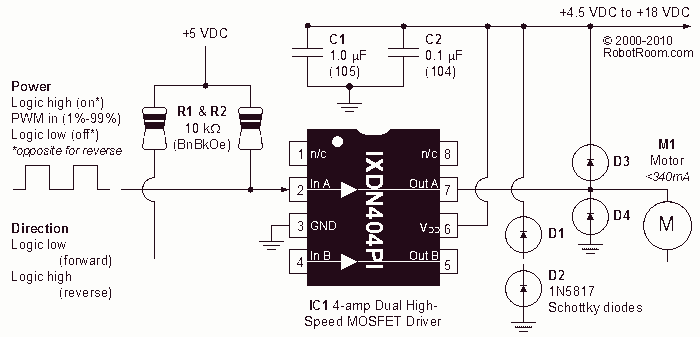
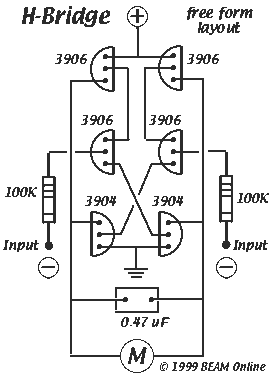
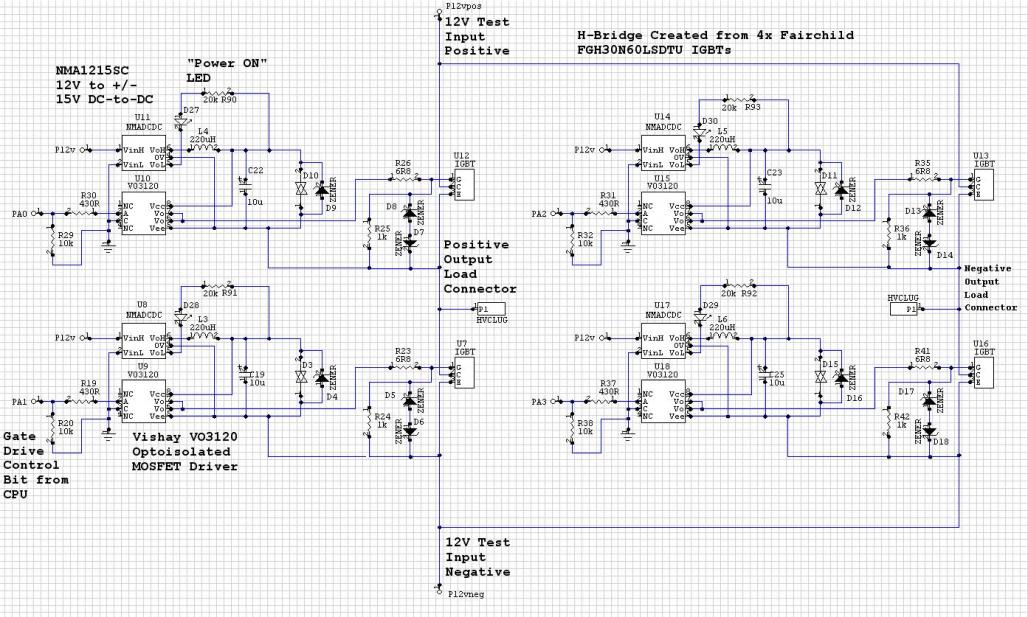
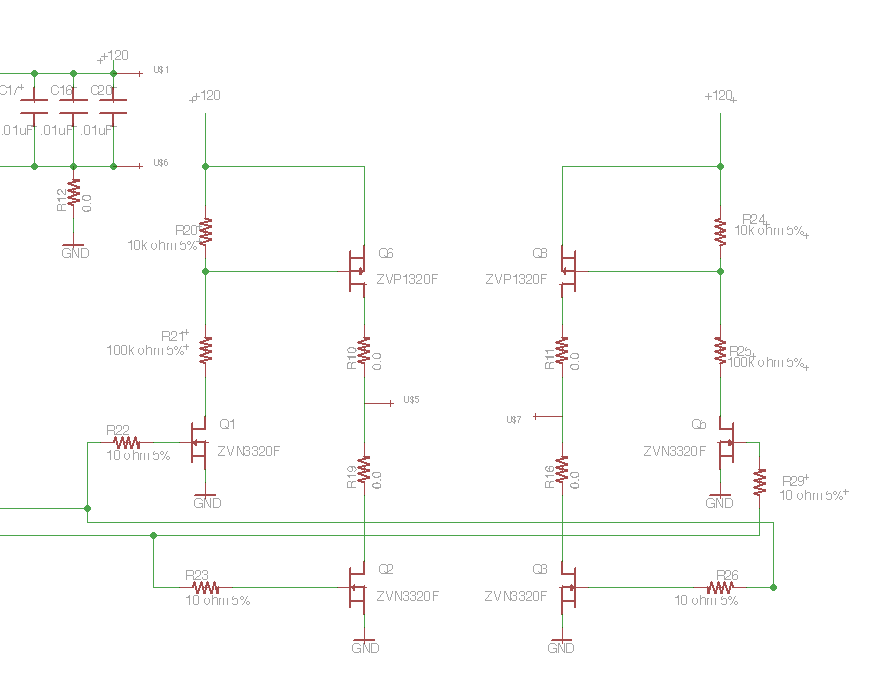
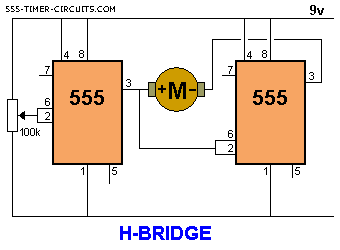
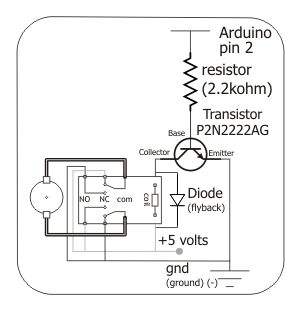
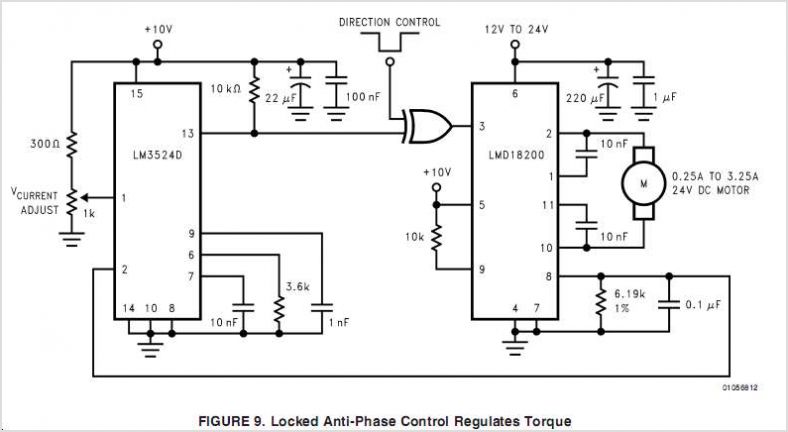
LMD18200 3A 55V H-Bridge
The LMV1090 is a fully analog dual differential input, differential output microphone array amplifier designed to reduce background acoustic noise while delivering exceptional speech clarity in voice communication applications. The LMV1090 effectively preserves near-field voice signals within 4 cm of the microphones while rejecting far-field acoustic noise greater than 50 cm from the microphones. Up to 20 dB of far-field rejection is achievable with a proper configuration using ±0.5 dB matched microphones. As part of the Powerwise family of energy-efficient solutions, the LMV1090 consumes only 600 µA of supply current, providing superior performance compared to DSP solutions that consume more than ten times the power. The dual microphone inputs and the processed signal output are differential to ensure excellent noise immunity. The microphones are biased with an internal low-noise bias supply. By National Semiconductor Corporation.
The LMV1090 microphone array amplifier is engineered to enhance voice communication by minimizing unwanted ambient noise, making it particularly suitable for applications where clarity is essential, such as teleconferencing and voice recognition systems. The dual differential inputs allow for the connection of two microphones, which can be strategically placed to capture sound from desired sources while rejecting noise from other directions. This configuration is beneficial in environments with significant background noise, as it focuses on sound sources that are directly in front of the microphones.
