Simple Infrared Control Extender
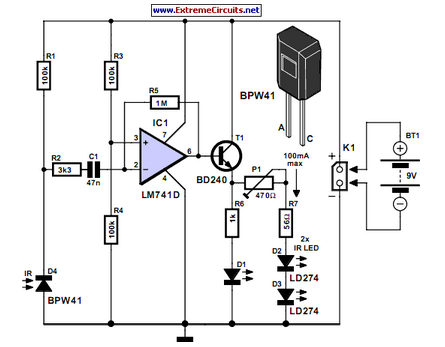
Many consumer electronic devices such as television sets, VCRs, CD players, and DVD players utilize infrared remote control technology. In certain situations, it is beneficial to extend the range of these remote controls.
Infrared (IR) remote controls operate by emitting modulated infrared light signals that are detected by a photodiode or phototransistor in the receiving device. The common components of an IR remote control system include the remote control transmitter, which contains an infrared LED, and the receiver, which typically consists of an IR sensor and associated circuitry for decoding the received signals.
To extend the range of an IR remote control, several methods can be employed. One approach is to enhance the transmitter's output power by using a more efficient infrared LED or by incorporating a lens to focus the emitted light. Additionally, the receiver can be improved by using a more sensitive photodiode or phototransistor, which can detect weaker signals from a greater distance.
Another method to extend the range is to utilize a series of IR repeaters. An IR repeater receives the signal from the remote control and retransmits it, effectively amplifying the signal over longer distances or through obstacles such as walls. These repeaters can be wired or wireless, depending on the application requirements.
In summary, extending the range of infrared remote controls involves improving the transmission and reception components, as well as utilizing repeaters to ensure reliable signal transmission over greater distances. This can enhance user experience and convenience in operating various consumer electronic devices.Lots of consumer electronic equipment like TV sets, VCRs, CD and DVD players employs infrared remote control. In some cases, it is desirable to extend the.. 🔗 External reference
Infrared (IR) remote controls operate by emitting modulated infrared light signals that are detected by a photodiode or phototransistor in the receiving device. The common components of an IR remote control system include the remote control transmitter, which contains an infrared LED, and the receiver, which typically consists of an IR sensor and associated circuitry for decoding the received signals.
To extend the range of an IR remote control, several methods can be employed. One approach is to enhance the transmitter's output power by using a more efficient infrared LED or by incorporating a lens to focus the emitted light. Additionally, the receiver can be improved by using a more sensitive photodiode or phototransistor, which can detect weaker signals from a greater distance.
Another method to extend the range is to utilize a series of IR repeaters. An IR repeater receives the signal from the remote control and retransmits it, effectively amplifying the signal over longer distances or through obstacles such as walls. These repeaters can be wired or wireless, depending on the application requirements.
In summary, extending the range of infrared remote controls involves improving the transmission and reception components, as well as utilizing repeaters to ensure reliable signal transmission over greater distances. This can enhance user experience and convenience in operating various consumer electronic devices.Lots of consumer electronic equipment like TV sets, VCRs, CD and DVD players employs infrared remote control. In some cases, it is desirable to extend the.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713