
interleaved pfc
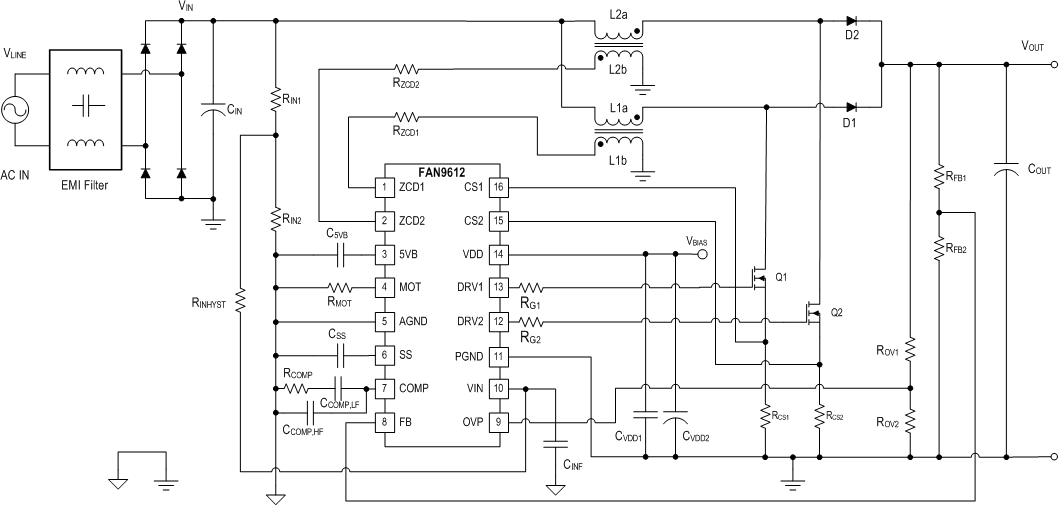
No description available.
Related Circuits
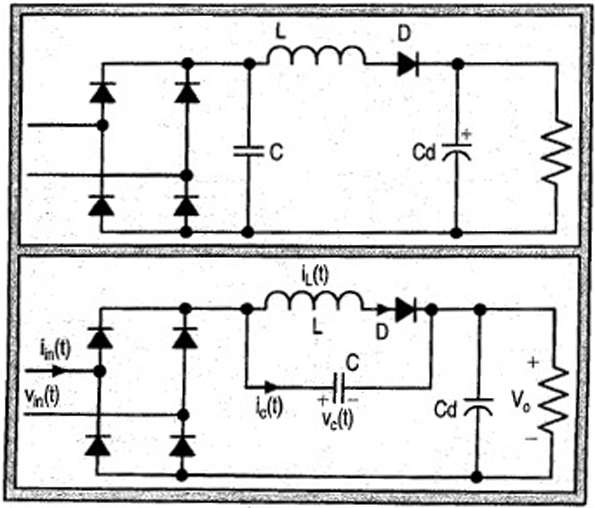
The input current for a passive power factor correction (PFC) circuit is not affected by variations in the output ripple, resulting in the need for a smaller inductance compared to earlier circuit designs. Passive power factor correction circuits are utilized...

The project is a continuation of the 5kW Boost converter project. After several unsuccessful attempts, the focus shifted towards achieving a higher power level, targeting approximately 10kW. The title was modified from 12kW to 8kW, although the converter is...
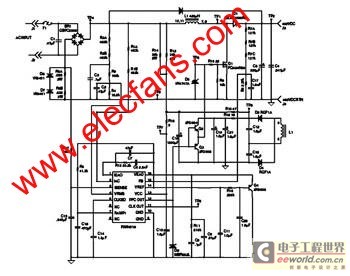
The FAN4810 operates as a continuous conduction mode (CCM) power factor correction (PFC) controller. It features an internal safety detection mechanism that prevents circuit malfunction due to component damage. The device has a power-handling capability of up to 1A,...
