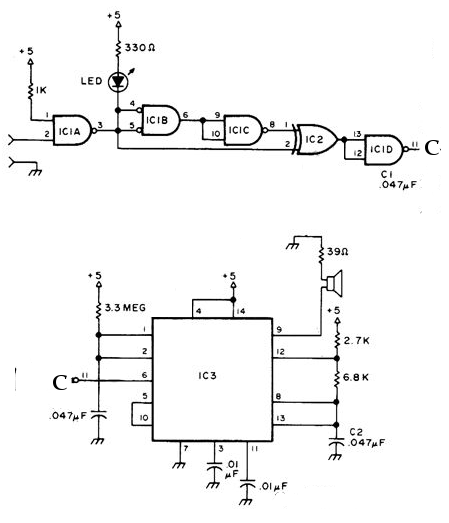
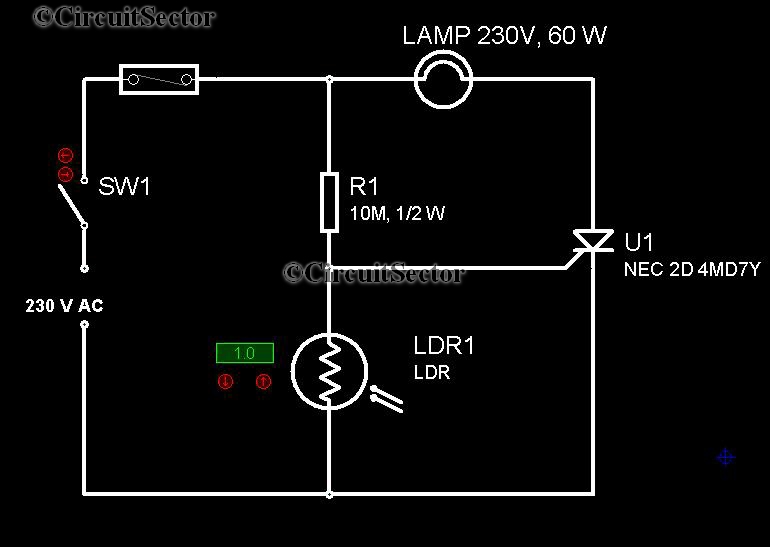
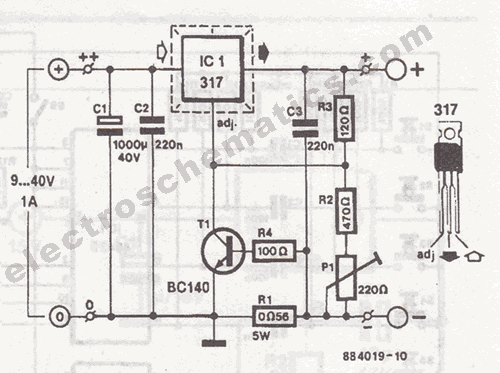
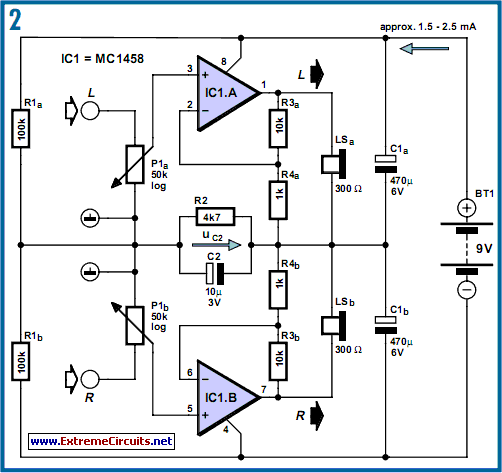
Joule thief AA battery led circuit
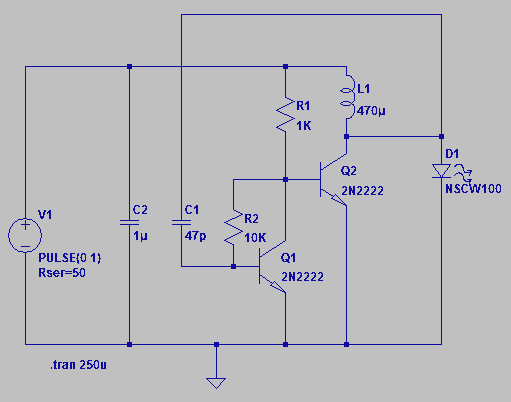
Four observations regarding the Joule Thief AA battery LED circuit. The schematic of the LED circuit illustrates the power source (V1), which symbolizes a depleted battery with only 1 volt remaining and an internal resistance.
The Joule Thief circuit is a simple and efficient boost converter designed to extract usable energy from a low-voltage source, such as a nearly depleted AA battery. The essential components of this circuit include a transistor (typically a NPN type), a resistor, an inductor, and a light-emitting diode (LED).
In the schematic, the power source (V1) represents the AA battery with a voltage of approximately 1 volt. This low voltage is insufficient to power most LEDs directly; however, the Joule Thief circuit utilizes the principles of inductive energy storage and oscillation to increase the voltage. The transistor acts as a switch that rapidly turns on and off, allowing current to flow through the inductor. When the transistor is on, the inductor stores energy in its magnetic field. When the transistor turns off, the magnetic field collapses, inducing a higher voltage across the inductor, which can then forward-bias the LED, allowing it to light up.
The resistor in the circuit is crucial as it limits the base current flowing into the transistor, ensuring that it operates within its safe limits. The LED serves as the load, providing visual feedback that the circuit is functioning. The efficiency of the Joule Thief circuit allows it to illuminate an LED even when the battery voltage is too low for direct use, making it an excellent solution for maximizing the lifespan of batteries that would otherwise be discarded.
Overall, the Joule Thief circuit is an innovative approach to energy conservation, demonstrating how simple electronic components can be utilized to harness energy from sources that are typically considered depleted.4 thoughts on Joule thief AA battery led circuit. In the schematic of the led circuit you can see the power source (V1) that represents an empty battery. It has only 1 volts remaining and an internal. 🔗 External reference
The Joule Thief circuit is a simple and efficient boost converter designed to extract usable energy from a low-voltage source, such as a nearly depleted AA battery. The essential components of this circuit include a transistor (typically a NPN type), a resistor, an inductor, and a light-emitting diode (LED).
In the schematic, the power source (V1) represents the AA battery with a voltage of approximately 1 volt. This low voltage is insufficient to power most LEDs directly; however, the Joule Thief circuit utilizes the principles of inductive energy storage and oscillation to increase the voltage. The transistor acts as a switch that rapidly turns on and off, allowing current to flow through the inductor. When the transistor is on, the inductor stores energy in its magnetic field. When the transistor turns off, the magnetic field collapses, inducing a higher voltage across the inductor, which can then forward-bias the LED, allowing it to light up.
The resistor in the circuit is crucial as it limits the base current flowing into the transistor, ensuring that it operates within its safe limits. The LED serves as the load, providing visual feedback that the circuit is functioning. The efficiency of the Joule Thief circuit allows it to illuminate an LED even when the battery voltage is too low for direct use, making it an excellent solution for maximizing the lifespan of batteries that would otherwise be discarded.
Overall, the Joule Thief circuit is an innovative approach to energy conservation, demonstrating how simple electronic components can be utilized to harness energy from sources that are typically considered depleted.4 thoughts on Joule thief AA battery led circuit. In the schematic of the led circuit you can see the power source (V1) that represents an empty battery. It has only 1 volts remaining and an internal. 🔗 External reference