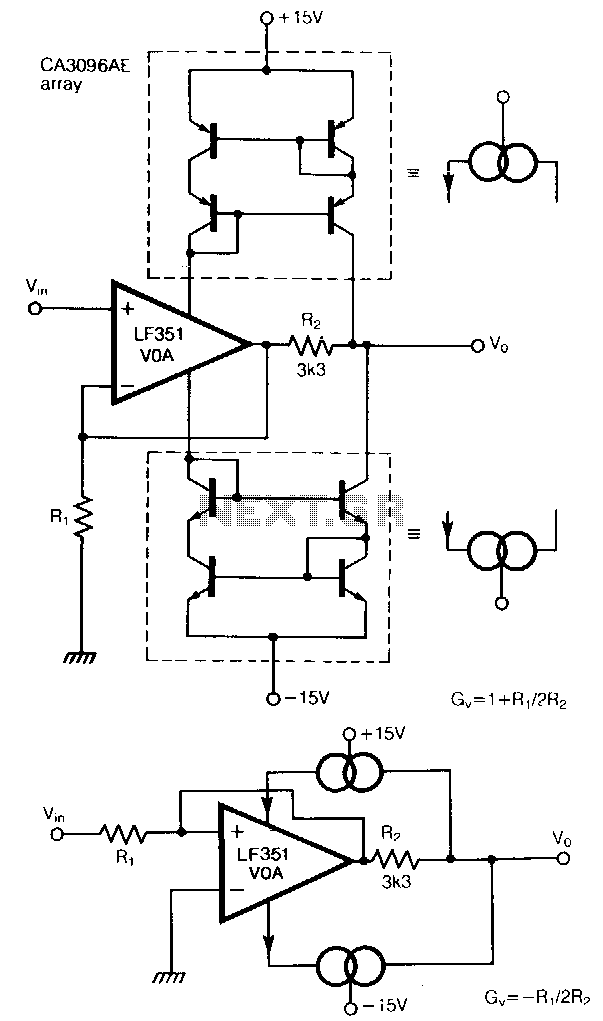
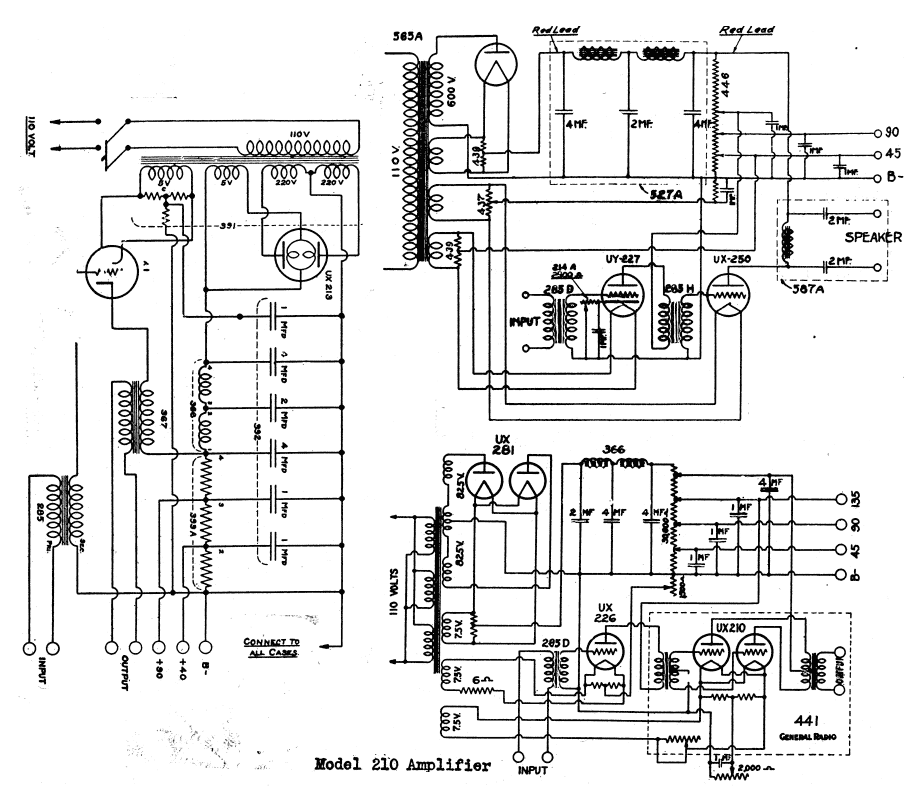
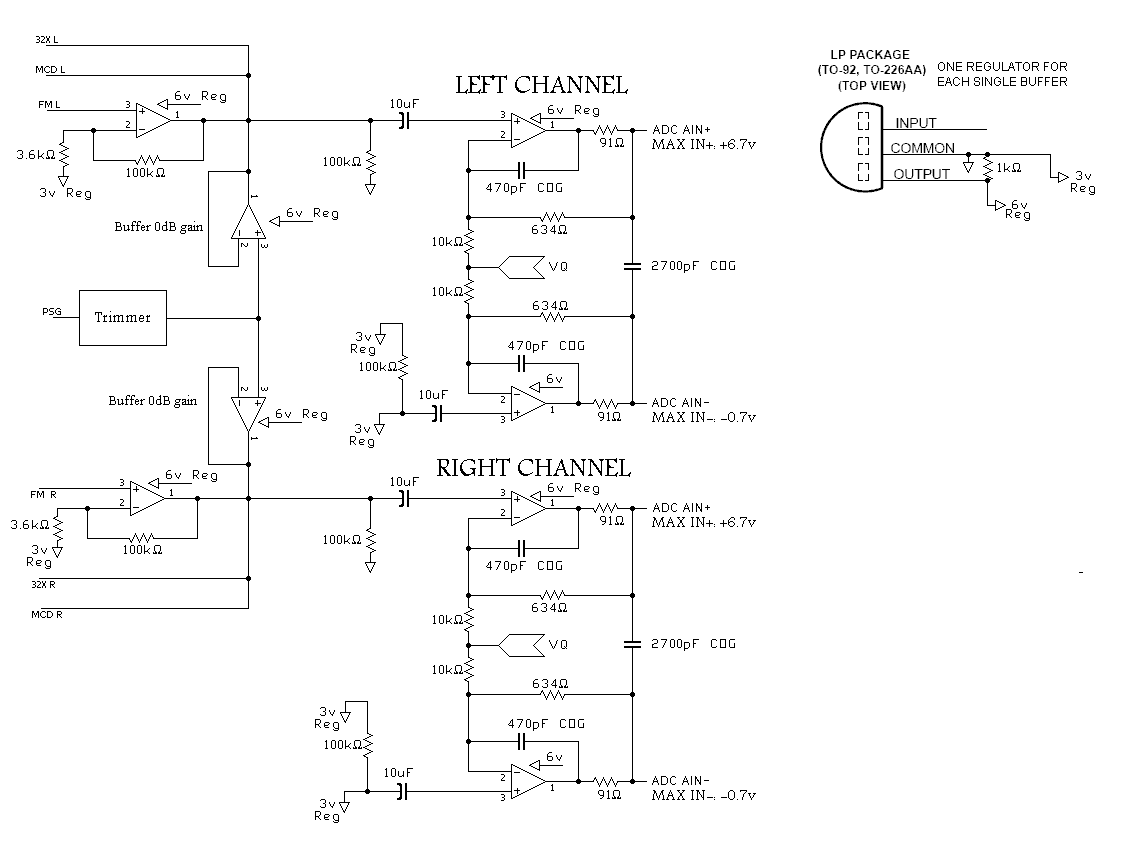
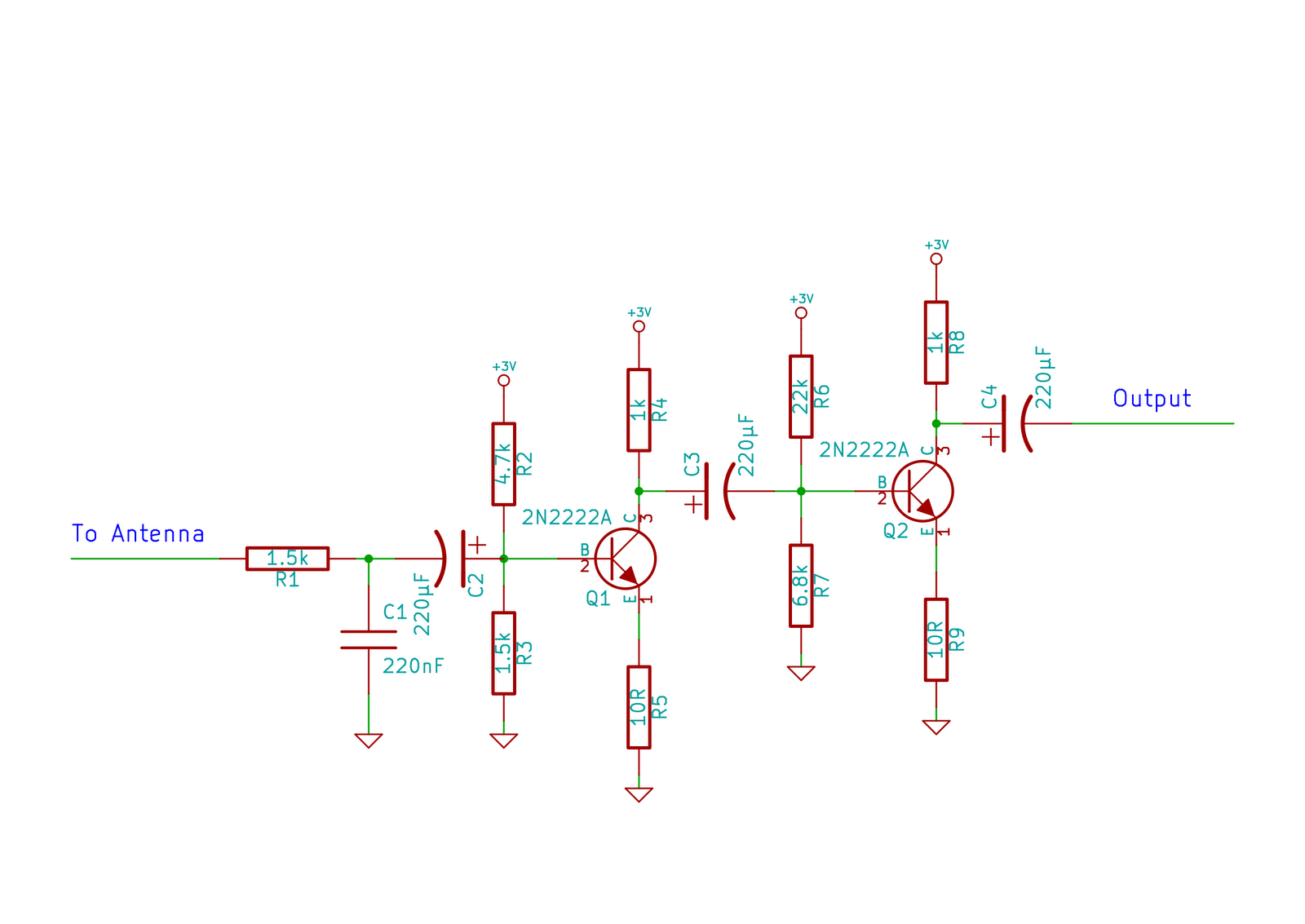
High Gain JFET Audio Amplifier
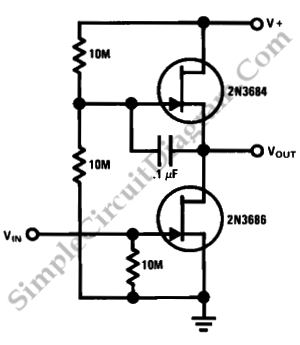
This is a simple high-gain JFET audio amplifier circuit. This circuit requires very low power but provides a high-gain amplification function. It is also referred to as JFET.
The JFET (Junction Field Effect Transistor) audio amplifier circuit is designed to amplify audio signals while maintaining low power consumption. The circuit typically consists of a JFET transistor configured in common source mode, which is known for its high voltage gain characteristics. The input signal is applied to the gate terminal of the JFET, and the output is taken from the drain terminal.
In this configuration, the JFET operates by controlling the flow of current between the source and drain terminals based on the voltage applied to the gate. The gate is reverse-biased, which allows for high input impedance and minimal loading on the preceding stage of the audio signal source. This feature is particularly advantageous in audio applications, as it preserves the integrity of the original signal.
