LED-Circuits 4
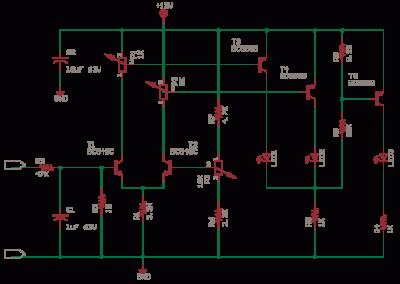
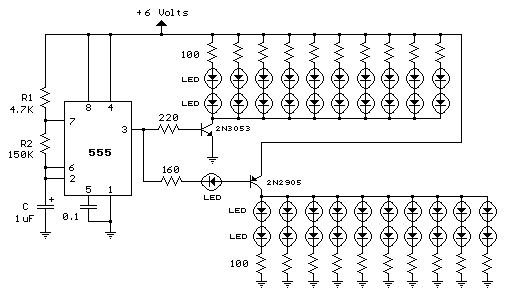
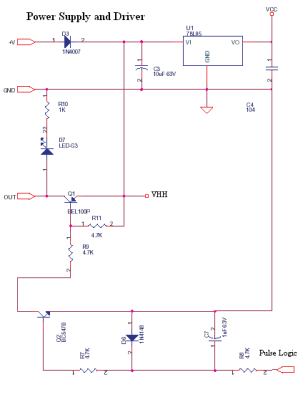
This is a constant current source using a FET. It serves as a simple replacement for a series resistor to limit current. The N-Channel FET BF256C can provide a current of 15mA. Before using integrated circuits, it is advisable to experiment with basic methods to gain a better understanding of LEDs. One method involves using a single resistor in series to limit the maximum current in a series LED chain. If a regulated supply with a fixed voltage is available, this method can be applied. For instance, using a 12V SMPS, each HB White LED has a forward voltage drop. This circuit is derived from a Siemens Application Note from 1974 and employs commonly available components. It holds significant educational value. The circuit has not been tested; however, it can be simulated or constructed for practical evaluation. Additionally, this circuit functions as a simple analog to digital converter, where optoisolators can be used in place of LEDs. Transistors T1 and T2 create a differential amplifier, while T3, T4, and T5 operate as comparators driving the LEDs. Further understanding of these components can be gained by studying circuits at 4QD-TEC. This circuit is designed to monitor mains supply voltage without using an isolation step-down transformer, and it should only be constructed by individuals with appropriate safety knowledge. Capacitor C1 limits the current and drops most of the voltage, while the zener-regulated supply powers the chip. The capacitance of C2 can be increased to 220uF or more if necessary, as the bar mode display may consume additional power. Resistors R2, R3, R5, and R6 form a voltage divider to sample the input voltage, and D11 with C3 converts this to a DC value. The preset resistor R5 can be adjusted with a logarithmic plastic tweaker to activate the fifth LED. This circuit also serves as a mains 230V AC load current indicator and is classified as a live circuit, necessitating caution. The resistors must be fusible ceramic wire-wound types. The circuit has been recalled from memory and has not been retested; it is recommended to verify its functionality before use. A 1A slow-blow fuse is advisable, and the shunt resistor R3 and fuse rating should be designed according to the load requirements. It is important to note that this circuit must be placed in series with the load, similar to an ammeter. The circuit utilizes an LM339 quad comparator, which can operate on single or dual supplies. The LM339 features an open-collector output capable of driving 15mA with low power consumption. Although this design remains untested, it is believed to function as intended. Numerous superior circuits are available in various circuit archives linked on the front page for further exploration. When measuring the open circuit voltage of a battery with a high-impedance digital multimeter (10M), the readings may be somewhat misleading.
The constant current source circuit utilizing the BF256C FET is a practical solution for LED applications, providing a steady output current of 15mA. This design is particularly useful in scenarios where precise current control is necessary, such as in LED lighting applications. The circuit's simplicity allows for easy construction, making it an excellent educational tool for those learning about FET operation and LED characteristics.
The use of a single resistor to limit current in series with an LED chain is a fundamental method that demonstrates Ohm's law and the principles of current limiting. When utilizing a regulated power supply, this approach ensures that the LEDs operate within their safe current ratings, preventing damage and extending their lifespan.
