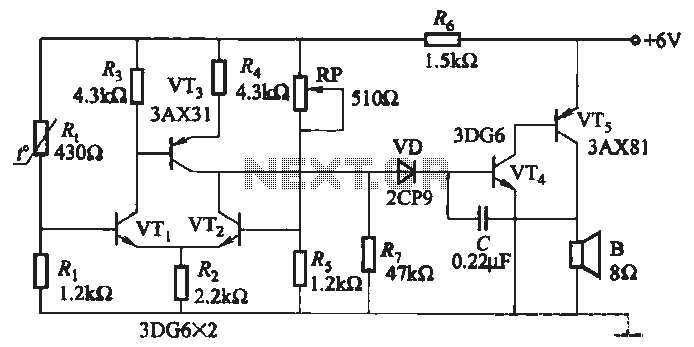
infrared detector circuit using pid20
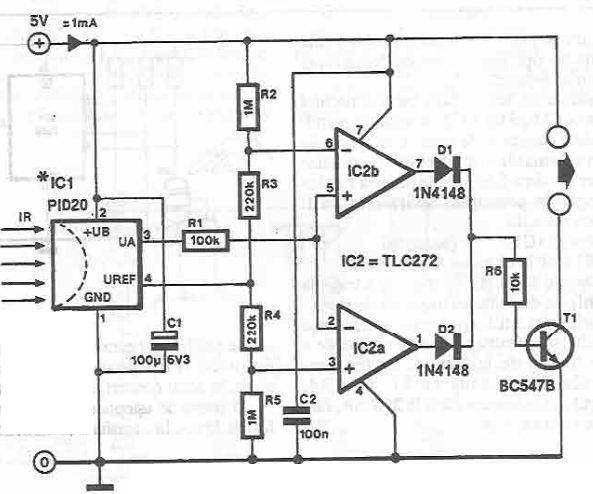
This infrared detector circuit utilizes the PID20 integrated circuit manufactured by Siemens, which converts thermal radiation into electrical impulses. It includes an operational amplifier and several electronic components. The output signal at pin 3 is compared to a reference voltage that is set to half the supply voltage. This reference voltage is derived from a voltage divider consisting of resistors R2, R3, R4, and R5. When an object that is warmer than the surrounding environment approaches, or when an object that is colder than the environment is removed, the output voltage increases. The variations in the sensor output are compared by the operational amplifiers IC2a and IC2b, which monitor voltages of 0.5 V above and below the reference voltage, respectively. Based on the output, one of the comparators will activate transistor T1.
The infrared detector circuit operates on the principle of detecting variations in thermal radiation emitted by objects in its vicinity. The PID20 integrated circuit serves as the core of the detection mechanism, converting thermal energy into a measurable electrical signal. The output from the PID20 is routed to pin 3, where it is subjected to comparison against a reference voltage. This reference voltage, established by the voltage divider formed by resistors R2, R3, R4, and R5, ensures that the circuit can accurately detect changes in temperature.
In practical applications, the circuit can be used in security systems, occupancy detection, or temperature-based automation. The operational amplifiers IC2a and IC2b are configured to monitor the output signal from the PID20. When the detected thermal signal exceeds the reference threshold, the comparator IC2a will trigger. Conversely, if the signal falls below the reference threshold, comparator IC2b will activate. This dual comparison mechanism allows for precise detection of both increases and decreases in temperature.
Transistor T1 acts as a switching element that can control a load based on the output from the comparators. When activated, T1 can turn on alarms, lights, or other devices, providing a practical response to the detected thermal changes. The design of the circuit emphasizes stability and responsiveness, making it suitable for various applications where infrared detection is essential.
Overall, this infrared detector circuit exemplifies a straightforward yet effective design for monitoring thermal variations in the environment, leveraging the capabilities of integrated circuits and operational amplifiers for enhanced performance and reliability.This infrared detector circuit is designed using the PID20 integrated circuit manufactured by Siemens (which converts thermal radiation into electrical impulses), an operational amplifier and a few electronic components. The output signal at pin 3 is compared with a reference voltage equal to half the supply voltage. Reference voltage is taken fro m the voltage divider R2-R3-R4-R5. When approaching an object warmer than the surrounding environment, or to remove an object colder than the environment, the output voltage increases. Variation of the sensor output will be compared, the IC2a and IC2b, located voltage of 0. 5 V under and over voltage reference respectively. Depending on the output, one of the comparators basculate and activates T1. 🔗 External reference
The infrared detector circuit operates on the principle of detecting variations in thermal radiation emitted by objects in its vicinity. The PID20 integrated circuit serves as the core of the detection mechanism, converting thermal energy into a measurable electrical signal. The output from the PID20 is routed to pin 3, where it is subjected to comparison against a reference voltage. This reference voltage, established by the voltage divider formed by resistors R2, R3, R4, and R5, ensures that the circuit can accurately detect changes in temperature.
In practical applications, the circuit can be used in security systems, occupancy detection, or temperature-based automation. The operational amplifiers IC2a and IC2b are configured to monitor the output signal from the PID20. When the detected thermal signal exceeds the reference threshold, the comparator IC2a will trigger. Conversely, if the signal falls below the reference threshold, comparator IC2b will activate. This dual comparison mechanism allows for precise detection of both increases and decreases in temperature.
Transistor T1 acts as a switching element that can control a load based on the output from the comparators. When activated, T1 can turn on alarms, lights, or other devices, providing a practical response to the detected thermal changes. The design of the circuit emphasizes stability and responsiveness, making it suitable for various applications where infrared detection is essential.
Overall, this infrared detector circuit exemplifies a straightforward yet effective design for monitoring thermal variations in the environment, leveraging the capabilities of integrated circuits and operational amplifiers for enhanced performance and reliability.This infrared detector circuit is designed using the PID20 integrated circuit manufactured by Siemens (which converts thermal radiation into electrical impulses), an operational amplifier and a few electronic components. The output signal at pin 3 is compared with a reference voltage equal to half the supply voltage. Reference voltage is taken fro m the voltage divider R2-R3-R4-R5. When approaching an object warmer than the surrounding environment, or to remove an object colder than the environment, the output voltage increases. Variation of the sensor output will be compared, the IC2a and IC2b, located voltage of 0. 5 V under and over voltage reference respectively. Depending on the output, one of the comparators basculate and activates T1. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713