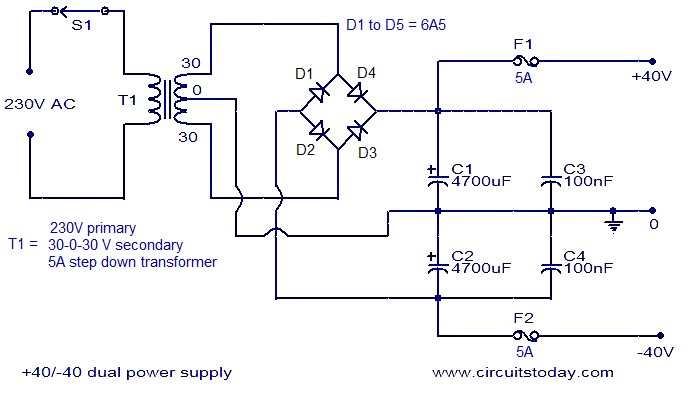
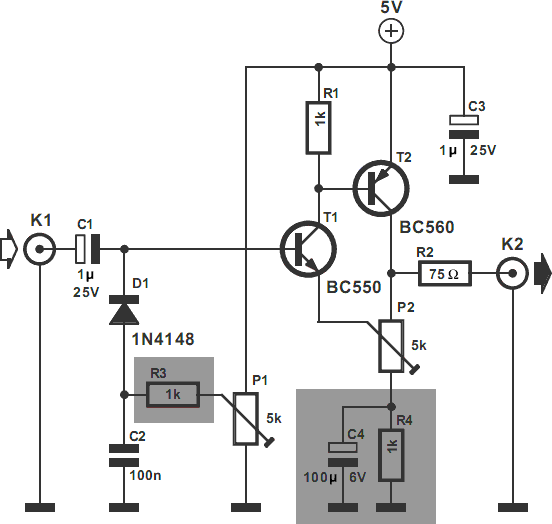
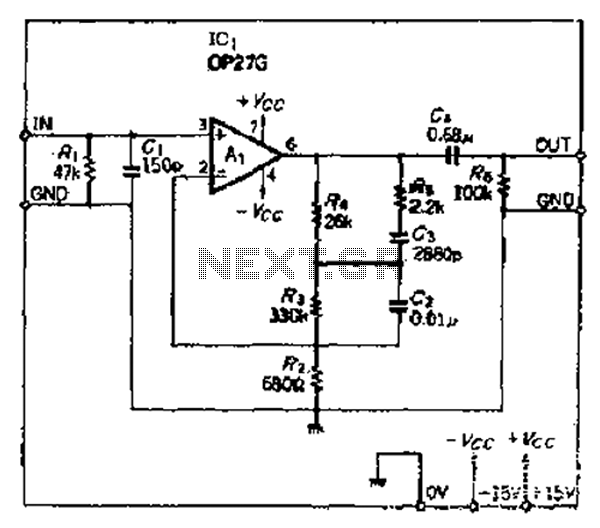
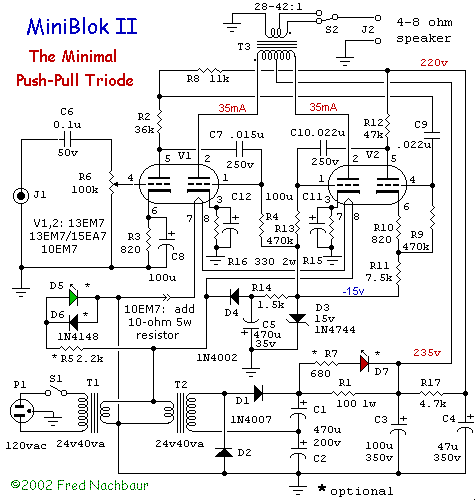
Make Lm324 Op Amp Swing Rail-To-Rail
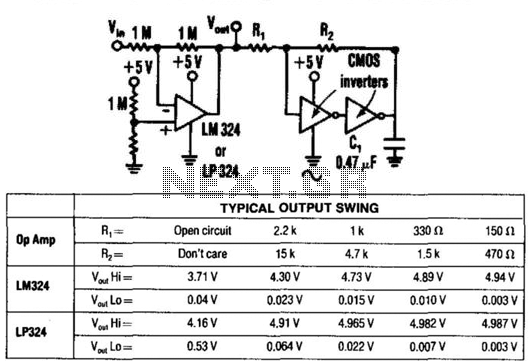
By utilizing two CMOS inverters, the output voltage of an LM324 operational amplifier can be increased from 3.5 V peak-to-peak (Vpp) to 4.9 Vpp. This circuit is recommended solely for light loads (less than 30 mA) and for relatively slow operational amplifiers. Any CMOS inverter, such as the 74C00, 74C02, 74C14, CD4001, CD4011, etc., can be employed.
