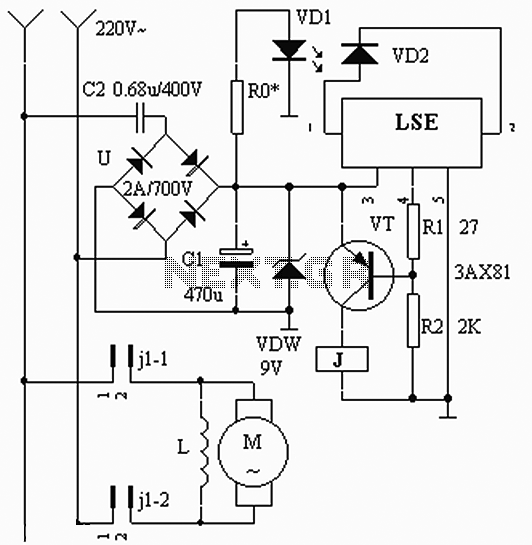
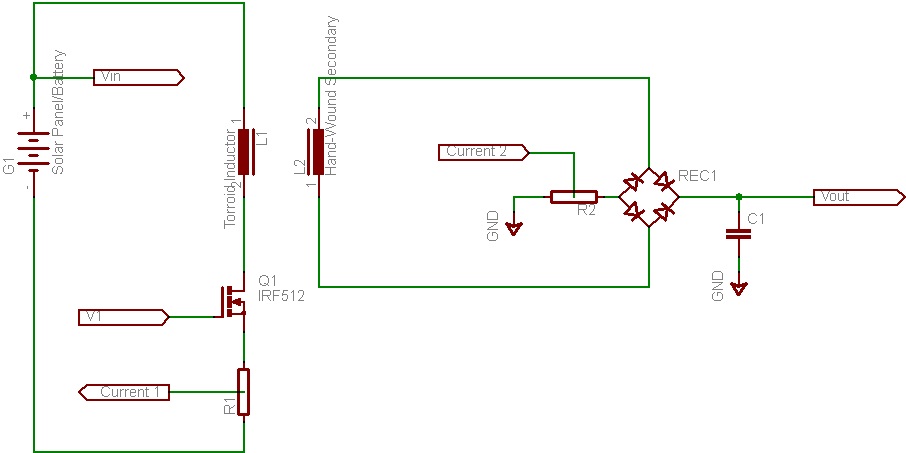
Light Dimmer/Speed Control
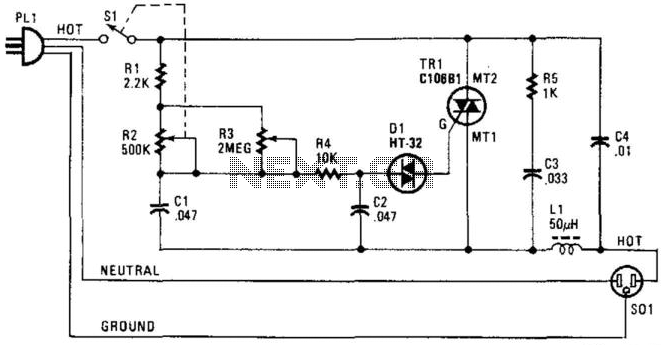
A phase-controlled triac (HT-32) circuit offers control over the effective voltage at the load. It is important to include LI and C4, as they are essential for RFI suppression. The maximum load capacity is approximately 500 W. WARNING: 120 Vac is present in this circuit—ensure adequate insulation and construction techniques are employed.
The phase-controlled triac circuit utilizing the HT-32 component is designed for effective voltage regulation at the load, allowing for precise control in various applications. The circuit operates by adjusting the phase angle of the AC voltage, which effectively modifies the amount of power delivered to the load. This method of control is particularly useful in applications such as light dimmers, motor speed controllers, and heating elements.
In this configuration, the inclusion of inductive elements (LI) and capacitor (C4) is crucial for radio frequency interference (RFI) suppression. LI serves to limit high-frequency noise that may arise from the switching action of the triac, while C4 acts as a filter to smooth out voltage spikes and transients, ensuring stable operation and compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards.
The circuit is rated for a maximum load of approximately 500 W, which indicates its suitability for moderate power applications. It is imperative to observe safety precautions, particularly due to the presence of 120 Vac within the circuit. Proper insulation techniques, such as using heat-shrink tubing and insulated connectors, alongside robust construction practices, must be employed to prevent electrical hazards.
Overall, this triac-based circuit exemplifies a reliable solution for controlling AC power with the added benefits of RFI suppression, making it an effective choice for various electronic applications. A phase-controlled triac (HT-32) circuit provides control of effective voltage at load. Do not omit LI and C4 be cause they are for RFI suppression. The maximum load is about 500 W. WARNING: 120 Vac is present on this circuit—provide adequate insulation and construction techniques. 🔗 External reference
The phase-controlled triac circuit utilizing the HT-32 component is designed for effective voltage regulation at the load, allowing for precise control in various applications. The circuit operates by adjusting the phase angle of the AC voltage, which effectively modifies the amount of power delivered to the load. This method of control is particularly useful in applications such as light dimmers, motor speed controllers, and heating elements.
In this configuration, the inclusion of inductive elements (LI) and capacitor (C4) is crucial for radio frequency interference (RFI) suppression. LI serves to limit high-frequency noise that may arise from the switching action of the triac, while C4 acts as a filter to smooth out voltage spikes and transients, ensuring stable operation and compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards.
The circuit is rated for a maximum load of approximately 500 W, which indicates its suitability for moderate power applications. It is imperative to observe safety precautions, particularly due to the presence of 120 Vac within the circuit. Proper insulation techniques, such as using heat-shrink tubing and insulated connectors, alongside robust construction practices, must be employed to prevent electrical hazards.
Overall, this triac-based circuit exemplifies a reliable solution for controlling AC power with the added benefits of RFI suppression, making it an effective choice for various electronic applications. A phase-controlled triac (HT-32) circuit provides control of effective voltage at load. Do not omit LI and C4 be cause they are for RFI suppression. The maximum load is about 500 W. WARNING: 120 Vac is present on this circuit—provide adequate insulation and construction techniques. 🔗 External reference