Infrared automatic hand washing device 3
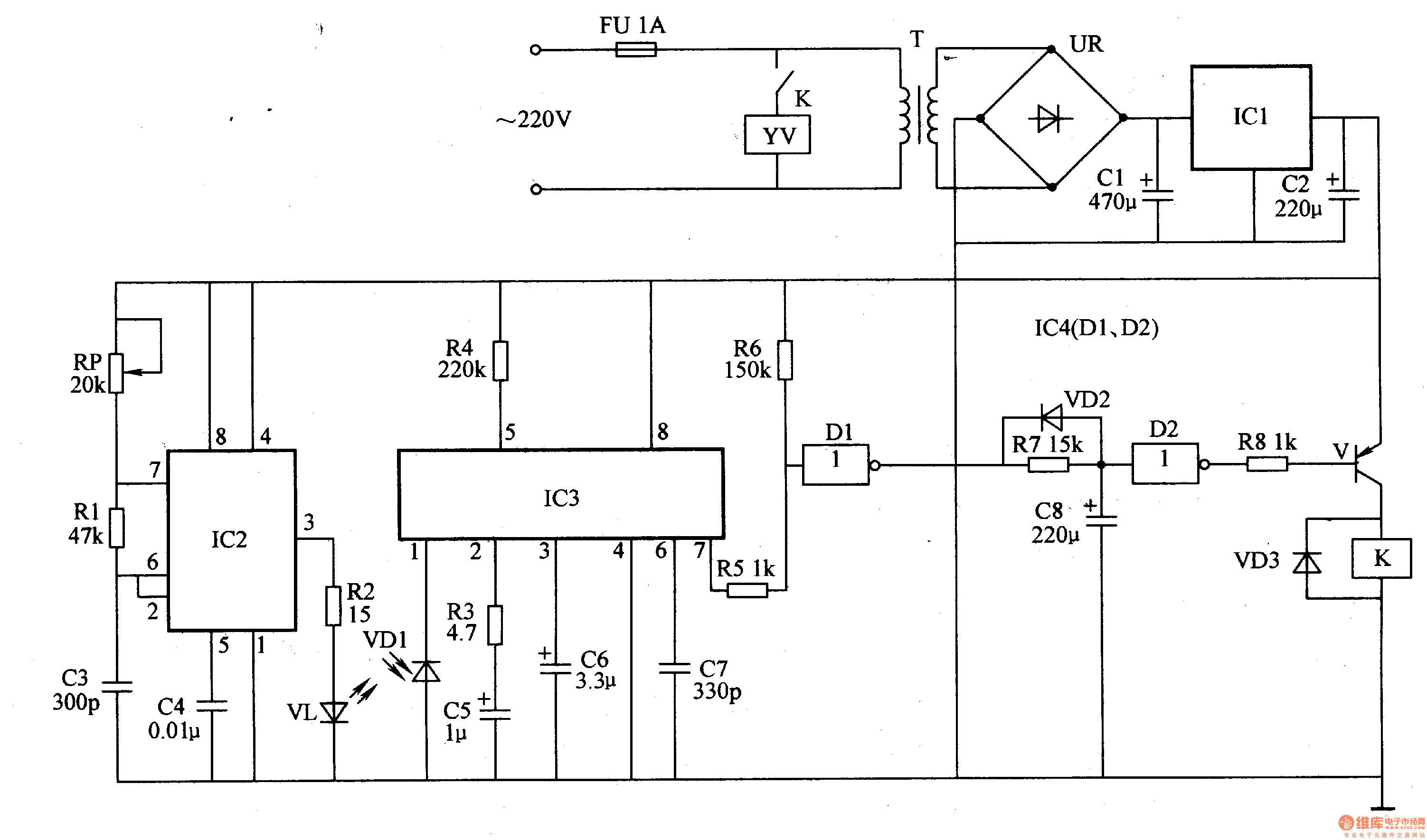
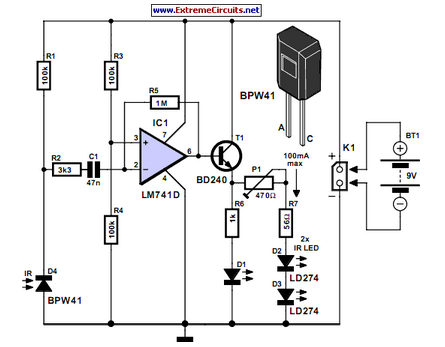
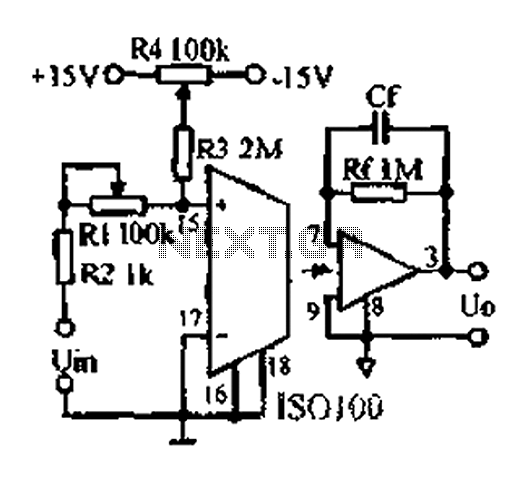
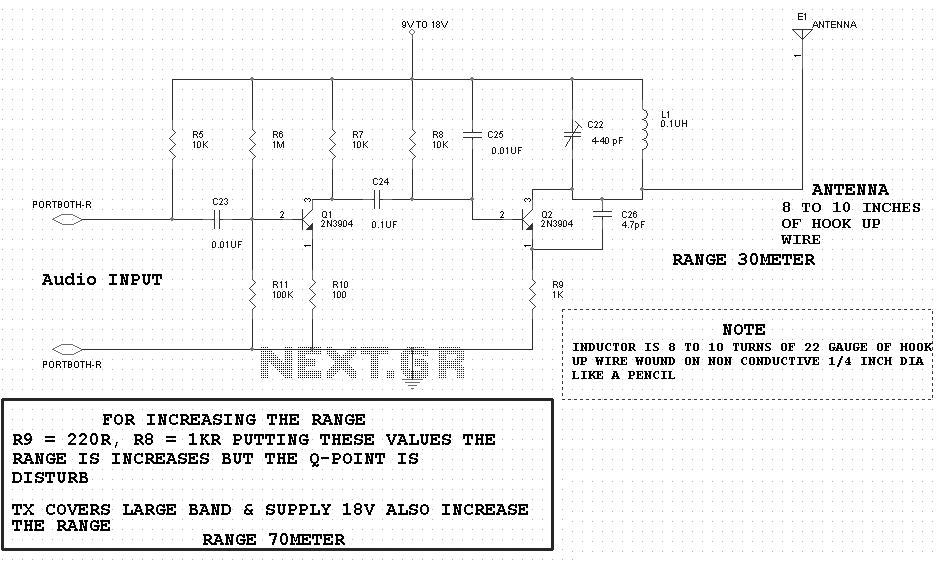
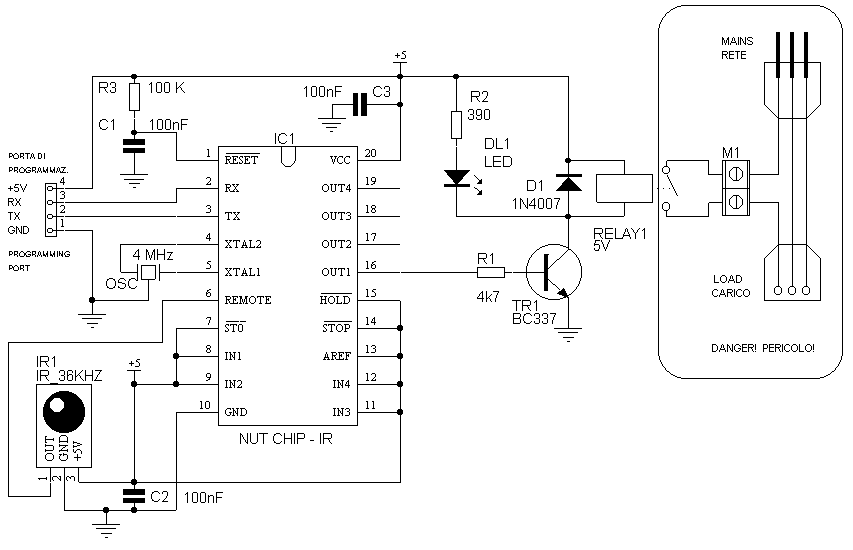
The operational theory of this infrared automatic hand washing device circuit includes a power supply, an infrared transmitting circuit, an infrared receiving circuit, and a control circuit. The circuit is illustrated in figure 9-121. The power supply circuit consists of a fuse (FU), a power transformer (T), a bridge rectifier (UR), and filter capacitors (C1, C2) along with a three-terminal regulator.
