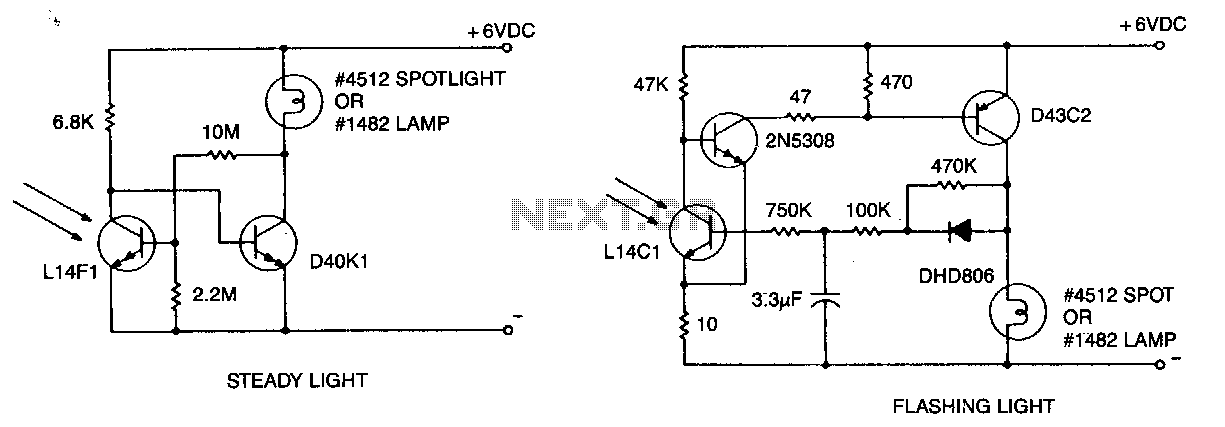
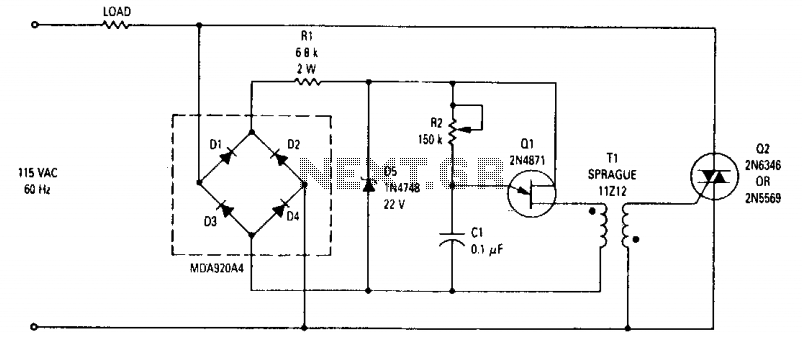
Light Sensitive Staircase Switch with Triac
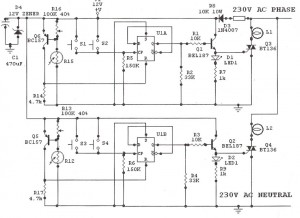
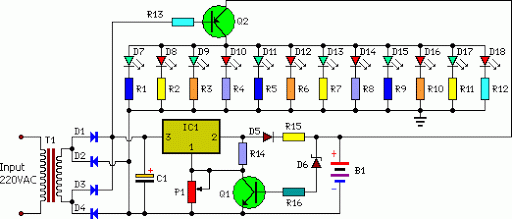
Light Sensitive Staircase Switch with Triac. The operation of the third circuit is quite similar, except that it incorporates photo sensitivity. The circuit is illustrated in the schematic. When there is insufficient light...
The light-sensitive staircase switch circuit utilizes a TRIAC for controlling the lighting based on ambient light levels. The primary function of this circuit is to automatically switch on the stairway lights when the surrounding light falls below a certain threshold, enhancing safety and convenience in low-light conditions.
The circuit typically consists of a light-dependent resistor (LDR) that acts as a sensor to detect light intensity. When the ambient light is insufficient, the resistance of the LDR increases, triggering the TRIAC to conduct and allowing current to flow to the connected lighting load. This configuration ensures that the lights are activated only when necessary, thereby conserving energy.
The schematic representation of the circuit includes the LDR connected in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor. The output from this divider is fed into the gate of the TRIAC. A capacitor may also be included in parallel with the TRIAC to provide a delay, ensuring that the lights do not flicker and remain stable once activated.
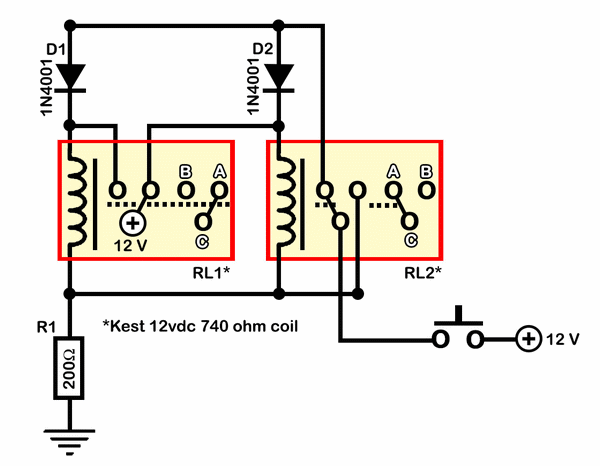
Additionally, a small relay can be integrated into the circuit to handle higher power loads safely, isolating the low-power control circuit from the high-power lighting circuit. The design may also incorporate a variable resistor to adjust the sensitivity of the LDR, allowing users to set the desired threshold for light activation based on personal preferences or specific environmental conditions.
Overall, this light-sensitive staircase switch circuit offers a practical solution for automatic lighting control, enhancing both functionality and energy efficiency in stairway illumination.Light Sensitive Staircase Switch with Triac , Operation of the third circuit is much similar except that it has photo sensitivity. The circuit is shown in Schematic When there is no sufficient l. 🔗 External reference
The light-sensitive staircase switch circuit utilizes a TRIAC for controlling the lighting based on ambient light levels. The primary function of this circuit is to automatically switch on the stairway lights when the surrounding light falls below a certain threshold, enhancing safety and convenience in low-light conditions.
The circuit typically consists of a light-dependent resistor (LDR) that acts as a sensor to detect light intensity. When the ambient light is insufficient, the resistance of the LDR increases, triggering the TRIAC to conduct and allowing current to flow to the connected lighting load. This configuration ensures that the lights are activated only when necessary, thereby conserving energy.
The schematic representation of the circuit includes the LDR connected in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor. The output from this divider is fed into the gate of the TRIAC. A capacitor may also be included in parallel with the TRIAC to provide a delay, ensuring that the lights do not flicker and remain stable once activated.
Additionally, a small relay can be integrated into the circuit to handle higher power loads safely, isolating the low-power control circuit from the high-power lighting circuit. The design may also incorporate a variable resistor to adjust the sensitivity of the LDR, allowing users to set the desired threshold for light activation based on personal preferences or specific environmental conditions.
Overall, this light-sensitive staircase switch circuit offers a practical solution for automatic lighting control, enhancing both functionality and energy efficiency in stairway illumination.Light Sensitive Staircase Switch with Triac , Operation of the third circuit is much similar except that it has photo sensitivity. The circuit is shown in Schematic When there is no sufficient l. 🔗 External reference