The circuit employs two CMOS inverters configured in series to amplify the output voltage from the LM324 op-amp. The LM324 is a versatile quad op-amp that typically outputs a maximum of 3.5 Vpp when powered by a standard dual supply. The use of CMOS inverters provides a means to boost this output to 4.9 Vpp, which can be beneficial in applications requiring higher voltage levels without significant power consumption.
The recommended load for this configuration is light, specifically under 30 mA, to prevent overloading the inverters, which could lead to distortion or failure. The choice of inverters is flexible, allowing for various models, including the 74C00, 74C02, 74C14, CD4001, and CD4011. These inverters are characterized by their high input impedance and low output impedance, making them suitable for this application.
In the schematic, the output of the LM324 is connected to the input of the first CMOS inverter. The output of this inverter is then fed into the input of the second inverter. The final output is taken from the output of the second inverter, which is now capable of delivering an increased voltage level. The power supply for the inverters should match their specifications, typically a dual supply of ±5V to ±15V, depending on the specific inverter model used.
It is crucial to ensure that the circuit is designed with appropriate bypass capacitors near the power supply pins of the inverters to maintain stability and reduce noise. Additionally, proper layout techniques should be employed to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can affect the performance of the circuit, especially at higher frequencies. By using two CMOS inverters, the output for an LM324 op amp can be increased from 3.5 Vpp to 4.9 Vpp. This circuit is only recommended for light loads (<30 mA) and for relatively slow op amps. Any CMOS inverter (74COO, 74C02, 74C14, CD4001, CD4011, etc.) can be used. 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs two CMOS inverters configured in series to amplify the output voltage from the LM324 op-amp. The LM324 is a versatile quad op-amp that typically outputs a maximum of 3.5 Vpp when powered by a standard dual supply. The use of CMOS inverters provides a means to boost this output to 4.9 Vpp, which can be beneficial in applications requiring higher voltage levels without significant power consumption.
The recommended load for this configuration is light, specifically under 30 mA, to prevent overloading the inverters, which could lead to distortion or failure. The choice of inverters is flexible, allowing for various models, including the 74C00, 74C02, 74C14, CD4001, and CD4011. These inverters are characterized by their high input impedance and low output impedance, making them suitable for this application.
In the schematic, the output of the LM324 is connected to the input of the first CMOS inverter. The output of this inverter is then fed into the input of the second inverter. The final output is taken from the output of the second inverter, which is now capable of delivering an increased voltage level. The power supply for the inverters should match their specifications, typically a dual supply of ±5V to ±15V, depending on the specific inverter model used.
It is crucial to ensure that the circuit is designed with appropriate bypass capacitors near the power supply pins of the inverters to maintain stability and reduce noise. Additionally, proper layout techniques should be employed to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can affect the performance of the circuit, especially at higher frequencies. By using two CMOS inverters, the output for an LM324 op amp can be increased from 3.5 Vpp to 4.9 Vpp. This circuit is only recommended for light loads (<30 mA) and for relatively slow op amps. Any CMOS inverter (74COO, 74C02, 74C14, CD4001, CD4011, etc.) can be used. 🔗 External reference