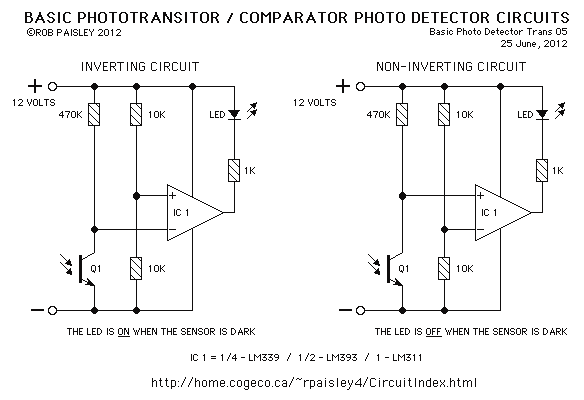
Ic Product Detectors
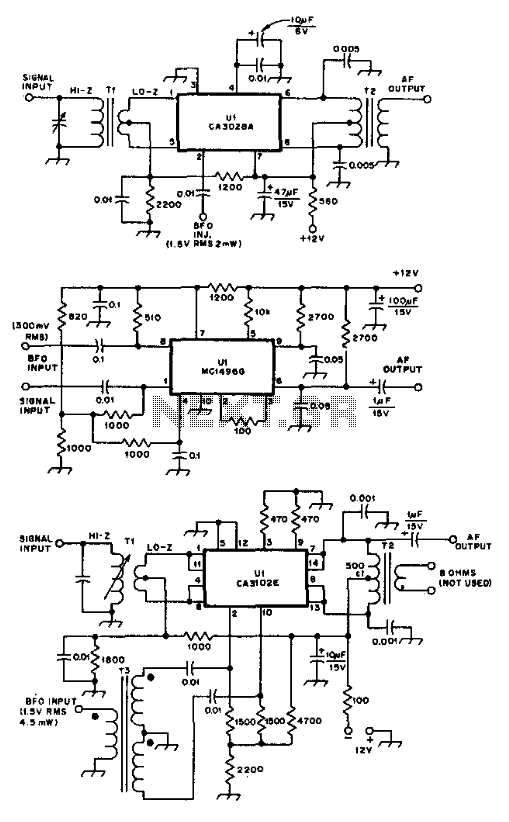
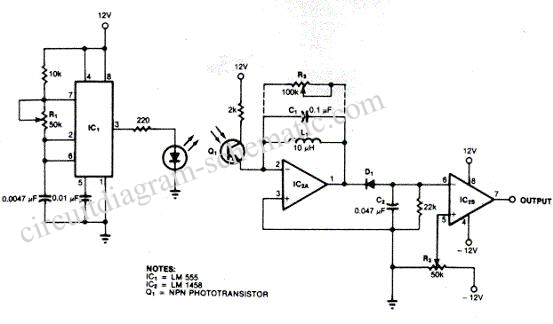
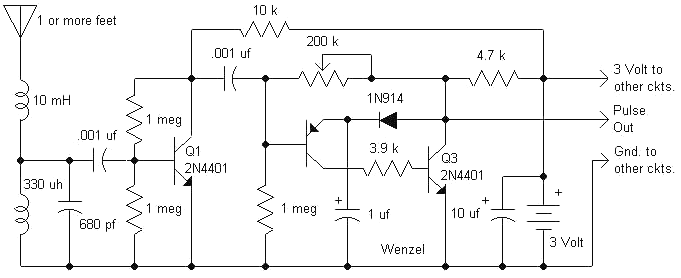
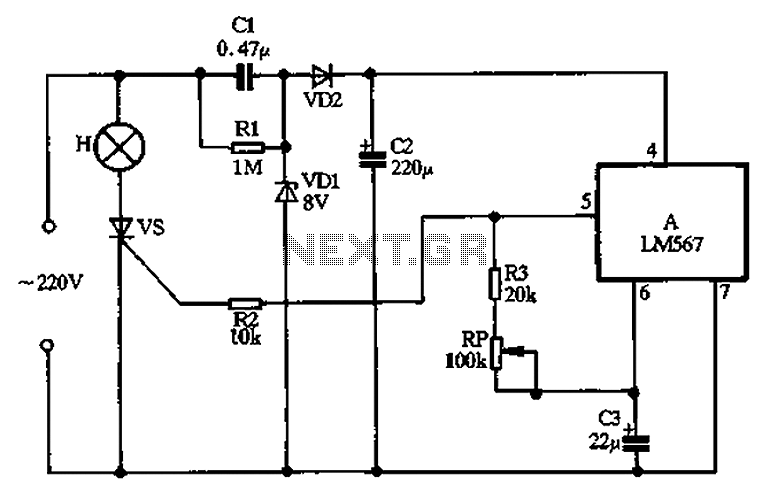
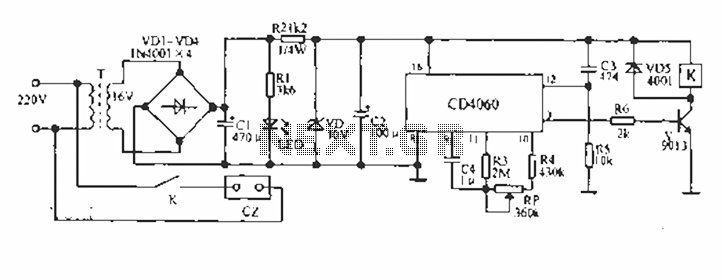
These product detectors utilize integrated circuit (IC) devices. They are capable of detecting single sideband (SSB) and continuous wave (CW) signals. The circuits are designed to operate effectively up to frequencies of 20 or 30 MHz. T3 in the schematic is a toroidal transformer with a 1:1:1 ratio, which is dependent on the beat frequency oscillator (BFO) frequency.
The described product detectors are essential components in radio frequency (RF) applications, particularly for receiving and demodulating SSB and CW signals. The use of integrated circuit devices allows for compact design and enhanced performance, making them suitable for various communication systems.
The operating frequency range of 20 to 30 MHz indicates that these detectors are intended for use in the high-frequency (HF) bands, commonly utilized in amateur radio and other communication systems. The ability to detect SSB signals is particularly important in these applications, as SSB is a widely used mode for voice communication in HF bands due to its efficient use of bandwidth.
The toroidal transformer T3, with its 1:1:1 winding ratio, serves a critical role in the circuit. This configuration is typically used to provide impedance matching and minimize losses in the signal path. The choice of a toroidal core helps to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improve overall performance by providing a high inductance in a compact form factor. The specific BFO frequency will determine the exact tuning and operational characteristics of the detector, allowing for precise signal demodulation.
