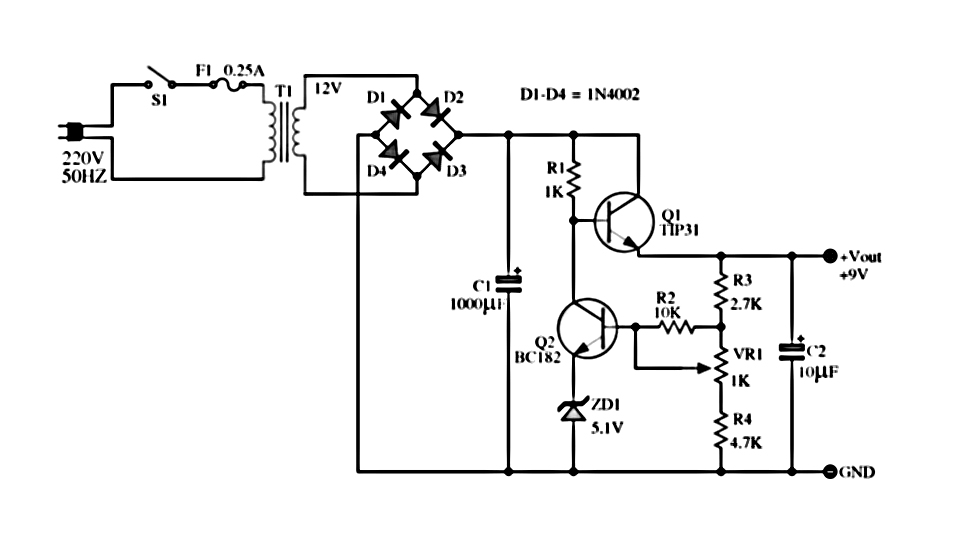
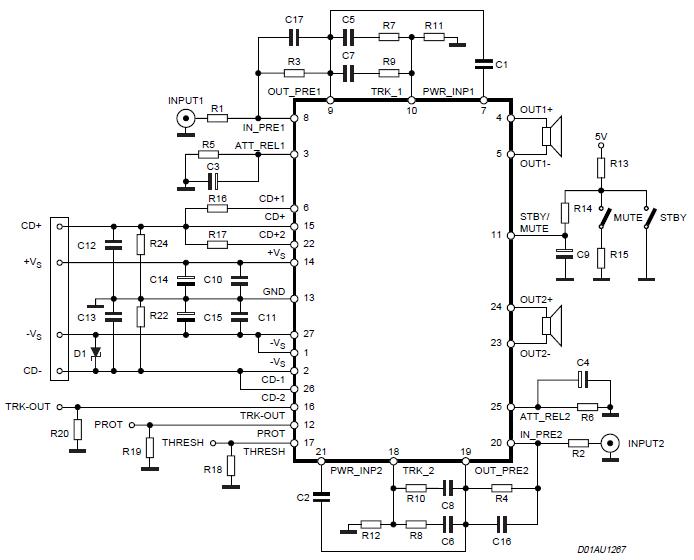
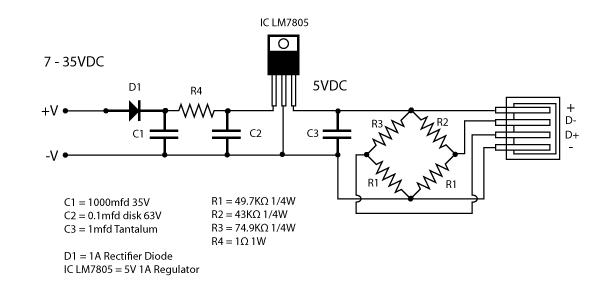
iPod charger Schematic
This document serves as a supplementary guide to numerous existing resources that detail the construction of a USB charger. It is assumed that the reader possesses a basic understanding of electronics.
The construction of a USB charger typically involves a few essential components: a power source, a voltage regulator, and USB output connectors. The power source can be a battery or an AC to DC adapter, which provides the necessary voltage and current to charge devices.
A common voltage regulator used in USB chargers is the LM7805, which steps down higher voltages to a stable 5V output suitable for USB devices. The input voltage range for the LM7805 is typically between 7V to 35V, allowing it to accommodate various power sources.
To design a basic USB charger circuit, the following components are required:
1. **Power Source**: An AC to DC adapter rated at 5V or higher (depending on the regulator used).
2. **Voltage Regulator**: An LM7805 or similar linear regulator.
3. **Capacitors**: Input and output capacitors (usually 0.33µF and 0.1µF respectively) are recommended to stabilize the voltage and reduce noise.
4. **USB Connector**: A standard USB Type-A or Type-B connector for output.
5. **Protection Diodes**: To prevent reverse polarity and protect the circuit from potential damage.
The circuit can be assembled on a breadboard for prototyping or soldered onto a PCB for a more permanent solution. The connections should be made as follows:
- Connect the input of the voltage regulator to the positive terminal of the power source.
- Connect the ground of the power source to the ground of the voltage regulator.
- Attach the output of the voltage regulator to the VBUS pin of the USB connector.
- Connect the ground of the USB connector to the common ground.
Testing the circuit involves measuring the output voltage with a multimeter to ensure it is stable at 5V. Once verified, the charger can be used to charge compatible USB devices safely. Proper heat dissipation methods should be considered, especially if the charger will be used for extended periods or with high current loads.First off I should mention that this is supplemental Instructable to the countless others that show you how to build a USB charger. I am assuming you.. 🔗 External reference
The construction of a USB charger typically involves a few essential components: a power source, a voltage regulator, and USB output connectors. The power source can be a battery or an AC to DC adapter, which provides the necessary voltage and current to charge devices.
A common voltage regulator used in USB chargers is the LM7805, which steps down higher voltages to a stable 5V output suitable for USB devices. The input voltage range for the LM7805 is typically between 7V to 35V, allowing it to accommodate various power sources.
To design a basic USB charger circuit, the following components are required:
1. **Power Source**: An AC to DC adapter rated at 5V or higher (depending on the regulator used).
2. **Voltage Regulator**: An LM7805 or similar linear regulator.
3. **Capacitors**: Input and output capacitors (usually 0.33µF and 0.1µF respectively) are recommended to stabilize the voltage and reduce noise.
4. **USB Connector**: A standard USB Type-A or Type-B connector for output.
5. **Protection Diodes**: To prevent reverse polarity and protect the circuit from potential damage.
The circuit can be assembled on a breadboard for prototyping or soldered onto a PCB for a more permanent solution. The connections should be made as follows:
- Connect the input of the voltage regulator to the positive terminal of the power source.
- Connect the ground of the power source to the ground of the voltage regulator.
- Attach the output of the voltage regulator to the VBUS pin of the USB connector.
- Connect the ground of the USB connector to the common ground.
Testing the circuit involves measuring the output voltage with a multimeter to ensure it is stable at 5V. Once verified, the charger can be used to charge compatible USB devices safely. Proper heat dissipation methods should be considered, especially if the charger will be used for extended periods or with high current loads.First off I should mention that this is supplemental Instructable to the countless others that show you how to build a USB charger. I am assuming you.. 🔗 External reference