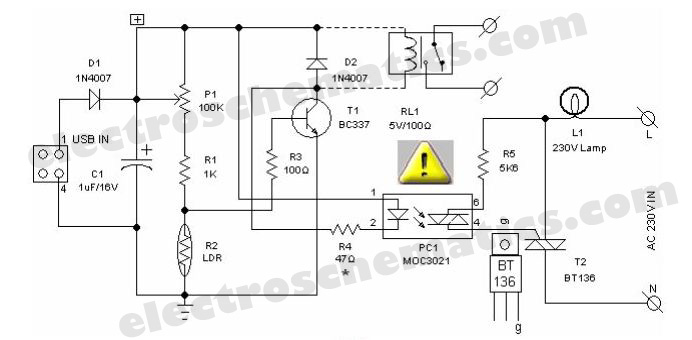
LDR PC Desk Lamp
Most of the PC desk lamps available in the market illuminate whenever there is input power. These do not consider whether there is an actual need for light.
The typical design of PC desk lamps operates on a straightforward principle: they activate upon receiving electrical power without assessing the ambient light conditions or user requirements. This results in unnecessary energy consumption and may lead to discomfort due to excessive brightness in low-light environments.
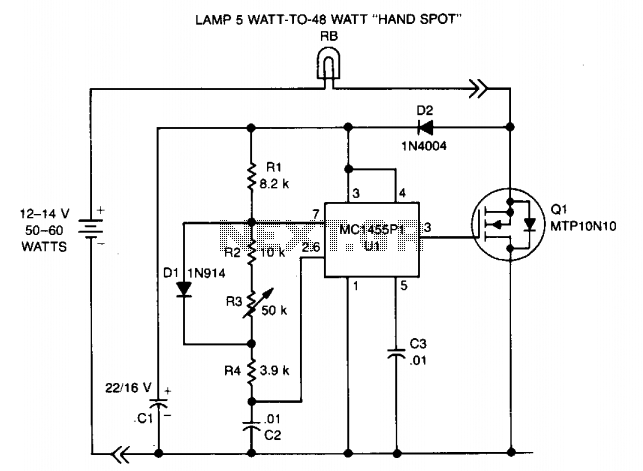
To enhance the functionality of PC desk lamps, a more sophisticated approach can be adopted. Incorporating a light sensor or a microcontroller can enable the lamp to adjust its brightness based on the surrounding light levels. For instance, a light-dependent resistor (LDR) can be integrated into the circuit to monitor ambient light. When the ambient light falls below a predetermined threshold, the LDR triggers the lamp to turn on, and conversely, it turns off when sufficient natural light is present.
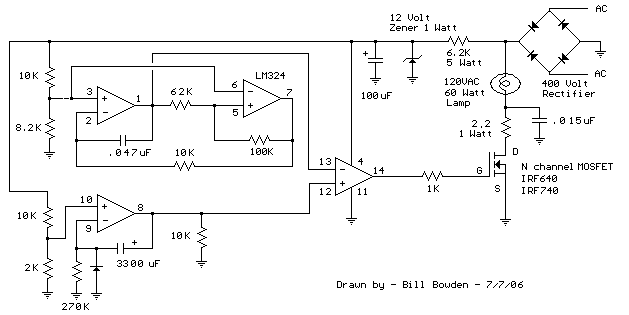
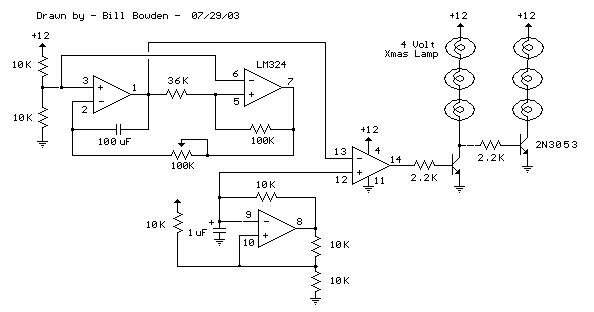
Additionally, a dimmable LED driver can be implemented to allow for variable brightness levels. This can be achieved through a pulse-width modulation (PWM) technique, which adjusts the average power delivered to the LEDs, thereby modifying their brightness according to user preferences or ambient conditions.
Furthermore, adding a user interface with buttons or a touch-sensitive panel can provide the user with control over the lamp's settings, including brightness levels and power status. An optional timer function could also be integrated, allowing the lamp to automatically turn off after a specified duration, further enhancing energy efficiency.
In summary, the evolution of PC desk lamps can significantly benefit from the integration of intelligent features that consider both energy efficiency and user comfort, transforming a simple lighting solution into a smart, adaptive device.Most of the PC desk lamps available in the market light up whenever there is an input power. These don`t take into account whether there is a real need for.. 🔗 External reference
The typical design of PC desk lamps operates on a straightforward principle: they activate upon receiving electrical power without assessing the ambient light conditions or user requirements. This results in unnecessary energy consumption and may lead to discomfort due to excessive brightness in low-light environments.
To enhance the functionality of PC desk lamps, a more sophisticated approach can be adopted. Incorporating a light sensor or a microcontroller can enable the lamp to adjust its brightness based on the surrounding light levels. For instance, a light-dependent resistor (LDR) can be integrated into the circuit to monitor ambient light. When the ambient light falls below a predetermined threshold, the LDR triggers the lamp to turn on, and conversely, it turns off when sufficient natural light is present.
Additionally, a dimmable LED driver can be implemented to allow for variable brightness levels. This can be achieved through a pulse-width modulation (PWM) technique, which adjusts the average power delivered to the LEDs, thereby modifying their brightness according to user preferences or ambient conditions.
Furthermore, adding a user interface with buttons or a touch-sensitive panel can provide the user with control over the lamp's settings, including brightness levels and power status. An optional timer function could also be integrated, allowing the lamp to automatically turn off after a specified duration, further enhancing energy efficiency.
In summary, the evolution of PC desk lamps can significantly benefit from the integration of intelligent features that consider both energy efficiency and user comfort, transforming a simple lighting solution into a smart, adaptive device.Most of the PC desk lamps available in the market light up whenever there is an input power. These don`t take into account whether there is a real need for.. 🔗 External reference