In summary, these product detectors represent a sophisticated solution for detecting SSB and CW signals in the specified frequency range, utilizing IC technology and a carefully designed transformer to achieve optimal performance in RF applications. These product detectors use IC devices. SSB and CW signals can be detected with them. The circuits should be useful up to 20 or 30 MHz. T3 in (c) is a 1:1:1 toroidal type, depending on the BFO frequency.
The described product detectors are essential components in radio frequency (RF) applications, particularly for receiving and demodulating SSB and CW signals. The use of integrated circuit devices allows for compact design and enhanced performance, making them suitable for various communication systems.
The operating frequency range of 20 to 30 MHz indicates that these detectors are intended for use in the high-frequency (HF) bands, commonly utilized in amateur radio and other communication systems. The ability to detect SSB signals is particularly important in these applications, as SSB is a widely used mode for voice communication in HF bands due to its efficient use of bandwidth.
The toroidal transformer T3, with its 1:1:1 winding ratio, serves a critical role in the circuit. This configuration is typically used to provide impedance matching and minimize losses in the signal path. The choice of a toroidal core helps to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improve overall performance by providing a high inductance in a compact form factor. The specific BFO frequency will determine the exact tuning and operational characteristics of the detector, allowing for precise signal demodulation.
In summary, these product detectors represent a sophisticated solution for detecting SSB and CW signals in the specified frequency range, utilizing IC technology and a carefully designed transformer to achieve optimal performance in RF applications. These product detectors use IC devices. SSB and CW signals can be detected with them. The circuits should be useful up to 20 or 30 MHz. T3 in (c) is a 1:1:1 toroidal type, depending on the BFO frequency.