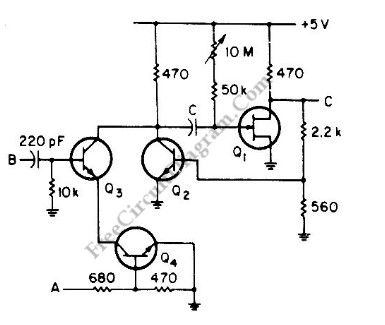
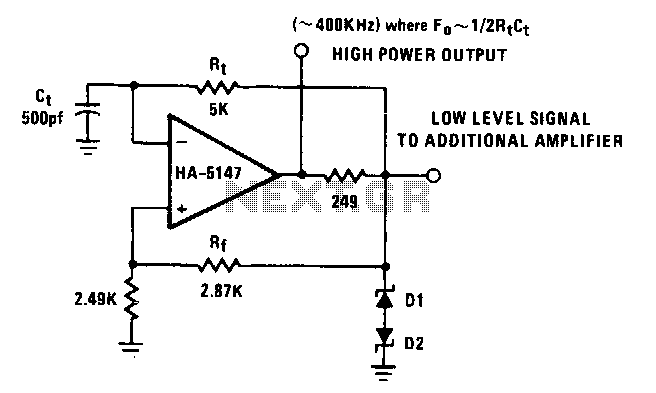
LM139 One-Shot Multivibrator
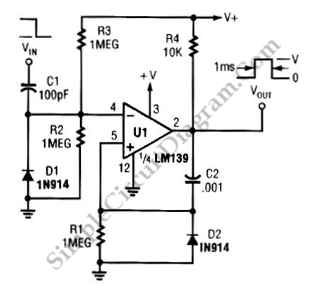
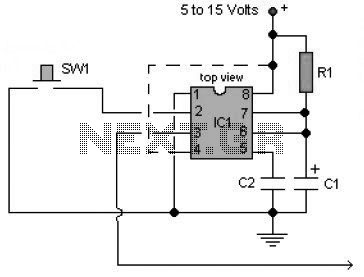
The circuit below is a one-shot multivibrator, also referred to as a monostable multivibrator or timer. The primary function of this circuit is to generate a single output pulse in response to an input trigger.
The one-shot multivibrator is a fundamental electronic circuit widely used in various applications, including timers, pulse width modulation, and signal conditioning. It operates in a monostable mode, meaning it has one stable state and can be triggered to switch to a temporary unstable state for a predetermined duration before returning to its stable state.
The circuit typically consists of a timing component (such as a resistor and capacitor) and a logic gate or an integrated circuit (IC) like the 555 timer. Upon receiving a trigger signal, the circuit momentarily changes its output state from low to high (or vice versa) for a specific time interval determined by the RC time constant. The duration of the output pulse can be calculated using the formula:
\[ T = 1.1 \times R \times C \]
where \( T \) is the time in seconds, \( R \) is the resistance in ohms, and \( C \) is the capacitance in farads.
In practical applications, the one-shot multivibrator can be used for debouncing switches, generating time delays, and producing clock pulses for digital circuits. The design considerations include selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values to achieve the desired timing characteristics, ensuring the trigger signal meets the required voltage levels, and managing power supply considerations for stable operation.
Overall, the one-shot multivibrator is a versatile and essential component in the realm of digital electronics, facilitating various timing and control functions in electronic systems.The circuit below is a one-shot multivibrator. One shot multivibrator is also known as monostable multivibrator, or timer. The main function of such circuit is.. 🔗 External reference
The one-shot multivibrator is a fundamental electronic circuit widely used in various applications, including timers, pulse width modulation, and signal conditioning. It operates in a monostable mode, meaning it has one stable state and can be triggered to switch to a temporary unstable state for a predetermined duration before returning to its stable state.
The circuit typically consists of a timing component (such as a resistor and capacitor) and a logic gate or an integrated circuit (IC) like the 555 timer. Upon receiving a trigger signal, the circuit momentarily changes its output state from low to high (or vice versa) for a specific time interval determined by the RC time constant. The duration of the output pulse can be calculated using the formula:
\[ T = 1.1 \times R \times C \]
where \( T \) is the time in seconds, \( R \) is the resistance in ohms, and \( C \) is the capacitance in farads.
In practical applications, the one-shot multivibrator can be used for debouncing switches, generating time delays, and producing clock pulses for digital circuits. The design considerations include selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values to achieve the desired timing characteristics, ensuring the trigger signal meets the required voltage levels, and managing power supply considerations for stable operation.
Overall, the one-shot multivibrator is a versatile and essential component in the realm of digital electronics, facilitating various timing and control functions in electronic systems.The circuit below is a one-shot multivibrator. One shot multivibrator is also known as monostable multivibrator, or timer. The main function of such circuit is.. 🔗 External reference