The amplifier's ability to maintain high-quality audio signals at close range (within 4 cm) while effectively suppressing noise from distances greater than 50 cm is attributed to its advanced signal processing capabilities. The design accommodates microphones that are matched to within ±0.5 dB, ensuring optimal performance and consistency in sound capture. The 20 dB far-field rejection is a key feature, allowing the LMV1090 to be integrated into systems where noise reduction is critical.
Power efficiency is another significant advantage of the LMV1090, consuming only 600 µA of supply current. This low power requirement is particularly advantageous in battery-operated devices, where extended operational life is a priority. The device's performance is notably superior compared to digital signal processing (DSP) solutions, which typically require much higher power consumption, thus making the LMV1090 a cost-effective choice for portable applications.
The differential output configuration enhances noise immunity, reducing the susceptibility of the signal to interference from electromagnetic sources. This is crucial for maintaining audio fidelity in various environments. Additionally, the internal low-noise bias supply ensures that the microphones operate optimally, further contributing to the overall performance of the amplifier.
In summary, the LMV1090 is a sophisticated solution for applications requiring high-quality voice communication, combining effective noise reduction, low power consumption, and robust performance characteristics. Its design principles and operational efficiencies make it a valuable component in modern audio processing systems.The LMV1090 is a fully Analog dual differential input, differ- ential output, Microphone array Amplifier designed to reduce background acoustic noise, while delivering superb speech clarity in voice Communication applications. The LMV1090 preserves near-field voice signals within 4cm of the Microphones while rejecting far-field acoustic noise grea
ter than 50cm from the Microphones Up to 20dB of far- field rejection is possible in a properly configured and using ±0. 5dB matched micropohones. Part of the Powerwise family of energy efficient solutions, the LMV1090 consumes only 600 A of supply current pro- viding superior performance over DSP solutions consuming greater than ten times the power.
The dual Microphone inputs and the processed signal output are differential to provide excellent noise immunity. The mi- crophones are biased with an internal low-noise bias supply. By National Semiconductor Corporation 🔗 External reference
The LMV1090 microphone array amplifier is engineered to enhance voice communication by minimizing unwanted ambient noise, making it particularly suitable for applications where clarity is essential, such as teleconferencing and voice recognition systems. The dual differential inputs allow for the connection of two microphones, which can be strategically placed to capture sound from desired sources while rejecting noise from other directions. This configuration is beneficial in environments with significant background noise, as it focuses on sound sources that are directly in front of the microphones.
The amplifier's ability to maintain high-quality audio signals at close range (within 4 cm) while effectively suppressing noise from distances greater than 50 cm is attributed to its advanced signal processing capabilities. The design accommodates microphones that are matched to within ±0.5 dB, ensuring optimal performance and consistency in sound capture. The 20 dB far-field rejection is a key feature, allowing the LMV1090 to be integrated into systems where noise reduction is critical.
Power efficiency is another significant advantage of the LMV1090, consuming only 600 µA of supply current. This low power requirement is particularly advantageous in battery-operated devices, where extended operational life is a priority. The device's performance is notably superior compared to digital signal processing (DSP) solutions, which typically require much higher power consumption, thus making the LMV1090 a cost-effective choice for portable applications.
The differential output configuration enhances noise immunity, reducing the susceptibility of the signal to interference from electromagnetic sources. This is crucial for maintaining audio fidelity in various environments. Additionally, the internal low-noise bias supply ensures that the microphones operate optimally, further contributing to the overall performance of the amplifier.
In summary, the LMV1090 is a sophisticated solution for applications requiring high-quality voice communication, combining effective noise reduction, low power consumption, and robust performance characteristics. Its design principles and operational efficiencies make it a valuable component in modern audio processing systems.The LMV1090 is a fully Analog dual differential input, differ- ential output, Microphone array Amplifier designed to reduce background acoustic noise, while delivering superb speech clarity in voice Communication applications. The LMV1090 preserves near-field voice signals within 4cm of the Microphones while rejecting far-field acoustic noise grea
ter than 50cm from the Microphones Up to 20dB of far- field rejection is possible in a properly configured and using ±0. 5dB matched micropohones. Part of the Powerwise family of energy efficient solutions, the LMV1090 consumes only 600 A of supply current pro- viding superior performance over DSP solutions consuming greater than ten times the power.
The dual Microphone inputs and the processed signal output are differential to provide excellent noise immunity. The mi- crophones are biased with an internal low-noise bias supply. By National Semiconductor Corporation 🔗 External reference