Long-range FM radio transmitter circuit
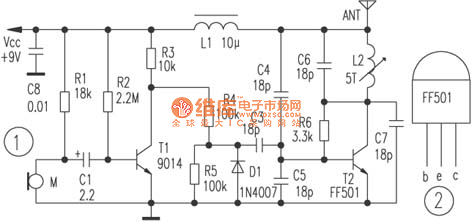
The circuit depicted utilizes a specialized launch tube T2 along with its associated components to create a high-frequency oscillator operating within the frequency range of 88 to 108 MHz. An electret microphone captures the audio signal, which is subsequently amplified by transistor T1. The amplified low-frequency signal is then used to modulate a high-frequency carrier wave. In the event that the electret microphone M is disconnected, the input can be connected to a cassette player, allowing for the transmission of music. The RF transmitter employs the dedicated tube T2, specifically the FF501 model, which is housed in a standard TO-92 package, similar to the 9000 series of transistors. The design and pin configuration are illustrated in Figure 2. This dedicated tube offers advantages such as excellent consistency, higher RF output power, ease of circuit adjustment, and the capability to operate in higher frequency bands.
The described circuit functions as a basic RF transmitter capable of modulating audio signals for wireless transmission. The electret microphone serves as the primary audio input, converting sound waves into electrical signals. The role of transistor T1 is critical as it amplifies these signals, ensuring that the modulation process can effectively alter the carrier wave produced by the oscillator circuit formed around tube T2.
The high-frequency oscillator is essential for generating the RF signal within the specified FM broadcast band. The choice of the FF501 tube is notable for its reliability and performance in RF applications, making it suitable for this type of circuit. The TO-92 package allows for easy integration into various circuit designs while maintaining a compact form factor.
When the microphone is not in use, the circuit can seamlessly switch to a cassette player input, broadening its functionality to include music transmission. This versatility is advantageous for applications such as personal FM transmitters or small-scale broadcasting setups.
The circuit's design emphasizes adjustability, allowing the user to fine-tune the output frequency and modulation characteristics to optimize performance. The output power of the RF signal is also a crucial consideration, as it determines the effective transmission range. By leveraging the properties of the FF501 tube, the circuit can achieve a robust output suitable for various transmission needs.
Overall, this RF transmitter circuit exemplifies a straightforward yet effective design for audio transmission, combining essential components to achieve reliable performance in the FM frequency range.In the circuit shown, the special launch tube T2 and its peripheral parts form a high-frequency oscillator with frequency in the range of 88 ~ 108MHz. The electret microphone picks up the audio signal, then the signal is amplified by T1, then the amplified low frequency signal makes modulation for high-frequency carrier.
If the electret microphone M disconnects, the input end connects cassette player, and it can transmit music. The RF transmitter dedicated tube T2 chooses FF501 which uses a standard T0-92 package (like the 9000 series of transistors ), shape, and pin arrangement is shown in Figure 2. The dedicated tube has the advantages of good consistency, the RF output power is greater, and the circuit is easy to adjust, and the FF501 also can work at a higher frequency band.
🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a basic RF transmitter capable of modulating audio signals for wireless transmission. The electret microphone serves as the primary audio input, converting sound waves into electrical signals. The role of transistor T1 is critical as it amplifies these signals, ensuring that the modulation process can effectively alter the carrier wave produced by the oscillator circuit formed around tube T2.
The high-frequency oscillator is essential for generating the RF signal within the specified FM broadcast band. The choice of the FF501 tube is notable for its reliability and performance in RF applications, making it suitable for this type of circuit. The TO-92 package allows for easy integration into various circuit designs while maintaining a compact form factor.
When the microphone is not in use, the circuit can seamlessly switch to a cassette player input, broadening its functionality to include music transmission. This versatility is advantageous for applications such as personal FM transmitters or small-scale broadcasting setups.
The circuit's design emphasizes adjustability, allowing the user to fine-tune the output frequency and modulation characteristics to optimize performance. The output power of the RF signal is also a crucial consideration, as it determines the effective transmission range. By leveraging the properties of the FF501 tube, the circuit can achieve a robust output suitable for various transmission needs.
Overall, this RF transmitter circuit exemplifies a straightforward yet effective design for audio transmission, combining essential components to achieve reliable performance in the FM frequency range.In the circuit shown, the special launch tube T2 and its peripheral parts form a high-frequency oscillator with frequency in the range of 88 ~ 108MHz. The electret microphone picks up the audio signal, then the signal is amplified by T1, then the amplified low frequency signal makes modulation for high-frequency carrier.
If the electret microphone M disconnects, the input end connects cassette player, and it can transmit music. The RF transmitter dedicated tube T2 chooses FF501 which uses a standard T0-92 package (like the 9000 series of transistors ), shape, and pin arrangement is shown in Figure 2. The dedicated tube has the advantages of good consistency, the RF output power is greater, and the circuit is easy to adjust, and the FF501 also can work at a higher frequency band.
🔗 External reference