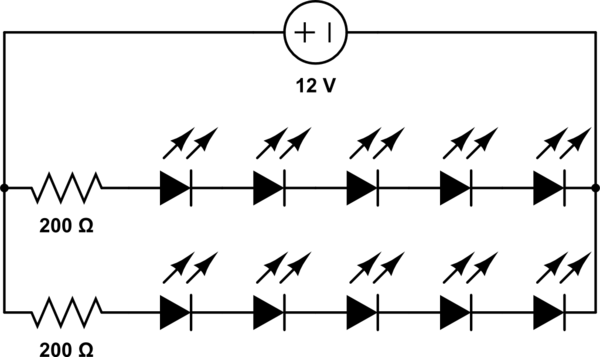
inverter circuit diagram
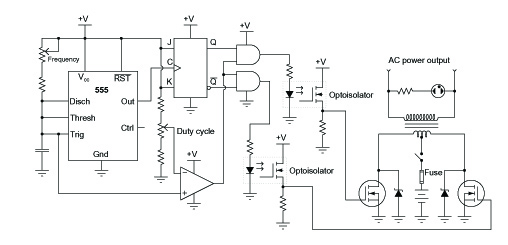
A common topology for DC-AC power converter circuits employs a pair of transistors to switch DC current through the center-tapped winding of a step-up transformer. Examine the check plot images from a PCB drafting program for a control board based on this inverter circuit design. Both the top and bottom copper layer plots are shown from the perspective of the board's top side. The six large pads around the periphery of the board are holes for mounting screws. Mark where discrete components (resistors, capacitors, and diodes) are placed on the PCB and identify which integrated circuits on the board layout are performing specific functions in the schematic. Note: the square pad on each IC indicates pin number 1.
The described DC-AC power converter circuit utilizes a topology that is widely recognized for its efficiency and effectiveness in transforming direct current into alternating current. The circuit features a pair of transistors that operate in a complementary fashion, effectively controlling the flow of current through the center-tapped winding of a step-up transformer. This configuration allows the circuit to boost the voltage level while converting the DC input.
The PCB layout includes detailed representations of both the top and bottom copper layers, providing a comprehensive view of the circuit's design. The six large pads located at the edges of the board are specifically designed for mounting screws, ensuring that the control board is securely fixed within its enclosure.
In the schematic, discrete components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes are strategically placed to facilitate various functions, including filtering, voltage regulation, and signal conditioning. Each component's placement is critical for the overall performance and stability of the inverter circuit. Furthermore, integrated circuits (ICs) on the board are responsible for specific tasks, such as control logic and signal processing. The square pad marking pin number 1 on each IC assists in proper orientation and connection during assembly.
This detailed layout and component arrangement are essential for achieving optimal performance in the inverter circuit, ensuring reliable operation in applications where DC to AC conversion is required. The design and implementation of such circuits are crucial in various fields, including renewable energy systems, power supplies, and motor drives.A common topology for DC-AC power converter circuits uses a pair of transistors to switch DC current through the center-tapped winding of a step-up transformer Examine these checkplot images from a PCB drafting program, for a control board based on this inverter circuit design. Both the top and bottom copper layer plots are shown from the perspect ive of the board`s top side. The six large pads around the periphery of the board are actually holes for mounting screws Mark where discrete components (resistors, capacitors, and diodes) go into the PCB, and identify which integrated circuits on the board layout are performing which functions in the schematic. Note: the square pad on each IC marks pin number 1 🔗 External reference
The described DC-AC power converter circuit utilizes a topology that is widely recognized for its efficiency and effectiveness in transforming direct current into alternating current. The circuit features a pair of transistors that operate in a complementary fashion, effectively controlling the flow of current through the center-tapped winding of a step-up transformer. This configuration allows the circuit to boost the voltage level while converting the DC input.
The PCB layout includes detailed representations of both the top and bottom copper layers, providing a comprehensive view of the circuit's design. The six large pads located at the edges of the board are specifically designed for mounting screws, ensuring that the control board is securely fixed within its enclosure.
In the schematic, discrete components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes are strategically placed to facilitate various functions, including filtering, voltage regulation, and signal conditioning. Each component's placement is critical for the overall performance and stability of the inverter circuit. Furthermore, integrated circuits (ICs) on the board are responsible for specific tasks, such as control logic and signal processing. The square pad marking pin number 1 on each IC assists in proper orientation and connection during assembly.
This detailed layout and component arrangement are essential for achieving optimal performance in the inverter circuit, ensuring reliable operation in applications where DC to AC conversion is required. The design and implementation of such circuits are crucial in various fields, including renewable energy systems, power supplies, and motor drives.A common topology for DC-AC power converter circuits uses a pair of transistors to switch DC current through the center-tapped winding of a step-up transformer Examine these checkplot images from a PCB drafting program, for a control board based on this inverter circuit design. Both the top and bottom copper layer plots are shown from the perspect ive of the board`s top side. The six large pads around the periphery of the board are actually holes for mounting screws Mark where discrete components (resistors, capacitors, and diodes) go into the PCB, and identify which integrated circuits on the board layout are performing which functions in the schematic. Note: the square pad on each IC marks pin number 1 🔗 External reference