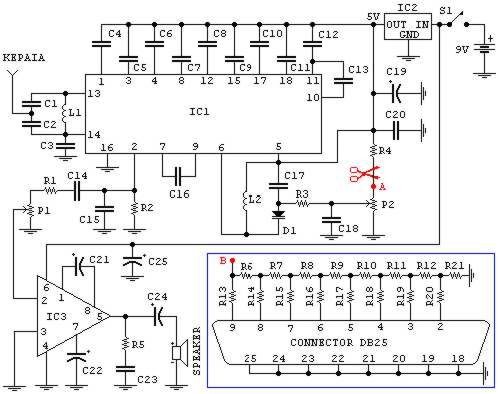
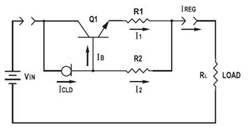
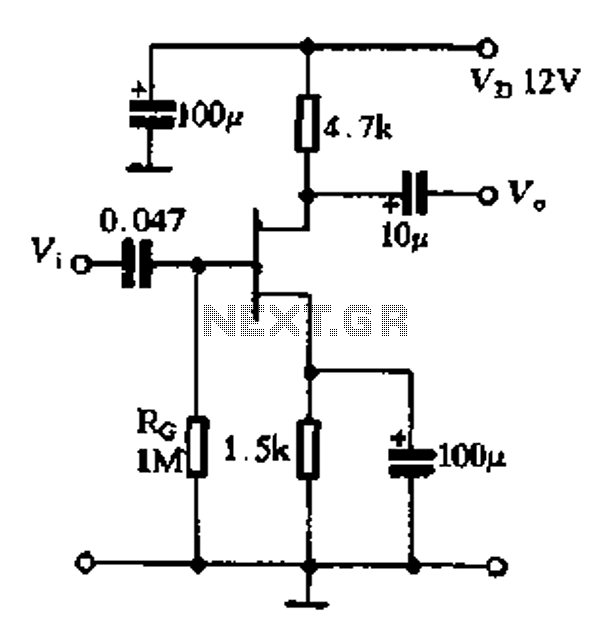
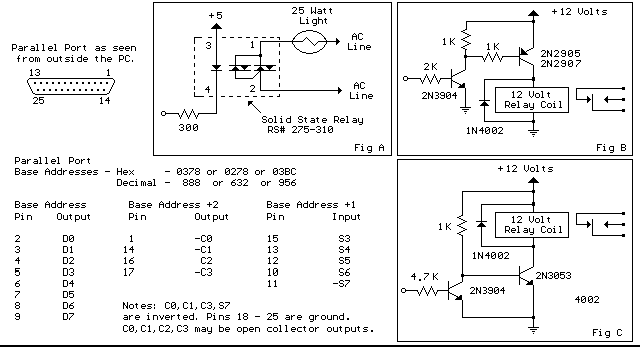
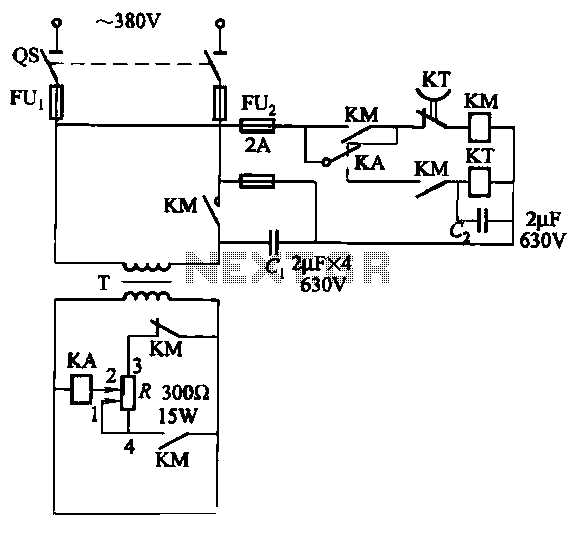
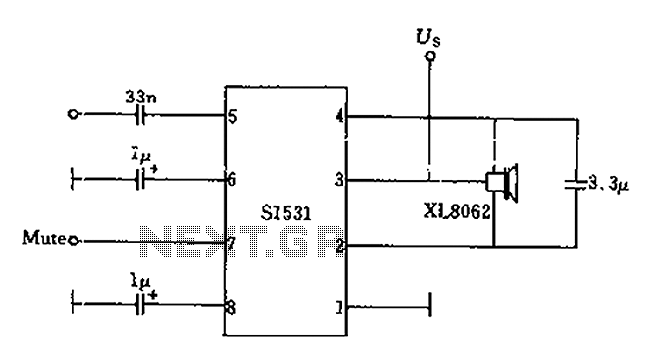
Lead and Acid Battery Charger Circuit
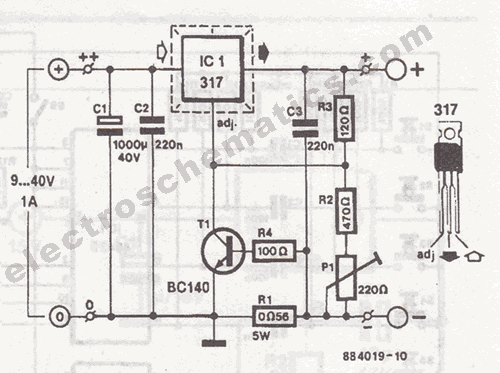
Modern acid batteries and lead plates are embodiments of simplicity in use. Unlike NiCd batteries, they must be recharged by connecting to a constant voltage source.
Modern acid batteries, commonly referred to as lead-acid batteries, consist of lead plates submerged in an electrolyte solution of sulfuric acid. These batteries are widely used in various applications, including automotive, renewable energy systems, and backup power supplies, due to their robustness and cost-effectiveness. The lead-acid battery operates on the principle of reversible chemical reactions, allowing it to be recharged after discharging.
The charging process involves connecting the battery to a constant voltage source, typically a regulated charger, which ensures that the voltage remains stable throughout the charging cycle. This method contrasts with nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries, which can be charged using a more flexible charging approach. The constant voltage charging technique is crucial for lead-acid batteries to prevent overcharging, which can lead to excessive gassing, reduced efficiency, and potential damage to the battery cells.
During the charging phase, the lead sulfate formed during discharge is converted back into lead dioxide (PbO2) at the positive plate and sponge lead (Pb) at the negative plate. The electrolyte also plays a critical role, as it facilitates the movement of ions between the plates, thus maintaining the chemical balance necessary for efficient operation.
In summary, lead-acid batteries are a reliable energy storage solution characterized by their simple design and straightforward charging requirements, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Their performance can be optimized by adhering to proper charging protocols, ensuring longevity and efficiency in energy storage systems.Modern acid batteries and lead plates, are embodiment of simplicity in use. Unlike NiCd batteries, they must be recharged by connecting to a constant volta.. 🔗 External reference
