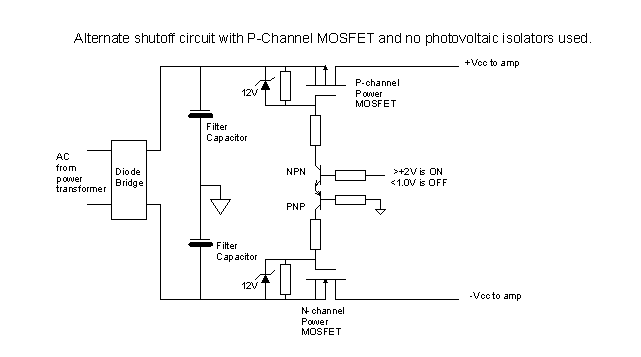
lm1893 power line modem circuit

This circuit is designed for an LM1893 power line modem, which facilitates information transfer between remote locations using the power mains. The LM1893 serves as a power line interface for half-duplex (bi-directional) communication of serial bit streams employing various coding methods. To maximize range, an impulse noise filter and a PLL-based demodulator are integrated for reception. During transmission, a sinusoidal carrier is applied and frequency-shift keying (FSK) modulation is utilized on the power line through a robust on-chip driver. In addition to the LM1893, the circuit incorporates a COPS controller and various discrete components.
The LM1893 power line modem circuit operates by utilizing the existing electrical wiring to transmit and receive data, effectively turning the power lines into a communication medium. The half-duplex nature of the communication allows for data to be sent and received, albeit not simultaneously, which is suitable for many applications where full-duplex communication is not critical.
The design includes essential elements such as an impulse noise filter that mitigates interference from electrical noise present on the power lines, ensuring clearer signal reception. The integrated phase-locked loop (PLL) demodulator enhances signal integrity by locking onto the carrier frequency, thus enabling precise extraction of the modulated data signal.
For the transmission side, the circuit applies a sinusoidal carrier wave that provides the necessary frequency for FSK modulation. This modulation technique allows the encoding of digital information onto the carrier wave by varying its frequency, which is particularly effective in noisy environments typical of power line communications. The rugged on-chip driver ensures that the signal can be transmitted over long distances without significant degradation.
The inclusion of a COPS controller allows for additional processing capabilities, enabling the system to handle various control tasks and improve overall functionality. The discrete components in the circuit complement the LM1893 and COPS controller, providing necessary support for filtering, amplification, and signal conditioning.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a robust solution for power line communication, leveraging existing infrastructure to facilitate data transfer, making it a versatile choice for remote communication applications.This is a circuit for an LM1893 power line modem circuit. This circuit is used to transfer information between remote location by using the power mains. This circuit uses LM1893 that is used as a power line interface for half-duplex (bi-directional) communication of serial bit stream of virtually any coding. This is the figure of the circuit; To g ive maximum range, impulse noise filter and a PLL-based demodulator are combined in reception. In transmission, a sinusoidal carrier is impressed and FSK modulated on most any power line via rugged on-chip driver. Besides LM1893, this circuit also uses a COPS controller and discrete components. [Circuit schematic source: National Semiconductor Notes] 🔗 External reference
The LM1893 power line modem circuit operates by utilizing the existing electrical wiring to transmit and receive data, effectively turning the power lines into a communication medium. The half-duplex nature of the communication allows for data to be sent and received, albeit not simultaneously, which is suitable for many applications where full-duplex communication is not critical.
The design includes essential elements such as an impulse noise filter that mitigates interference from electrical noise present on the power lines, ensuring clearer signal reception. The integrated phase-locked loop (PLL) demodulator enhances signal integrity by locking onto the carrier frequency, thus enabling precise extraction of the modulated data signal.
For the transmission side, the circuit applies a sinusoidal carrier wave that provides the necessary frequency for FSK modulation. This modulation technique allows the encoding of digital information onto the carrier wave by varying its frequency, which is particularly effective in noisy environments typical of power line communications. The rugged on-chip driver ensures that the signal can be transmitted over long distances without significant degradation.
The inclusion of a COPS controller allows for additional processing capabilities, enabling the system to handle various control tasks and improve overall functionality. The discrete components in the circuit complement the LM1893 and COPS controller, providing necessary support for filtering, amplification, and signal conditioning.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a robust solution for power line communication, leveraging existing infrastructure to facilitate data transfer, making it a versatile choice for remote communication applications.This is a circuit for an LM1893 power line modem circuit. This circuit is used to transfer information between remote location by using the power mains. This circuit uses LM1893 that is used as a power line interface for half-duplex (bi-directional) communication of serial bit stream of virtually any coding. This is the figure of the circuit; To g ive maximum range, impulse noise filter and a PLL-based demodulator are combined in reception. In transmission, a sinusoidal carrier is impressed and FSK modulated on most any power line via rugged on-chip driver. Besides LM1893, this circuit also uses a COPS controller and discrete components. [Circuit schematic source: National Semiconductor Notes] 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713