Joule ThiefCircuits
Warning: Undefined array key "extension" in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 468
Deprecated: strtolower(): Passing null to parameter #1 ($string) of type string is deprecated in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 468
This topic will be locked and will display all of the circuits and some photos of the devices being worked on in the Joule Thief topic. This process will take some time, so patience is appreciated. If any errors are noticed or if additional information is needed, please send a message for corrections. Thank you.
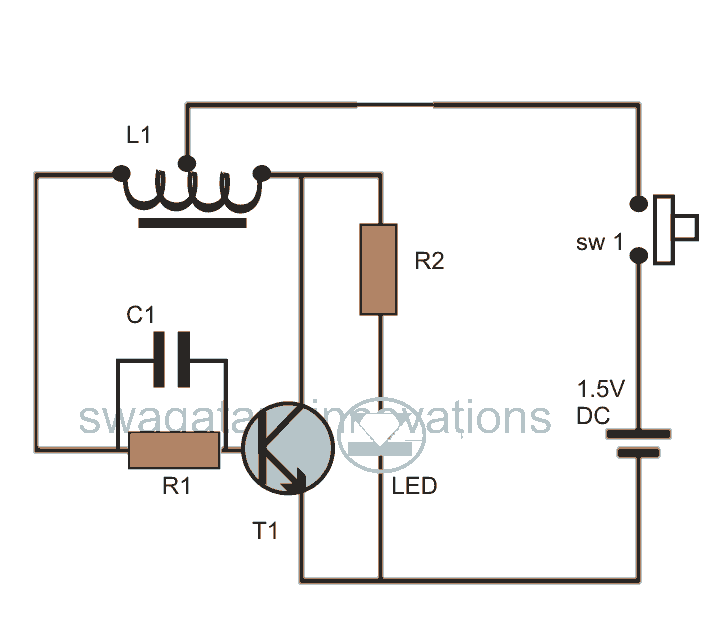
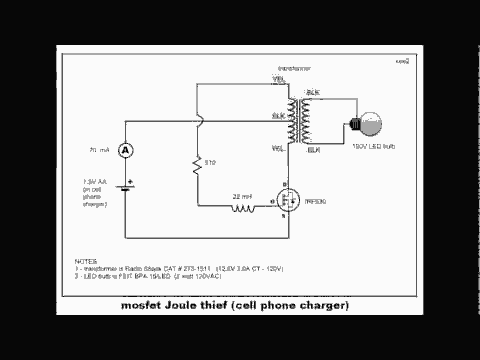
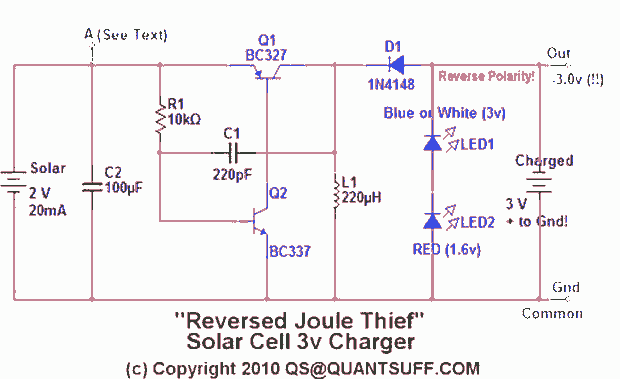
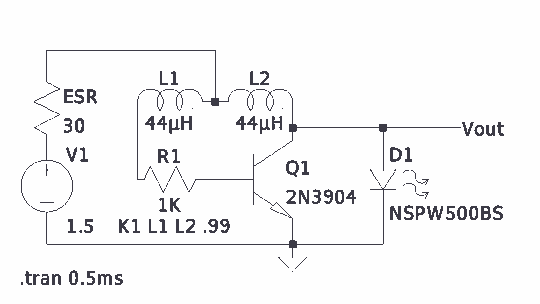
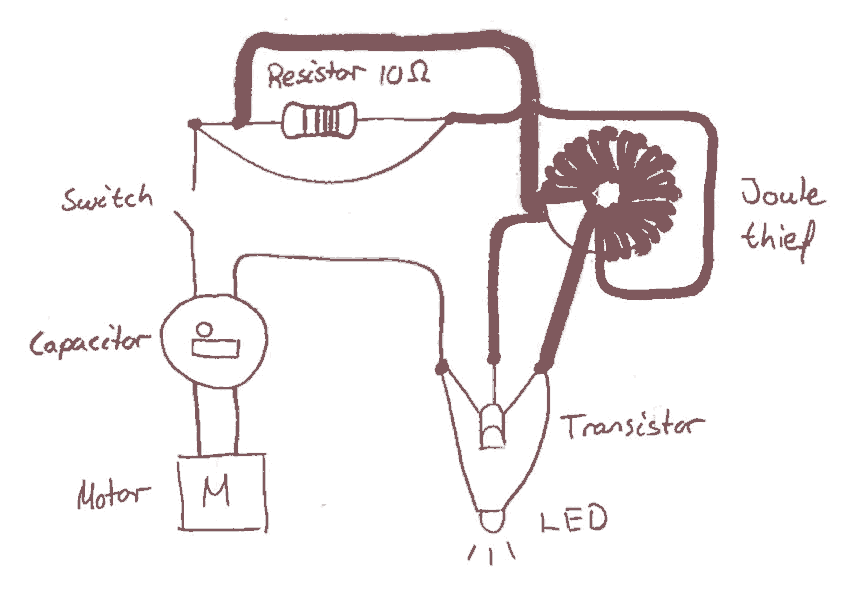
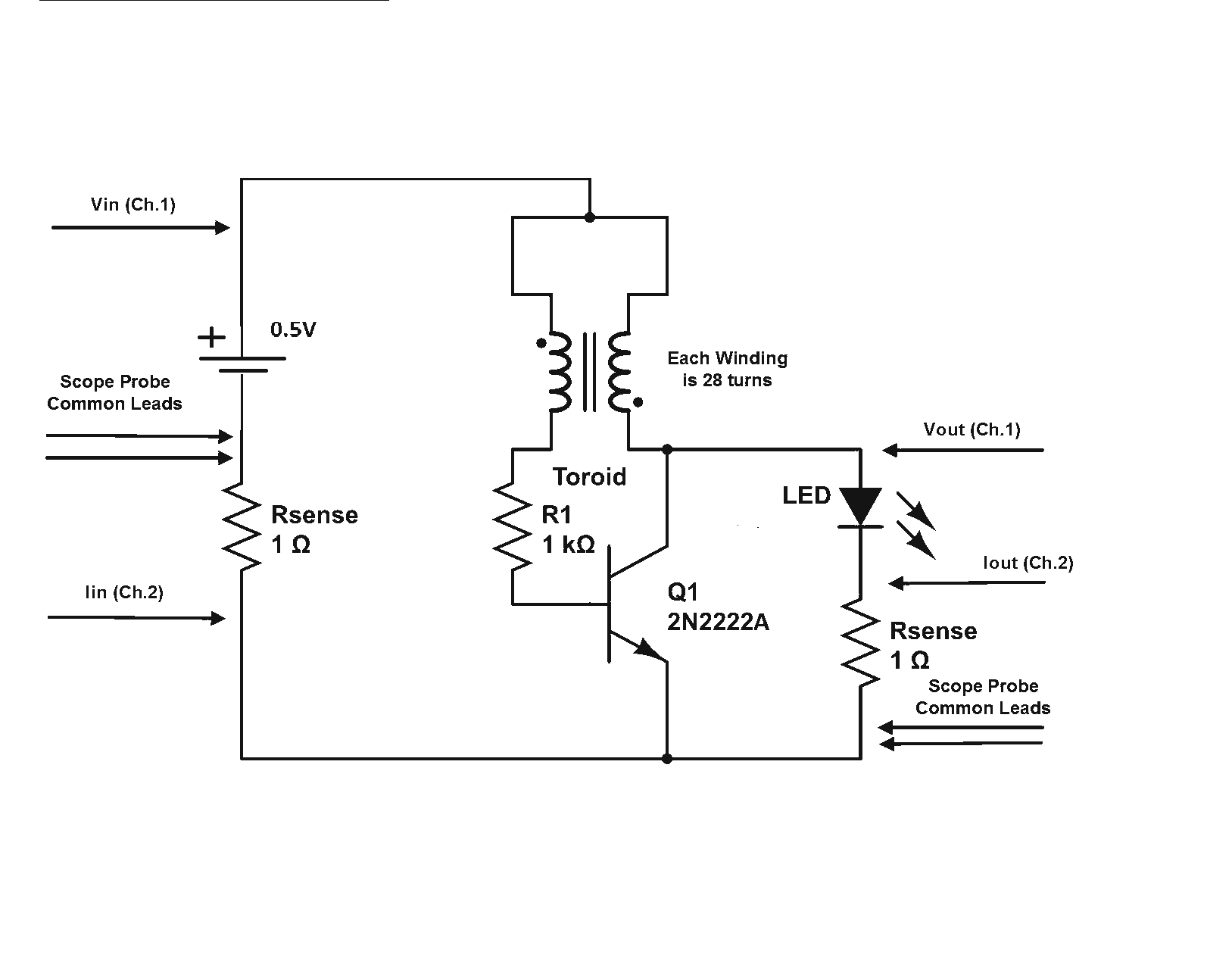
The Joule Thief is a minimalistic circuit designed to extract usable power from low-voltage sources, such as depleted batteries. It typically consists of a few key components: a transistor, a resistor, a coil (inductor), and a diode. The circuit operates on the principle of boosting voltage, allowing it to power devices that require a higher voltage than what is available from the low-voltage source.
In a standard Joule Thief configuration, the transistor acts as a switch. When the circuit is powered, the initial current flows through the base of the transistor via a resistor, turning it on. This allows current to flow through the coil, creating a magnetic