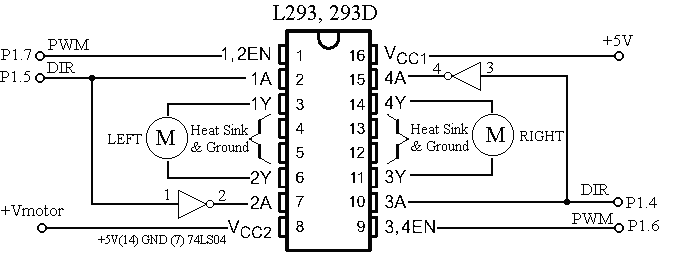
MC CONTROL TRANSMITTER
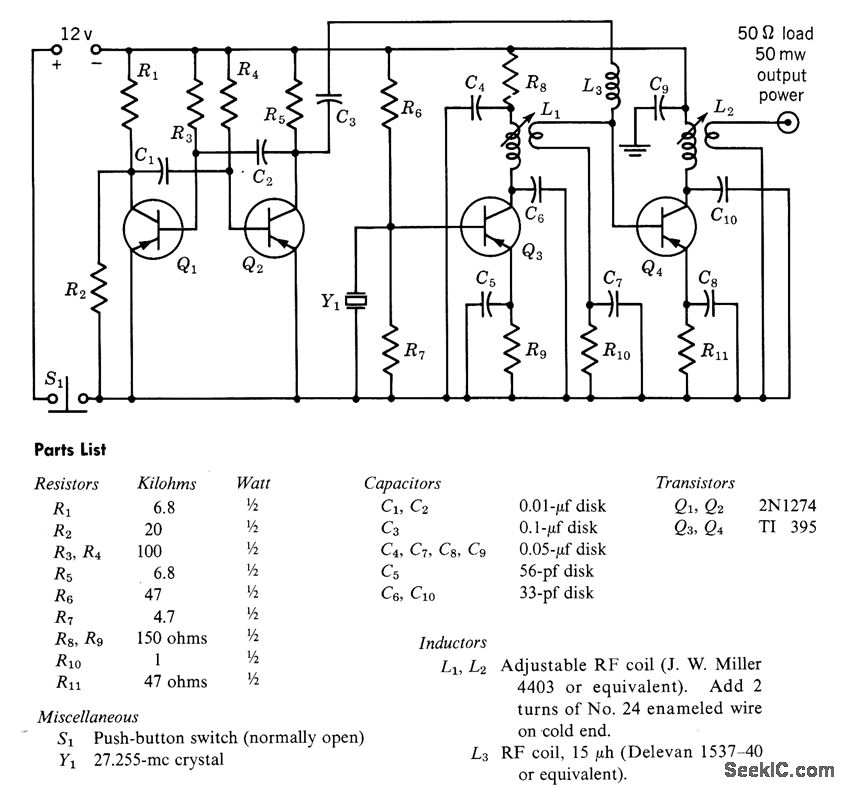
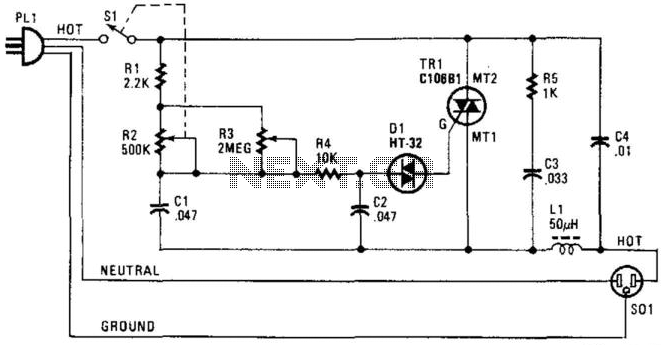
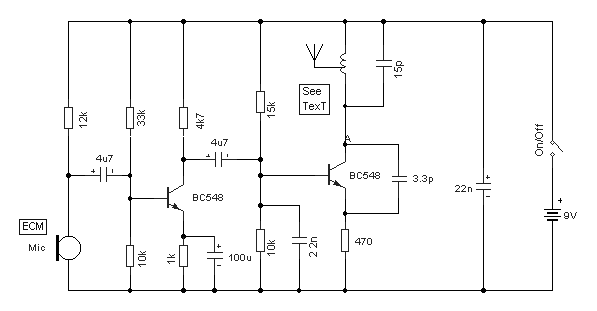
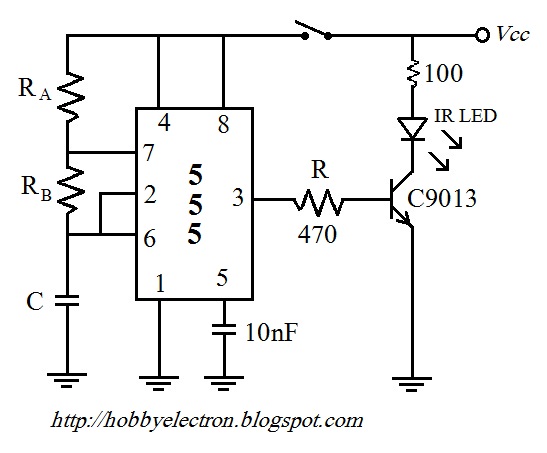
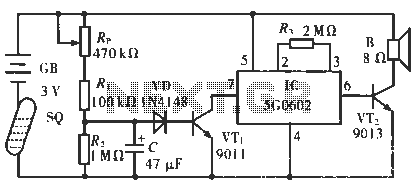
A free-running multivibrator activates power amplifier Q4 for audio applications. The operational range is approximately 1 mile, and capacitor C6 is used to tune the collector of the oscillator to the crystal frequency. - Texas Instruments Inc., "Transistor Circuit Design," McGraw-Hill, N.Y., 1963, p. 361.
The described circuit utilizes a free-running multivibrator configuration, which is a type of astable multivibrator that generates a continuous square wave output without requiring an external trigger. This output is utilized to control the power amplifier Q4, which is designed to amplify audio signals effectively. The free-running nature of the multivibrator allows for consistent operation, making it suitable for various audio applications.
The operational range of approximately 1 mile indicates that the circuit is likely intended for use in wireless audio transmission systems, where the amplified audio signal can be transmitted over a significant distance. This range is influenced by the power output of the amplifier, the efficiency of the antenna used, and the surrounding environmental conditions.
Capacitor C6 plays a crucial role in the circuit by tuning the collector of the oscillator to the frequency of a crystal. This tuning is essential for maintaining frequency stability and ensuring that the oscillator operates at the desired frequency. The use of a crystal oscillator provides a precise frequency reference, which is vital in applications where signal integrity is critical.
In summary, the circuit integrates a free-running multivibrator with a power amplifier, utilizing a capacitor for frequency tuning, to create a reliable audio transmission system capable of operating over a distance of approximately 1 mile. The design principles and components referenced are based on established practices in transistor circuit design, as outlined in the literature from Texas Instruments.Free-running multivibrator keys power amplifier Q4 at audio role. Range is about 1 mile C6 tunes collector of oscillator to crystal frequency. -Texas lnstruments Inc. , "Transistor Circuit Design, " McGraw-Hill, N. Y. , 1963, p 361. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a free-running multivibrator configuration, which is a type of astable multivibrator that generates a continuous square wave output without requiring an external trigger. This output is utilized to control the power amplifier Q4, which is designed to amplify audio signals effectively. The free-running nature of the multivibrator allows for consistent operation, making it suitable for various audio applications.
The operational range of approximately 1 mile indicates that the circuit is likely intended for use in wireless audio transmission systems, where the amplified audio signal can be transmitted over a significant distance. This range is influenced by the power output of the amplifier, the efficiency of the antenna used, and the surrounding environmental conditions.
Capacitor C6 plays a crucial role in the circuit by tuning the collector of the oscillator to the frequency of a crystal. This tuning is essential for maintaining frequency stability and ensuring that the oscillator operates at the desired frequency. The use of a crystal oscillator provides a precise frequency reference, which is vital in applications where signal integrity is critical.
In summary, the circuit integrates a free-running multivibrator with a power amplifier, utilizing a capacitor for frequency tuning, to create a reliable audio transmission system capable of operating over a distance of approximately 1 mile. The design principles and components referenced are based on established practices in transistor circuit design, as outlined in the literature from Texas Instruments.Free-running multivibrator keys power amplifier Q4 at audio role. Range is about 1 mile C6 tunes collector of oscillator to crystal frequency. -Texas lnstruments Inc. , "Transistor Circuit Design, " McGraw-Hill, N. Y. , 1963, p 361. 🔗 External reference