The differential amplifier configuration formed by transistors T1 and T2 is crucial for amplifying small voltage differences, making it suitable for applications requiring precise voltage measurements. The comparators T3, T4, and T5 facilitate the operation of the LED indicators, providing visual feedback based on the input voltage levels. This feedback mechanism is essential for monitoring and controlling circuit behavior.
The inclusion of a zener diode for voltage regulation ensures that the operational amplifier receives a stable supply voltage, critical for consistent performance. The voltage divider created by resistors R2, R3, R5, and R6 is instrumental in scaling down the mains voltage to a manageable level for the circuit's components, allowing for accurate voltage monitoring.
Safety considerations are paramount when working with mains voltage. The circuit's design, which avoids the use of isolation transformers, emphasizes the necessity for skilled construction and adherence to safety protocols. The use of fusible resistors enhances the circuit's reliability by providing a fail-safe mechanism in case of overload conditions.
In summary, this circuit exemplifies a versatile approach to current regulation and voltage monitoring, integrating fundamental electronic principles with practical applications. Proper understanding and careful construction are essential for safe and effective operation.This is a constant current source using a FET. This is the most simple replacement to series resistor to limit current. The N-Channel FET BF256C can give 15mA current. Simple Methods Before you get to use chips, experiment with some methods, which will help you learn about the LEDs better. The first is just One Resistor in series. This is to Limit the max current in a Series LED Chain. If you have a Regulated Supply with a Fixed Voltage, then you can use this method. Let us take a 12V SMPS, Each HB White LED has a drop of Read More This circuit is derived from a Siemens Application Note 1974. This circuit uses common components of today. The circuit is here as it is of high educational value. I have not tested it. You can simulate and test` or wire it up and try` and let me know how it worked. The Circuit is also a simple analog to digital converter. You can use optos in place of LEDs. T1 and T2 make a differential amplifier. T3, T4 and T5 driving the LEDs are comparators. Now to learn more on how they work you have to study circuits at 4QD-TEC Read More This Circuit helps in the monitoring of mains supply voltage.
It does not use a isolation step down transformer. This has to be constructed only by skilled people with knowledge of safety requirements. C1 limits the current and drops most of the voltage. The zener regulated supply is for the chip. C2 can be raised to 220uF or more if required. The bar mode display may consume more power. R2-R3-R5-R6 form a voltage divider to get a sample of the input voltage, D11-C3 get the DC value. Adjust R5 preset with a log Plastic tweaker to get the 5th led Read More This Circuit helps in the monitoring of mains supply voltage. It does not use a isolation step down transformer. This has to be constructed only by skilled people with knowledge of safety requirements. C1 0. 47uF can be brought down to 0. 22uF for low LED currents, use high efficiency ultra bright LEDs. C1 should be 440V AC or 630V DC plastic axial yellow, polyester, polycarbonate, polypropylene, metalized film.
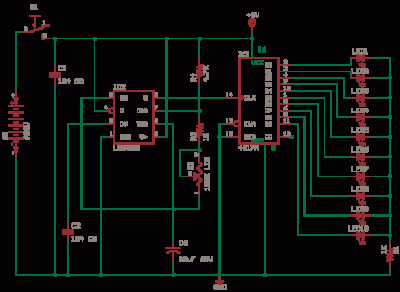
R3-R6-R9-R14-R18 resistor divider determines the LED turn on or threshold switch points, 10M for hysteresis. Adjust R16 preset with a log Plastic tweaker to get the led D2 to turn on when input voltage Read More This is a mains 230V AC load current indicator and is a LIVE CIRCUIT, so take care.
The Resistors have to be a fusible ceramic wire wound. This circuit has been drawn from my memory and i have not tried it out again, just see if it is ok and then try. You should use the fuse of 1A a slow blow if you want but it is very important. You can design the shunt R3 and Fuse rating as required by your load. Note that this circuit is to be put in series with the load like an ammeter. Read More This circuit uses a LM339, a quad comparator. LM339 can work on single or dual supplies, it has a open collector output that can drive 15mA, low power consumption.
The circuit is an untested design but it should work. I did it as many searches were made in my webpages with these keywords. There are many better circuits in the various circuit archives i have linked on the front page, you just have to look around. When you measure the open circuit voltage of a battery with a high impedance DMM (10M), the value may be a bit misleading.
