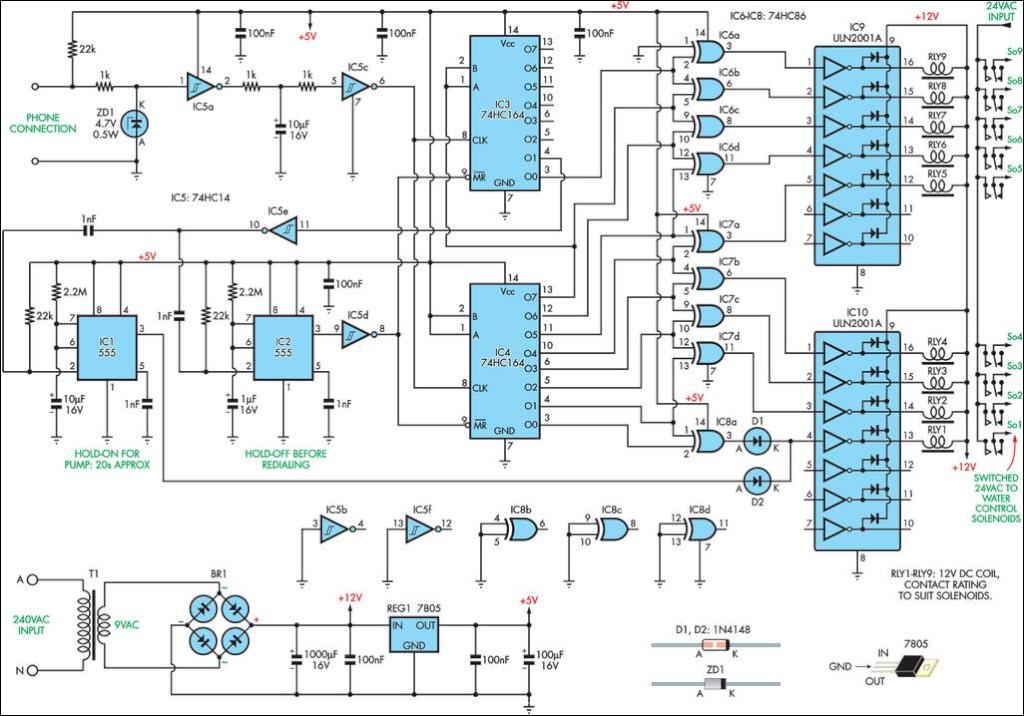
Laser Communication System
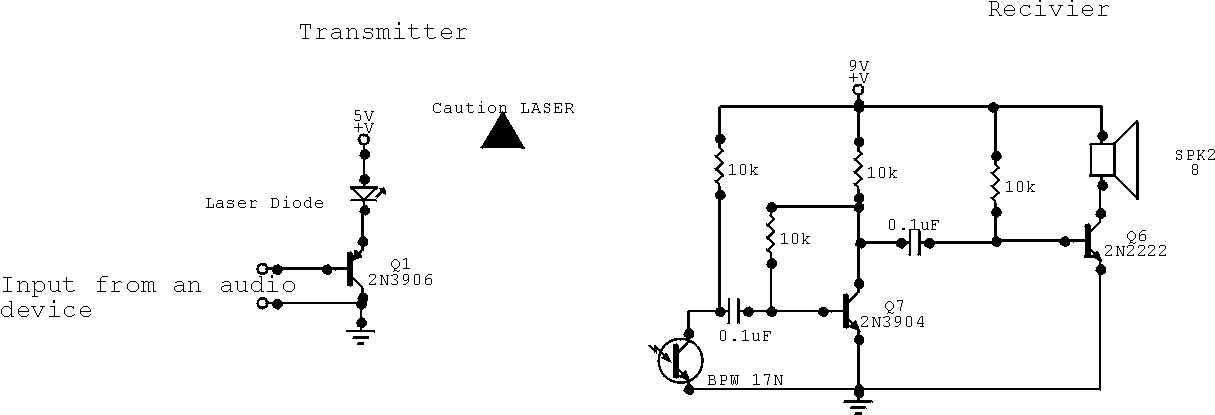
This is a simple Laser communication system. It can transmit and receive signal from any audio device. Communication distance is few meters. All components are not critical. Transistor 2N2222 may be on the coolrib. Laser diode is from laser pointer.
The described laser communication system is a basic yet effective method for transmitting audio signals wirelessly over short distances. The system utilizes a laser diode, typically sourced from a standard laser pointer, to convert electrical audio signals into light signals. The 2N2222 transistor is employed in the circuit to amplify the audio signal before it is sent to the laser diode, ensuring that the transmitted signal maintains clarity over the communication distance of a few meters.
In the schematic, the audio input from any audio device is fed into the base of the 2N2222 transistor, which is configured in a common-emitter arrangement. This configuration provides the necessary gain to the signal. The collector of the transistor is connected to the laser diode, which is powered by an appropriate voltage source. The laser diode emits a modulated light beam corresponding to the audio signal, which can be directed towards a photodiode or phototransistor at the receiving end.
At the receiver, the photodiode or phototransistor detects the modulated light beam and converts it back into an electrical signal. This signal can then be amplified, if necessary, and output to an audio device for playback. The system is designed to operate effectively within a few meters, making it suitable for applications such as wireless audio transmission in small rooms or for educational demonstrations.
The components used in this circuit are non-critical, allowing for flexibility in sourcing parts. However, attention should be paid to the alignment of the laser beam and the sensitivity of the photodetector to ensure optimal performance. The use of a heat sink, or coolrib, for the 2N2222 transistor is advisable to prevent overheating during operation, especially in prolonged use scenarios. Overall, this simple laser communication system exemplifies the principles of optical communication and can serve as an educational tool for understanding basic electronic concepts.This is a simple Laser communication system. It can transmit and receive signal from any audio device.Communication distance is few meters. All components are not critical. Transistor 2N2222 may be on the coolrib. Laser diode is from laser pointer. 🔗 External reference
The described laser communication system is a basic yet effective method for transmitting audio signals wirelessly over short distances. The system utilizes a laser diode, typically sourced from a standard laser pointer, to convert electrical audio signals into light signals. The 2N2222 transistor is employed in the circuit to amplify the audio signal before it is sent to the laser diode, ensuring that the transmitted signal maintains clarity over the communication distance of a few meters.
In the schematic, the audio input from any audio device is fed into the base of the 2N2222 transistor, which is configured in a common-emitter arrangement. This configuration provides the necessary gain to the signal. The collector of the transistor is connected to the laser diode, which is powered by an appropriate voltage source. The laser diode emits a modulated light beam corresponding to the audio signal, which can be directed towards a photodiode or phototransistor at the receiving end.
At the receiver, the photodiode or phototransistor detects the modulated light beam and converts it back into an electrical signal. This signal can then be amplified, if necessary, and output to an audio device for playback. The system is designed to operate effectively within a few meters, making it suitable for applications such as wireless audio transmission in small rooms or for educational demonstrations.
The components used in this circuit are non-critical, allowing for flexibility in sourcing parts. However, attention should be paid to the alignment of the laser beam and the sensitivity of the photodetector to ensure optimal performance. The use of a heat sink, or coolrib, for the 2N2222 transistor is advisable to prevent overheating during operation, especially in prolonged use scenarios. Overall, this simple laser communication system exemplifies the principles of optical communication and can serve as an educational tool for understanding basic electronic concepts.This is a simple Laser communication system. It can transmit and receive signal from any audio device.Communication distance is few meters. All components are not critical. Transistor 2N2222 may be on the coolrib. Laser diode is from laser pointer. 🔗 External reference