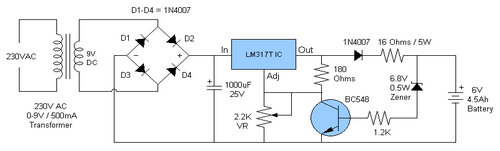
Make a Remote Controlled Toy Car Circuit
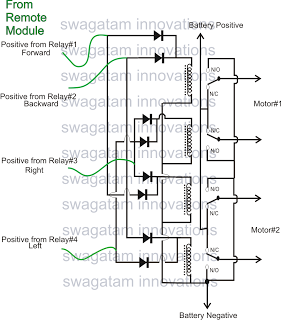
The market is filled with high-end remote-controlled toy cars; however, for hobbyists, creating one at home can be a unique experience. The following article explains how to configure a simple remote-controlled toy car using a pre-made 4-relay remote control module. Previous articles contain information regarding the purchase of ready-made, ready-to-use remote control modules or devices, which only require wiring according to the provided data. This allows users to control any electrical device within a range of 100 meters with the press of a button on the remote handset. This article focuses solely on the circuit and wiring aspects; constructing the car body and fitting the motors and wheels is left to the user, who may seek assistance from a carpenter or fabricator for designing the vehicle body. The discussed remote control module utilizes four discrete relays, which can be toggled individually through the four switches on the remote handset.
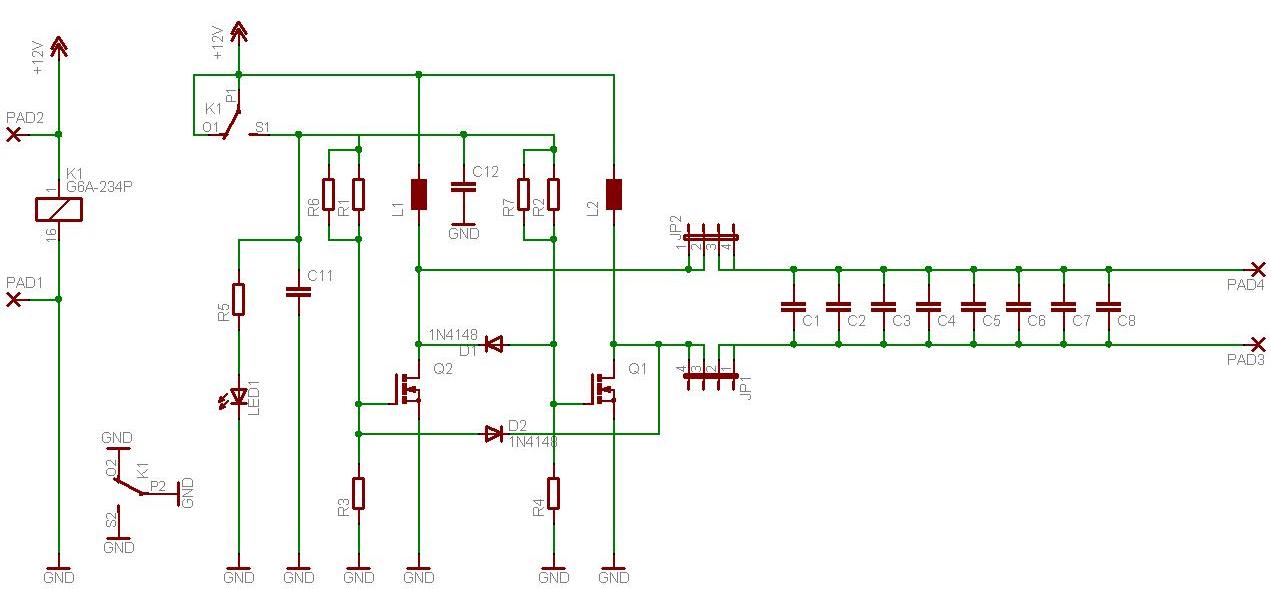
The configuration of the remote-controlled toy car involves integrating a 4-relay remote control module, which serves as the central component for controlling the car's movements. Each relay corresponds to a specific function, allowing for discrete control of various actions such as forward, backward, left, and right movements. The remote control module typically operates at a frequency that ensures reliable communication between the remote handset and the receiver unit installed in the car.
