Line Following Robot circuit
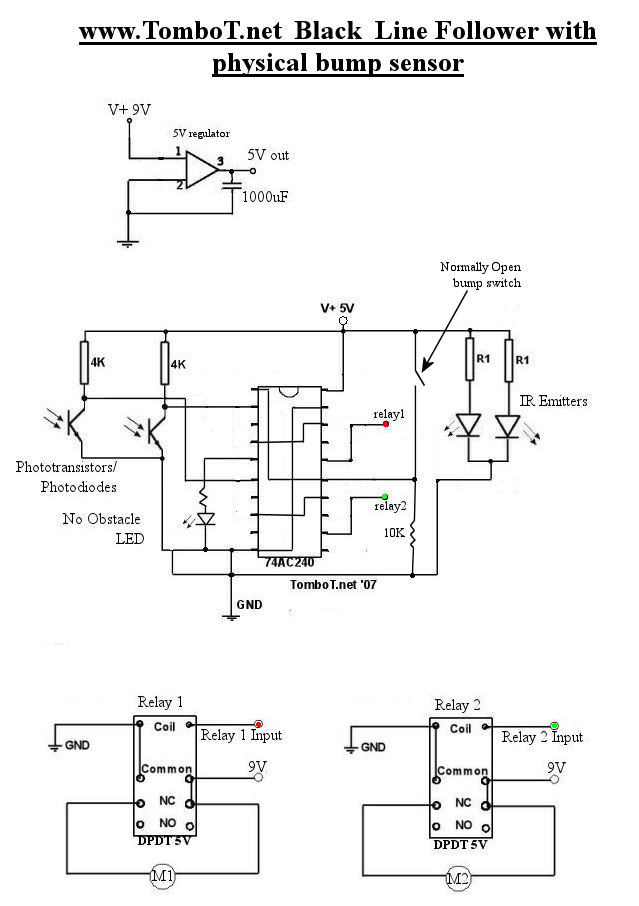
The motors will be powered by the full source voltage, so it is important to ensure that this does not cause the robot to operate too quickly. The Firebot utilizes GM3 motors powered by a 9V battery; however, in this circuit, the motors are only supplied with 5V from the voltage regulator. The line detectors control the relays based on their status, where the left line detector is responsible for driving the right motor and vice versa. The obstacle detector manages the inputs on the line-following chip, which is feasible due to the chip having two sets of inputs, each with its own enable function. The obstacle detector employs the second set of inverters, which remain grounded (enabled) at all times.
The described circuit operates a robotic system utilizing GM3 motors, which are typically rated for higher voltages but are limited to 5V in this configuration to manage speed and control. The power supply is critical, as the motors must be driven at a controlled voltage to prevent excessive speed that could compromise maneuverability and safety.
The line-following capability of the robot is facilitated through the use of line detectors that communicate with relay switches. These relays toggle based on the input status from the detectors, allowing for precise control of motor direction. Specifically, the left line detector is configured to activate the right motor, while the right line detector activates the left motor. This cross-activation is essential for maintaining the robot's trajectory along a designated path.
Moreover, the obstacle detection system plays a significant role in enhancing the robot's operational capabilities. By utilizing a dedicated set of inputs on the line-following chip, the circuit can dynamically enable or disable functionalities based on the presence of obstacles. The second set of inverters, which are continuously grounded, ensures that the obstacle detection mechanism is always active, allowing for real-time adjustments to the robot's navigation strategy.
This design emphasizes the importance of voltage regulation, motor control, and sensor integration in creating an effective and responsive robotic system. Proper attention to these elements ensures that the robot can navigate its environment effectively while adhering to safety constraints.The motors will be driven from the full source voltage, so make sure this isn`t going to make your robot too fast! Firebot has GM3 motors driven with a 9V battery, however the circuit differed and the motors were only driven by 5V from the voltage regulator.
The line detectors drive the relays on or off dependant upon their status, remember that t he left line detector should drive the right motor and vice versa. The obstacle detector enables/disables the inputs on the line following chip. This is made possible by the fact that the chip has two sets of inputs, both with their own enables. The obstacle detector uses the second set of invereters which is grounded (enabled) constantly. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates a robotic system utilizing GM3 motors, which are typically rated for higher voltages but are limited to 5V in this configuration to manage speed and control. The power supply is critical, as the motors must be driven at a controlled voltage to prevent excessive speed that could compromise maneuverability and safety.
The line-following capability of the robot is facilitated through the use of line detectors that communicate with relay switches. These relays toggle based on the input status from the detectors, allowing for precise control of motor direction. Specifically, the left line detector is configured to activate the right motor, while the right line detector activates the left motor. This cross-activation is essential for maintaining the robot's trajectory along a designated path.
Moreover, the obstacle detection system plays a significant role in enhancing the robot's operational capabilities. By utilizing a dedicated set of inputs on the line-following chip, the circuit can dynamically enable or disable functionalities based on the presence of obstacles. The second set of inverters, which are continuously grounded, ensures that the obstacle detection mechanism is always active, allowing for real-time adjustments to the robot's navigation strategy.
This design emphasizes the importance of voltage regulation, motor control, and sensor integration in creating an effective and responsive robotic system. Proper attention to these elements ensures that the robot can navigate its environment effectively while adhering to safety constraints.The motors will be driven from the full source voltage, so make sure this isn`t going to make your robot too fast! Firebot has GM3 motors driven with a 9V battery, however the circuit differed and the motors were only driven by 5V from the voltage regulator.
The line detectors drive the relays on or off dependant upon their status, remember that t he left line detector should drive the right motor and vice versa. The obstacle detector enables/disables the inputs on the line following chip. This is made possible by the fact that the chip has two sets of inputs, both with their own enables. The obstacle detector uses the second set of invereters which is grounded (enabled) constantly. 🔗 External reference