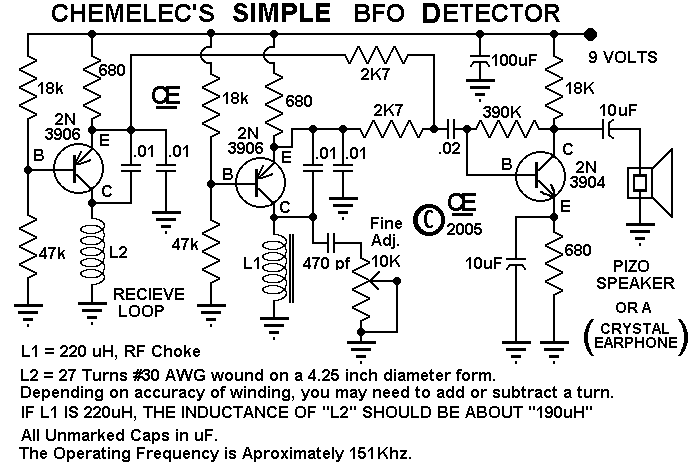
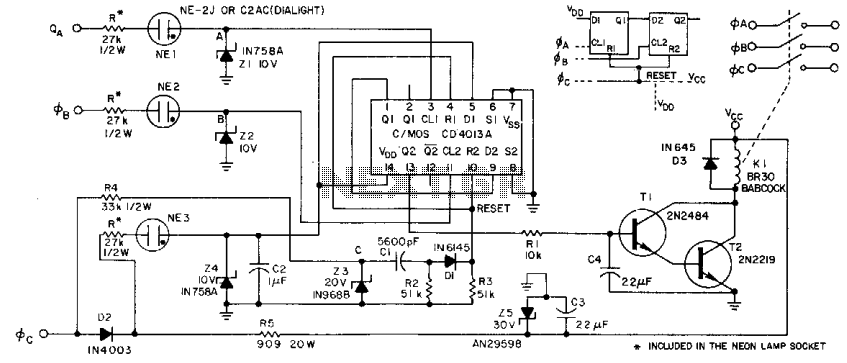
JFET static detector
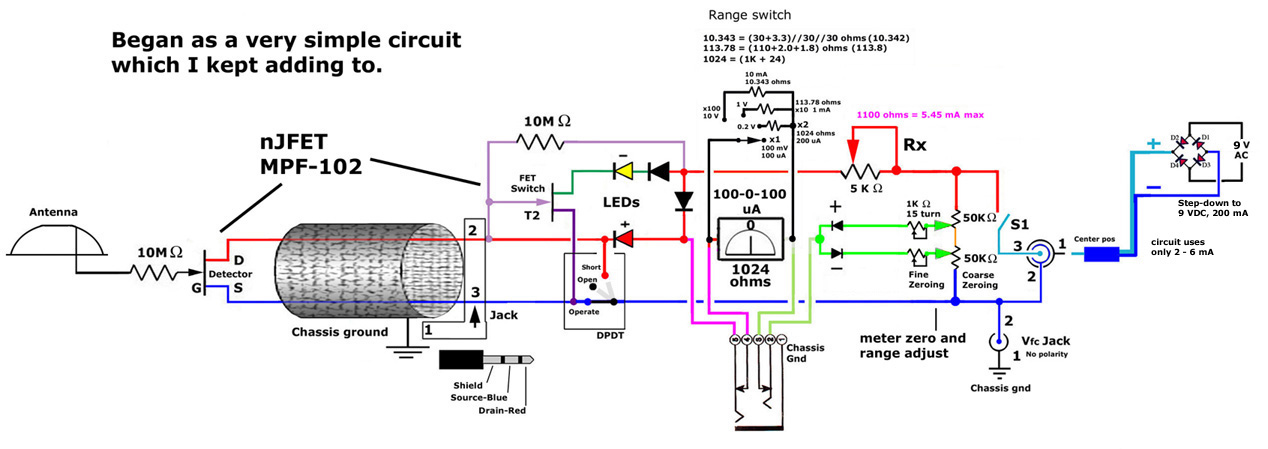
This post discusses the construction of multiple versions of JFET static charge detectors, highlighting observed differences that are not easily explained.