To begin the assembly, the user must first wire the relay module according to the provided schematic. The relays are connected to the motor driver circuit, which interfaces with the DC motors responsible for propelling the vehicle. The power supply for the entire system should be carefully selected to match the voltage and current ratings of both the motors and the relay module, ensuring efficient operation without overloading any components.
The remote control handset is equipped with four buttons, each linked to a specific relay. When a button is pressed, the corresponding relay is activated, allowing current to flow to the associated motor or function. This setup enables precise control of the toy car's direction and speed, making it an engaging project for hobbyists.
While the article emphasizes the circuit and wiring, the physical construction of the toy car body requires creativity and engineering skills. The user is encouraged to design a lightweight chassis that accommodates the motors, relay module, and power supply. Materials such as plastic, wood, or metal can be utilized, depending on the desired durability and aesthetics of the final product.
In conclusion, this project not only provides a practical application of electronics and remote control technology but also fosters creativity and hands-on skills in designing and building a functional remote-controlled toy car.The market may be full of these hi-end remote controlled toy cars, but for a hobbyists making one at home can be entirely a different experience. The article belowexplainshow to configure a simple remote controlled toy car using a ready made 4-relay remote control module.
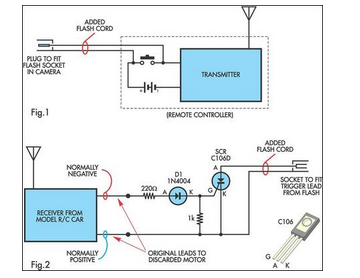
If you refer one of the previous articles you will find some data regarding buying of ready made, ready to use remote control modules or devices, which just requires to be wired as per the data and you are able to control any electrical device within a range of 100 meters with a press of a button over the remote handset. In this article only the circuit and the wiring part has been discussed, making the car body and fitting of the motors and the wheels will be entirely left on the user, the user may take the help of a carpenter or some fabricator for designing the vehicle body.
The remote control module which is being discussed here uses four discrete relays, which can be toggleed discreretly through the 4 individual switches over the remote handset. 🔗 External reference
The configuration of the remote-controlled toy car involves integrating a 4-relay remote control module, which serves as the central component for controlling the car's movements. Each relay corresponds to a specific function, allowing for discrete control of various actions such as forward, backward, left, and right movements. The remote control module typically operates at a frequency that ensures reliable communication between the remote handset and the receiver unit installed in the car.
To begin the assembly, the user must first wire the relay module according to the provided schematic. The relays are connected to the motor driver circuit, which interfaces with the DC motors responsible for propelling the vehicle. The power supply for the entire system should be carefully selected to match the voltage and current ratings of both the motors and the relay module, ensuring efficient operation without overloading any components.
The remote control handset is equipped with four buttons, each linked to a specific relay. When a button is pressed, the corresponding relay is activated, allowing current to flow to the associated motor or function. This setup enables precise control of the toy car's direction and speed, making it an engaging project for hobbyists.
While the article emphasizes the circuit and wiring, the physical construction of the toy car body requires creativity and engineering skills. The user is encouraged to design a lightweight chassis that accommodates the motors, relay module, and power supply. Materials such as plastic, wood, or metal can be utilized, depending on the desired durability and aesthetics of the final product.
In conclusion, this project not only provides a practical application of electronics and remote control technology but also fosters creativity and hands-on skills in designing and building a functional remote-controlled toy car.The market may be full of these hi-end remote controlled toy cars, but for a hobbyists making one at home can be entirely a different experience. The article belowexplainshow to configure a simple remote controlled toy car using a ready made 4-relay remote control module.
If you refer one of the previous articles you will find some data regarding buying of ready made, ready to use remote control modules or devices, which just requires to be wired as per the data and you are able to control any electrical device within a range of 100 meters with a press of a button over the remote handset. In this article only the circuit and the wiring part has been discussed, making the car body and fitting of the motors and the wheels will be entirely left on the user, the user may take the help of a carpenter or some fabricator for designing the vehicle body.
The remote control module which is being discussed here uses four discrete relays, which can be toggleed discreretly through the 4 individual switches over the remote handset. 🔗 External reference