The infrared automatic hand washing device operates by utilizing an infrared sensor to detect the presence of hands. The power supply section ensures that the entire circuit receives the necessary voltage and current. The fuse (FU) serves as a protective element, preventing overcurrent conditions that could damage the circuit components. The power transformer (T) steps down the mains voltage to a lower level suitable for the circuit operation.
The bridge rectifier (UR) converts the alternating current (AC) output from the transformer into direct current (DC), which is then filtered by capacitors (C1, C2) to smooth out voltage fluctuations. The output is regulated by a three-terminal voltage regulator, which provides a stable DC voltage for the infrared transmitting and receiving circuits.
The infrared transmitting circuit emits infrared light, which is reflected off of hands when they are placed within the sensing range. The infrared receiving circuit detects this reflected light, sending a signal to the control circuit. The control circuit processes this signal and activates the washing mechanism, such as a motor or solenoid, to dispense water or soap as needed.
This automatic hand washing device enhances hygiene by minimizing the need for physical contact, thereby reducing the risk of cross-contamination. The simplicity of the circuit design ensures reliability and ease of maintenance, making it suitable for various applications in public restrooms, kitchens, and healthcare facilities.The circuit work theory This infrared automatic hand washing device circuit is composed of power supply, infrared transmitting circuit, infrared receiving circuit and control circuit, the circuit is shown in the figure 9-121. The power supply circuit is made of fuse FU, power transformer T, bridge rectifier UR, filter capacitors C1, C2 and three terminal r..
🔗 External reference
The infrared automatic hand washing device operates by utilizing an infrared sensor to detect the presence of hands. The power supply section ensures that the entire circuit receives the necessary voltage and current. The fuse (FU) serves as a protective element, preventing overcurrent conditions that could damage the circuit components. The power transformer (T) steps down the mains voltage to a lower level suitable for the circuit operation.
The bridge rectifier (UR) converts the alternating current (AC) output from the transformer into direct current (DC), which is then filtered by capacitors (C1, C2) to smooth out voltage fluctuations. The output is regulated by a three-terminal voltage regulator, which provides a stable DC voltage for the infrared transmitting and receiving circuits.
The infrared transmitting circuit emits infrared light, which is reflected off of hands when they are placed within the sensing range. The infrared receiving circuit detects this reflected light, sending a signal to the control circuit. The control circuit processes this signal and activates the washing mechanism, such as a motor or solenoid, to dispense water or soap as needed.
This automatic hand washing device enhances hygiene by minimizing the need for physical contact, thereby reducing the risk of cross-contamination. The simplicity of the circuit design ensures reliability and ease of maintenance, making it suitable for various applications in public restrooms, kitchens, and healthcare facilities.The circuit work theory This infrared automatic hand washing device circuit is composed of power supply, infrared transmitting circuit, infrared receiving circuit and control circuit, the circuit is shown in the figure 9-121. The power supply circuit is made of fuse FU, power transformer T, bridge rectifier UR, filter capacitors C1, C2 and three terminal r..
🔗 External reference