Apply Read More 🔗 External reference
The constant current source circuit utilizing the BF256C FET is a practical solution for LED applications, providing a steady output current of 15mA. This design is particularly useful in scenarios where precise current control is necessary, such as in LED lighting applications. The circuit's simplicity allows for easy construction, making it an excellent educational tool for those learning about FET operation and LED characteristics.
The use of a single resistor to limit current in series with an LED chain is a fundamental method that demonstrates Ohm's law and the principles of current limiting. When utilizing a regulated power supply, this approach ensures that the LEDs operate within their safe current ratings, preventing damage and extending their lifespan.
The differential amplifier configuration formed by transistors T1 and T2 is crucial for amplifying small voltage differences, making it suitable for applications requiring precise voltage measurements. The comparators T3, T4, and T5 facilitate the operation of the LED indicators, providing visual feedback based on the input voltage levels. This feedback mechanism is essential for monitoring and controlling circuit behavior.
The inclusion of a zener diode for voltage regulation ensures that the operational amplifier receives a stable supply voltage, critical for consistent performance. The voltage divider created by resistors R2, R3, R5, and R6 is instrumental in scaling down the mains voltage to a manageable level for the circuit's components, allowing for accurate voltage monitoring.
Safety considerations are paramount when working with mains voltage. The circuit's design, which avoids the use of isolation transformers, emphasizes the necessity for skilled construction and adherence to safety protocols. The use of fusible resistors enhances the circuit's reliability by providing a fail-safe mechanism in case of overload conditions.
In summary, this circuit exemplifies a versatile approach to current regulation and voltage monitoring, integrating fundamental electronic principles with practical applications. Proper understanding and careful construction are essential for safe and effective operation.This is a constant current source using a FET. This is the most simple replacement to series resistor to limit current. The N-Channel FET BF256C can give 15mA current. Simple Methods Before you get to use chips, experiment with some methods, which will help you learn about the LEDs better. The first is just One Resistor in series. This is to Limit the max current in a Series LED Chain. If you have a Regulated Supply with a Fixed Voltage, then you can use this method. Let us take a 12V SMPS, Each HB White LED has a drop of Read More This circuit is derived from a Siemens Application Note 1974. This circuit uses common components of today. The circuit is here as it is of high educational value. I have not tested it. You can simulate and test` or wire it up and try` and let me know how it worked. The Circuit is also a simple analog to digital converter. You can use optos in place of LEDs. T1 and T2 make a differential amplifier. T3, T4 and T5 driving the LEDs are comparators. Now to learn more on how they work you have to study circuits at 4QD-TEC Read More This Circuit helps in the monitoring of mains supply voltage.
It does not use a isolation step down transformer. This has to be constructed only by skilled people with knowledge of safety requirements. C1 limits the current and drops most of the voltage. The zener regulated supply is for the chip. C2 can be raised to 220uF or more if required. The bar mode display may consume more power. R2-R3-R5-R6 form a voltage divider to get a sample of the input voltage, D11-C3 get the DC value. Adjust R5 preset with a log Plastic tweaker to get the 5th led Read More This Circuit helps in the monitoring of mains supply voltage. It does not use a isolation step down transformer. This has to be constructed only by skilled people with knowledge of safety requirements. C1 0. 47uF can be brought down to 0. 22uF for low LED currents, use high efficiency ultra bright LEDs. C1 should be 440V AC or 630V DC plastic axial yellow, polyester, polycarbonate, polypropylene, metalized film.
R3-R6-R9-R14-R18 resistor divider determines the LED turn on or threshold switch points, 10M for hysteresis. Adjust R16 preset with a log Plastic tweaker to get the led D2 to turn on when input voltage Read More This is a mains 230V AC load current indicator and is a LIVE CIRCUIT, so take care.
The Resistors have to be a fusible ceramic wire wound. This circuit has been drawn from my memory and i have not tried it out again, just see if it is ok and then try. You should use the fuse of 1A a slow blow if you want but it is very important. You can design the shunt R3 and Fuse rating as required by your load. Note that this circuit is to be put in series with the load like an ammeter. Read More This circuit uses a LM339, a quad comparator. LM339 can work on single or dual supplies, it has a open collector output that can drive 15mA, low power consumption.
The circuit is an untested design but it should work. I did it as many searches were made in my webpages with these keywords. There are many better circuits in the various circuit archives i have linked on the front page, you just have to look around. When you measure the open circuit voltage of a battery with a high impedance DMM (10M), the value may be a bit misleading.
Apply Read More 🔗 External reference