Modern acid batteries, commonly referred to as lead-acid batteries, consist of lead plates submerged in an electrolyte solution of sulfuric acid. These batteries are widely used in various applications, including automotive, renewable energy systems, and backup power supplies, due to their robustness and cost-effectiveness. The lead-acid battery operates on the principle of reversible chemical reactions, allowing it to be recharged after discharging.
The charging process involves connecting the battery to a constant voltage source, typically a regulated charger, which ensures that the voltage remains stable throughout the charging cycle. This method contrasts with nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries, which can be charged using a more flexible charging approach. The constant voltage charging technique is crucial for lead-acid batteries to prevent overcharging, which can lead to excessive gassing, reduced efficiency, and potential damage to the battery cells.
During the charging phase, the lead sulfate formed during discharge is converted back into lead dioxide (PbO2) at the positive plate and sponge lead (Pb) at the negative plate. The electrolyte also plays a critical role, as it facilitates the movement of ions between the plates, thus maintaining the chemical balance necessary for efficient operation.
In summary, lead-acid batteries are a reliable energy storage solution characterized by their simple design and straightforward charging requirements, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Their performance can be optimized by adhering to proper charging protocols, ensuring longevity and efficiency in energy storage systems.Modern acid batteries and lead plates, are embodiment of simplicity in use. Unlike NiCd batteries, they must be recharged by connecting to a constant volta.. 🔗 External reference