The circuit also includes biasing resistors connected to the gate and drain to establish the proper operating point for the JFET, ensuring that it remains in the active region during operation. Capacitors may be used for coupling the input and output signals, blocking any DC components while allowing AC signals to pass through.
Furthermore, the design can be enhanced by incorporating feedback mechanisms to stabilize the gain and improve linearity. By adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors, the gain can be tailored to meet specific application requirements.
Overall, this simple high-gain JFET audio amplifier circuit is suitable for various audio applications, including microphones, musical instruments, and other low-level audio sources, providing an efficient solution for signal amplification.This is a simple high gain JFET audio amplifier circuit. This circuit need very low power but it provides high gain amplifying function. It also called `JFET.. 🔗 External reference
The JFET (Junction Field Effect Transistor) audio amplifier circuit is designed to amplify audio signals while maintaining low power consumption. The circuit typically consists of a JFET transistor configured in common source mode, which is known for its high voltage gain characteristics. The input signal is applied to the gate terminal of the JFET, and the output is taken from the drain terminal.
In this configuration, the JFET operates by controlling the flow of current between the source and drain terminals based on the voltage applied to the gate. The gate is reverse-biased, which allows for high input impedance and minimal loading on the preceding stage of the audio signal source. This feature is particularly advantageous in audio applications, as it preserves the integrity of the original signal.
The circuit also includes biasing resistors connected to the gate and drain to establish the proper operating point for the JFET, ensuring that it remains in the active region during operation. Capacitors may be used for coupling the input and output signals, blocking any DC components while allowing AC signals to pass through.
Furthermore, the design can be enhanced by incorporating feedback mechanisms to stabilize the gain and improve linearity. By adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors, the gain can be tailored to meet specific application requirements.
Overall, this simple high-gain JFET audio amplifier circuit is suitable for various audio applications, including microphones, musical instruments, and other low-level audio sources, providing an efficient solution for signal amplification.This is a simple high gain JFET audio amplifier circuit. This circuit need very low power but it provides high gain amplifying function. It also called `JFET.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713