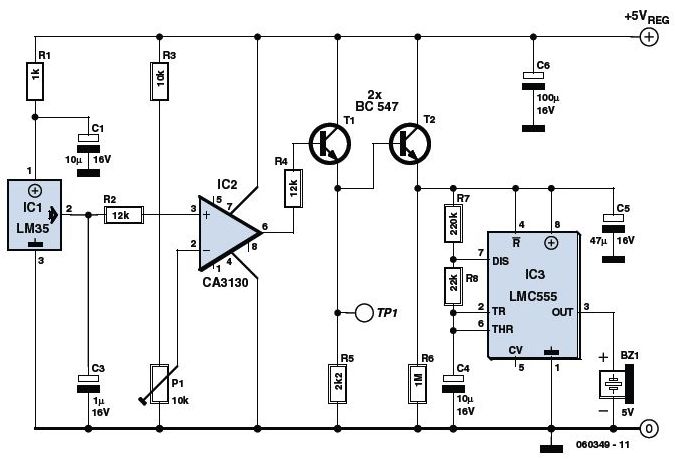
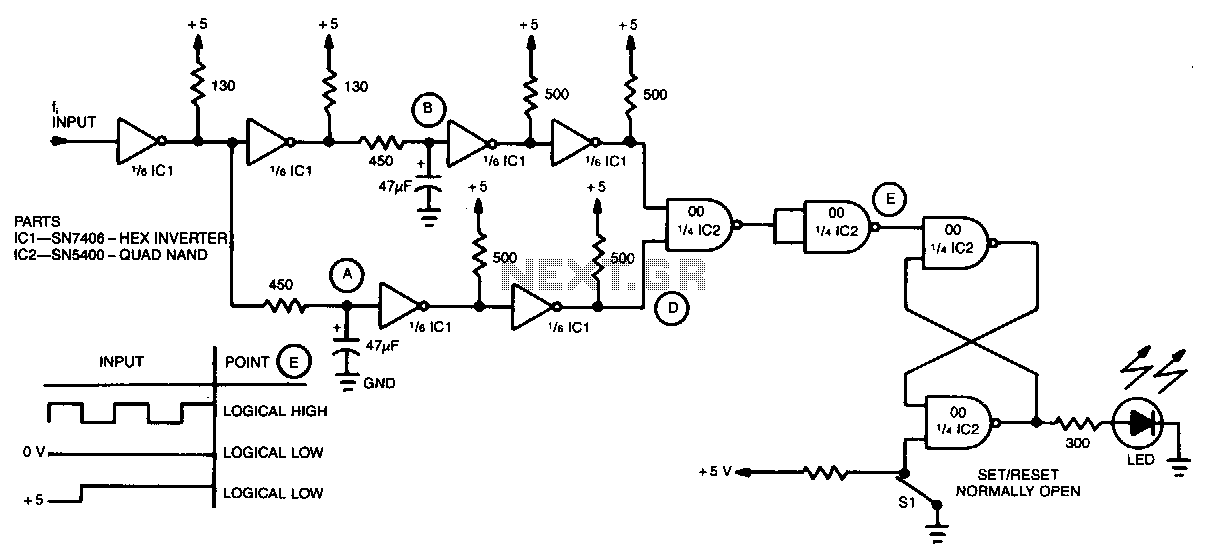
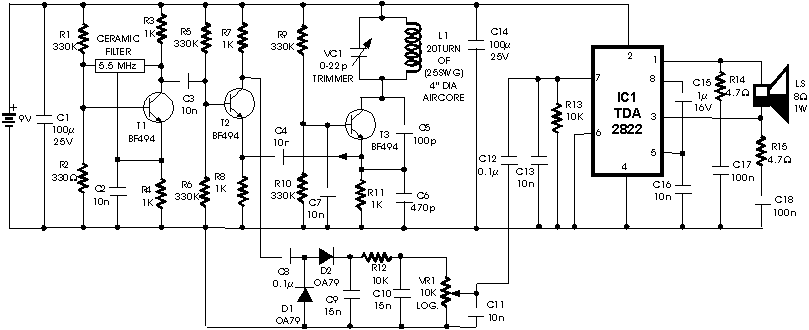
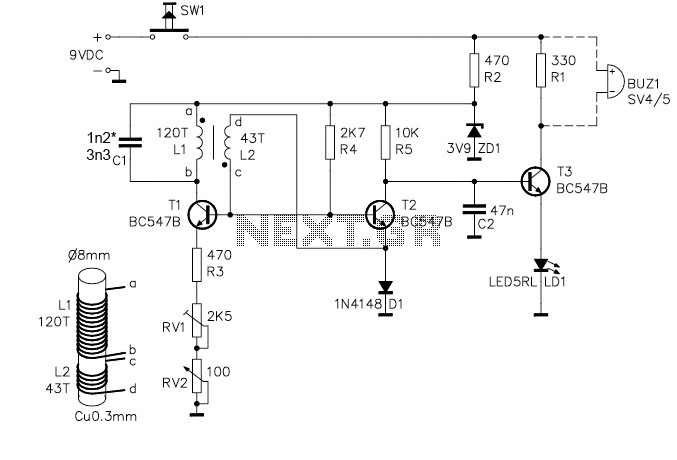
The JFET (Junction Field Effect Transistor) static charge detector operates by utilizing the unique characteristics of JFETs to sense variations in electric fields. The basic configuration typically includes a JFET connected in a common-source or common-drain arrangement, which allows for high input impedance and sensitivity to static charges.
In the design, the gate of the JFET is exposed to the environment, enabling it to detect electric fields generated by static charges. The output can be monitored through a load resistor connected to the drain, where the voltage variations reflect the presence of static charge. It is crucial to ensure proper biasing of the JFET to keep it in the active region, thus maintaining its sensitivity.
The differences observed in various versions of the static charge detectors could stem from several factors, including variations in JFET specifications, differences in the circuit layout, or the use of different materials for the gate. Additionally, environmental factors such as humidity and temperature can influence the performance of these detectors.
To enhance the performance of the static charge detector, it is advisable to implement a shielding mechanism to minimize interference from external electric fields. Furthermore, incorporating a feedback mechanism could stabilize the output and improve the accuracy of the readings.
Overall, JFET static charge detectors serve as valuable tools in applications requiring the detection of static electricity, and understanding the nuances of their design and operation is essential for optimizing their performance.Hello, this is my first post here. I built several versions of JFET static charge detectors and I`m seeing some differences I can`t explain so I`m.. 🔗 External reference
