How to Shock People with Your Fingertips circuit
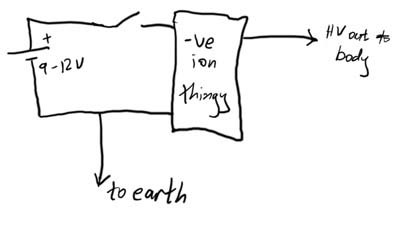
This article demonstrates how to create a simple yet effective static electricity generator. This device enables the user to carry a constant static charge on their body and discharge it onto anything grounded or of opposite polarity. The generated electricity is approximately 8-10 kV at a very low current. The shock produced is sufficient to startle individuals, similar to a static shock experienced from a trampoline or a carpeted room. Some experience in soldering and circuit design is required to build the project. Required materials and tools include a soldering iron, flux-core solder, wire, and a negative ion generator.
The static electricity generator operates on the principle of electrostatic induction, utilizing a negative ion generator to create a high voltage charge. The basic components of the circuit include the negative ion generator, a power supply, a discharge mechanism, and a collection system for the static charge.
The negative ion generator is responsible for producing negative ions, which accumulate on the surface of the device. This accumulation leads to a high voltage potential difference, typically in the range of 8-10 kV. The circuit design must ensure that the current remains low, as high currents can pose safety risks.
The discharge mechanism can be as simple as a metal probe or a conductive surface that allows the stored charge to be released when it comes into contact with a grounded object or a person of opposite polarity. The design should also incorporate safety features to prevent accidental discharge, which could lead to unintended shocks.
The collection system may consist of a series of capacitors or conductive plates that enhance the accumulation of static charge. The circuit layout should be carefully planned to minimize losses and ensure efficient charge transfer. Attention should be given to the insulation of components to prevent unintended discharges and to protect the user from high voltage.
Overall, building a static electricity generator requires a solid understanding of circuit design principles, careful selection of components, and adherence to safety protocols to ensure a functional and safe device.In this article, I`ll be showing you how to make a simple yet effective static electricity generator. Basically, this device allows you to carry a constant static charge on your body and discharge it on anything grounded or of opposite polarity.
The electricity generated is around 8-10 kV, at a very low current. The shock is enough to startle your friends, just like a static shock from a trampoline or carpeted room. You`ll need a little experience in soldering and circuit design to build the project. Materials and Tools Soldering iron Flux-core solder Wire Negative ion generator (These can.. 🔗 External reference
The static electricity generator operates on the principle of electrostatic induction, utilizing a negative ion generator to create a high voltage charge. The basic components of the circuit include the negative ion generator, a power supply, a discharge mechanism, and a collection system for the static charge.
The negative ion generator is responsible for producing negative ions, which accumulate on the surface of the device. This accumulation leads to a high voltage potential difference, typically in the range of 8-10 kV. The circuit design must ensure that the current remains low, as high currents can pose safety risks.
The discharge mechanism can be as simple as a metal probe or a conductive surface that allows the stored charge to be released when it comes into contact with a grounded object or a person of opposite polarity. The design should also incorporate safety features to prevent accidental discharge, which could lead to unintended shocks.
The collection system may consist of a series of capacitors or conductive plates that enhance the accumulation of static charge. The circuit layout should be carefully planned to minimize losses and ensure efficient charge transfer. Attention should be given to the insulation of components to prevent unintended discharges and to protect the user from high voltage.
Overall, building a static electricity generator requires a solid understanding of circuit design principles, careful selection of components, and adherence to safety protocols to ensure a functional and safe device.In this article, I`ll be showing you how to make a simple yet effective static electricity generator. Basically, this device allows you to carry a constant static charge on your body and discharge it on anything grounded or of opposite polarity.
The electricity generated is around 8-10 kV, at a very low current. The shock is enough to startle your friends, just like a static shock from a trampoline or carpeted room. You`ll need a little experience in soldering and circuit design to build the project. Materials and Tools Soldering iron Flux-core solder Wire Negative ion generator (These can.. 🔗 External reference