field. As the magnetic field builds, it induces a voltage in the coil. Once the magnetic field reaches a certain level, the transistor turns off, collapsing the magnetic field and inducing a higher voltage in the opposite direction. This induced voltage is then rectified by the diode, allowing it to charge a capacitor or power a load.
The design can be modified by adjusting the values of the resistor and the coil to optimize performance for specific applications. Variations of the Joule Thief may include additional components such as capacitors for smoothing the output or multiple transistors for increased efficiency. The simplicity and effectiveness of the Joule Thief circuit make it an ideal choice for low-power applications, including LED lighting and small electronic devices utilizing scavenged energy.This topic will be locked and display all of the circuits and some photos of the devices being worked on in the Joule Thief topic. This is going to take me a while to do so please be patient. If you feel there is an error, or I need to include something else that is not here, please feel free to im me and I will fix it.
Thank you. 🔗 External reference
The Joule Thief is a minimalistic circuit designed to extract usable power from low-voltage sources, such as depleted batteries. It typically consists of a few key components: a transistor, a resistor, a coil (inductor), and a diode. The circuit operates on the principle of boosting voltage, allowing it to power devices that require a higher voltage than what is available from the low-voltage source.
In a standard Joule Thief configuration, the transistor acts as a switch. When the circuit is powered, the initial current flows through the base of the transistor via a resistor, turning it on. This allows current to flow through the coil, creating a magnetic field. As the magnetic field builds, it induces a voltage in the coil. Once the magnetic field reaches a certain level, the transistor turns off, collapsing the magnetic field and inducing a higher voltage in the opposite direction. This induced voltage is then rectified by the diode, allowing it to charge a capacitor or power a load.
The design can be modified by adjusting the values of the resistor and the coil to optimize performance for specific applications. Variations of the Joule Thief may include additional components such as capacitors for smoothing the output or multiple transistors for increased efficiency. The simplicity and effectiveness of the Joule Thief circuit make it an ideal choice for low-power applications, including LED lighting and small electronic devices utilizing scavenged energy.This topic will be locked and display all of the circuits and some photos of the devices being worked on in the Joule Thief topic. This is going to take me a while to do so please be patient. If you feel there is an error, or I need to include something else that is not here, please feel free to im me and I will fix it.
Thank you. 🔗 External reference