The JFET (Junction Field Effect Transistor) static charge detector operates by utilizing the unique characteristics of JFETs to sense variations in electric fields. The basic configuration typically includes a JFET connected in a common-source or common-drain arrangement, which allows for high input impedance and sensitivity to static charges.
In the design, the gate of the JFET is exposed to the environment, enabling it to detect electric fields generated by static charges. The output can be monitored through a load resistor connected to the drain, where the voltage variations reflect the presence of static charge. It is crucial to ensure proper biasing of the JFET to keep it in the active region, thus maintaining its sensitivity.
The differences observed in various versions of the static charge detectors could stem from several factors, including variations in JFET specifications, differences in the circuit layout, or the use of different materials for the gate. Additionally, environmental factors such as humidity and temperature can influence the performance of these detectors.
To enhance the performance of the static charge detector, it is advisable to implement a shielding mechanism to minimize interference from external electric fields. Furthermore, incorporating a feedback mechanism could stabilize the output and improve the accuracy of the readings.
Overall, JFET static charge detectors serve as valuable tools in applications requiring the detection of static electricity, and understanding the nuances of their design and operation is essential for optimizing their performance.Hello, this is my first post here. I built several versions of JFET static charge detectors and I`m seeing some differences I can`t explain so I`m.. 🔗 External reference