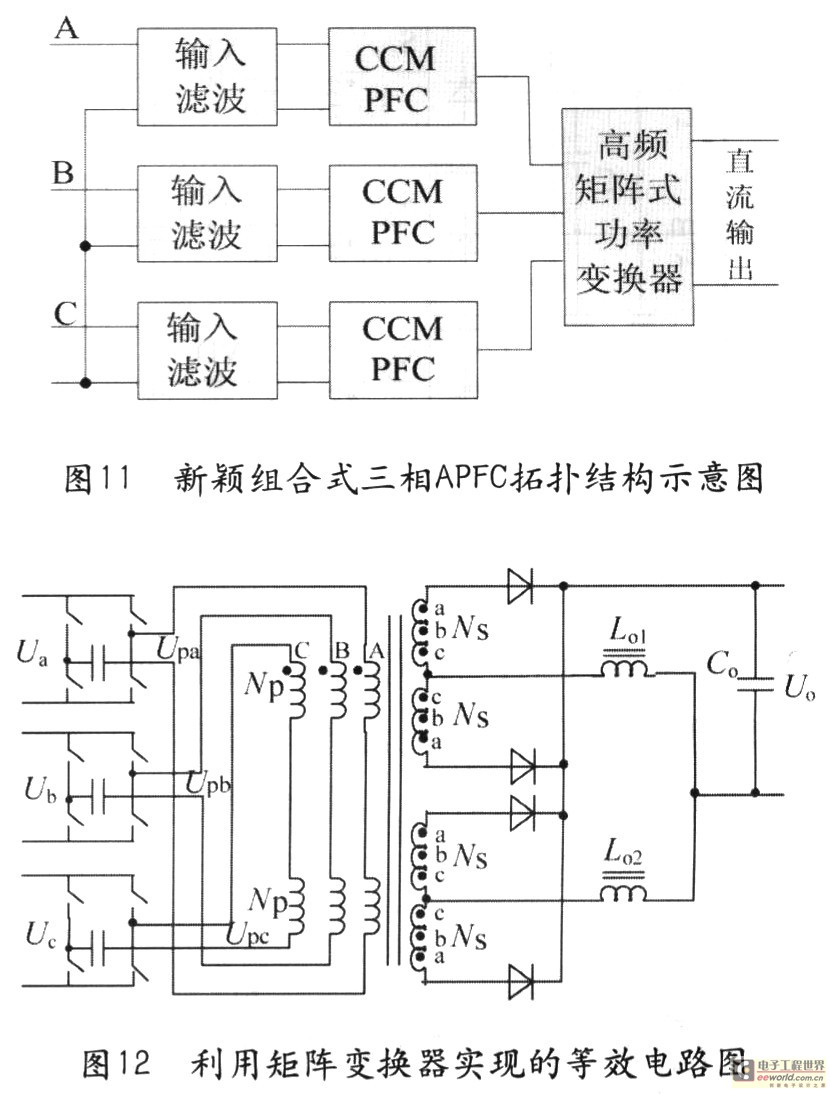
Tape isolate single-phase power factor correction (PFC) that utilizes DC/DC converters, consisting of two cables. The three-phase PFC is formed by connecting three single-phase PFCs in parallel at the output. This configuration is based on a matrix-type DC/DC converter...
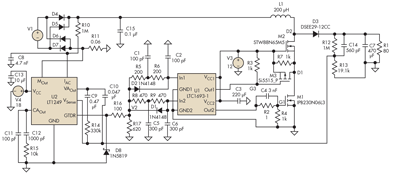
Adding a discharge path to the upper MOSFET of a cascode circuit significantly reduces the unavoidable Miller effect, thereby enhancing the Power Factor Correction (PFC) performance of a power supply's front end. In a cascode configuration, the upper MOSFET is...
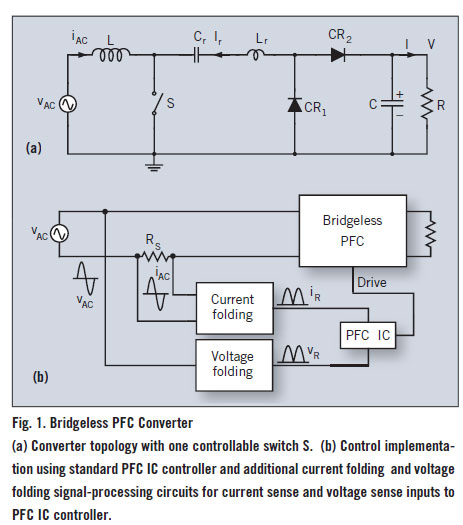
A bridgeless Power Factor Correction (PFC) converter utilizing an innovative switching method eliminates the need for full-bridge rectifiers, thereby reducing the size and cost of switching power supplies. The bridgeless PFC converter operates by directly converting the AC input voltage...
We use cookies to enhance your experience, analyze traffic, and serve personalized ads. By clicking "Accept", you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more